Abstract
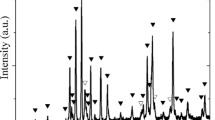
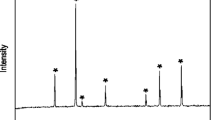
Nanocomposites consisting of strontium ferrite and magnetite are prepared to investigate the effect of exchange coupling between the hard and soft magnetic phases. Hexagonal strontium ferrite, SrFe12O19, synthesized using a solid-state route involving the sintering of precursors at 1000 °C gives a coercivity value as high as 3.73 kOe. An increase in the sintering temperature results in an increase in particle size and a decrease in coercivity. The soft ferrite phase Fe3O4 synthesized by a reverse co-precipitation method shows a saturation magnetization as high as 84 emu/g. Simple homogenous mixing of soft and hard components resulted in an exchange-coupled magnetic nanocomposite. With an increase in the soft magnetic content, the magnetization of the composite increases while the coercivity decreases. On sintering the nanocomposites at 1000 °C, coercivity remains intact even for an increasing soft magnetic content indicating an exchange decoupling between the soft and hard phases. This is attributed to the phase transformation of Fe3O4 to α-Fe2O3 at elevated temperatures.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coey, J.M.D.: Permanent magnet applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 248, 441–456 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(02)00335-9
Gutfleisch, O., Willard, M.A., Brück, E., Chen, C.H., Sankar, S.G., Liu, J.P.: Magnetic materials and devices for the 21st century: stronger, lighter, and more energy efficient. Adv. Mater. 23, 821–842 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201002180
Skomski, R., Coey, J.M.D.: Giant energy product in nanostructured two-phase magnets. Phys. Rev. B. 48, 15812–15816 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.48.15812
Buschow, K.H.J., de Boer, F.R.: Physics of magnetism and magnetic materials. Springer, Boston, MA, (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/b100503
Guo, Z.B., Ding, W.P., Zhong, W., Zhang, J.R., Du, Y.W.: Preparation and magnetic properties of SrFe12O19 particles prepared by the salt-melt method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 175, 333–336 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(97)00206-0
Park, J., Hong, Y.K., Kim, S.G., Kim, S., Liyanage, L.S.I., Lee, J., Lee, W., Abo, G.S., Hur, K.H., An, S.Y.: Maximum energy product at elevated temperatures for hexagonal strontium ferrite (SrFe12O19) magnet. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 355, 1–6 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2013.11.032
Kneller, E.F., Hawig, R.: The exchange-spring magnet: a new material principle for permanent magnets. IEEE Trans. Magn. 27, 3588–3600 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1109/20.102931
Remya, K.P., Prabhu, D., Amirthapandian, S., Viswanathan, C., Ponpandian, N.: Exchange spring magnetic behavior in BaFe12O19/Fe3O4 nanocomposites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 406, 233–238 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.01.024
Zeng, Q., Jiang, D., Yang, S.: Enhancement of magnetic properties in hard/soft CoFe2O4/ Fe3O4 nanocomposites. RSC Adv. 6, 46143–46148 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra02993k
Volodchenkov, A.D., Kodera, Y., Garay, J.E.: Synthesis of strontium ferrite/iron oxide exchange coupled nano-powders with improved energy product for rare earth free permanent magnet applications. J. Mater. Chem. C. 4, 5593–5601 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6tc01300g
Roy, D., Anil Kumar, P.S.: Exchange spring behaviour in SrFe12O19-CoFe2O4 nanocomposites. AIP Adv. 5, 077137 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4927150
Liu, X., Zhong, W., Gu, B., Du, Y.: Exchange-coupling interaction in nanocomposite SrFe12O19/γ-Fe2O3 permanent ferrites. J. Appl. Phys. 92, 1028–1032 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1487908
Xia, A., Zuo, C., Zhang, L., Cao, C., Deng, Y., Xu, W., Xie, M., Ran, S., Jin, C., Liu, X.: Magnetic properties, exchange coupling and novel stripe domains in bulk SrFe12O19/(Ni, Zn) Fe_2O_4 composites. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 47, 415004 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/47/41/415004
Mohseni, F., Pullar, R.C., Vieira, J.M., Amaral, J.S.: Bonded ferrite-based exchange-coupled nanocomposite magnet produced by warm compaction. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 53, 494003 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/abb0bd
Petrecca, M., Muzzi, B., Oliveri, S.M., Albino, M., Yaacoub, N., Peddis, D., De Julián Fernández, C., Innocenti, C., Sangregorio, C.: Optimizing the magnetic properties of hard and soft materials for producing exchange spring permanent magnets. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 54, 134003 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/abd354
Dahal, J.N., Neupane, D., Poudel, T.P.: Synthesis and magnetic properties of 4:1 hard-soft SrFe12O19-La1-xSrxMnO3 nanocomposite prepared by auto-combustion method. AIP Adv. 9, 075308 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5096530
Xu, X., Hong, Y.K., Park, J., Lee, W., Lane, A.M.: Ex situ synthesis of magnetically exchange coupled SrFe12O19/Fe-Co composites. AIP Adv. 6, 056026 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4944703
Viet Nga, T.T., Lan, N.T.: Fabrication and exchange-spring properties of SrFe12O19@Fe3O4 nanocomposites with core-shell structure. Mater. Chem. Phys. 251, 123084 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123084
Verma, A., Pandey, O.P., Sharma, P.: Strontium ferrite permanent magnet - an overview, Indian J. Eng. Mater. Sci. 7, 364–369 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1002/chin.200138258
İçi̇n, K., Öztürk, S., Çakil, D.D., Sünbül, S.E.: Effect of the stoichiometric ratio on phase evolution and magnetic properties of SrFe12O19 produced with mechanochemical process using mill scale. Ceram. Int. 46, 14150–14160 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.02.222
Cullity, B.D., Graham, C.D.: Introduction to magnetic materials. Second ed., John Wiley and Sons. (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470386323
Park, J., Hong, Y.K., Lee, W., An, S.Y., Seo, J.W., Hur, K.H.: Coercivity of SrFe12O19 hexaferrite platelets near single domain size. IEEE Magn. Lett. 6, 5500203 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/LMAG.2015.2460215
Chen, D.H., Chen, Y.Y.: Synthesis of strontium ferrite ultrafine particles using microemulsion processing. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 236, 41–46 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.2000.7389
Wang, J., Sun, J., Sun, Q., Chen, Q.: One-step hydrothermal process to prepare highly crystalline Fe3O4 nanoparticles with improved magnetic properties. Mater. Res. Bull. 38, 1113–1118 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-5408(03)00129-6
Erokhin, S., Berkov, D.: Optimization of nanocomposite materials for permanent magnets: micromagnetic simulations of the effects of intergrain exchange and the shapes of hard grains. Phys. Rev. Appl. 7, 014011 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevApplied.7.014011
Kazeminezhad, I., Mosivand, S.: Phase transition of electrooxidized Fe3O4 to γ and α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles using sintering treatment. Acta Phys. Pol. A. 125, 1210–1214 (2014). https://doi.org/10.12693/APhysPolA.125.1210
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by the Cochin University of Science and Technology via SMNRI Grant (No. PL.(UGC)1/SPG//SMNRI/2017-18 dated 02/11/2017) and University Grants Commission via Start-up Grant (No. F.30-415/2018(BSR) dated 06/02/2019). SAS acknowledges the Junior Research Fellowship received from the Science and Engineering Research Board (No. ECR/2017/001782 dated 04/10/2018). Fruitful discussions with Navya Joseph and Archana V N are gratefully acknowledged. The authors acknowledge DST-FIST for creating the FE-SEM facility at the Department of Physics, Cochin University of Science and Technology, Kochi, Kerala, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sam, S.A., Balan, A.P., Kaipamangalath, A. et al. Nanocomposite Permanent Magnets Based on SrFe12O19-Fe3O4 Hard-Soft Ferrites. J Supercond Nov Magn 34, 3333–3344 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-021-06070-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-021-06070-y