Abstract
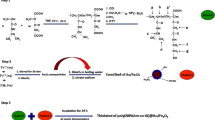
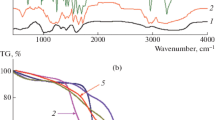
In novel drug delivery systems, polymeric materials are combined with drugs or active agents where the drug is released in the presence of external stimuli like pH, temperature, magnetic field, etc. Magnetic drug delivery systems can be used in cancer treatment. Fe3O4 nanoparticles have been applied in biomedical applications due to their biocompatibility and biodegradability properties. In this study, magnetic nanocomposites were developed and demonstrated to be responsive to the magnetic field. Fe3O4 nanoparticles were synthesized by the co-precipitation method. The synthesized nanoparticles were modified by (3-aminopropyl) triethoxysilane (APTES) (Fe3O4@SiO2) and coated with polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP). Magnetic properties of the nanoparticles and hydrogel were characterized by vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM). In the present study, doxorubicin (DOX) is used as a cancer drug, loaded in the nanocomposite. The attachment of Dox, PVP to the Fe3O4 nanoparticles was confirmed by FTIR analysis. Different characterizations were carried out, such as swelling measurements, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and X-ray diffraction (XRD) as well as rheological parameters. The drug release from the untreated and treated nanoparticles was investigated in two different pHs by using UV–Vis. Our findings show that the rate of drug release is higher at pH = 5 than pH = 7.4. Altogether, the magnetic nanocomposite hydrogels are promising products for magnetically targeted drug delivery systems.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu, T.Y., et al.: Preparation and characterization of smart magnetic hydrogels and its use for drug release. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 304(1), 397–399 (2006)
Liu, T.Y., et al.: Magnetic-sensitive behavior of intelligent ferrogels for controlled release of drug. Langmuir 22(14), 5974–5978 (2006)
Uhrich, K.E., et al.: Polymeric systems for controlled drug release. Chem. Rev. 99(11), 3181–3198 (1999)
Kim, S.W., Petersen, R.V., Feijen, J.: Polymeric drug delivery systems. Drug. Des. 10, 193–250 (2016)
Mali, A.D.: An updated review on transdermal drug delivery systems. Skin 8, 9 (2015)
Siegel, R.A., Rathbone M.J.: Overview of controlled release mechanisms. J. Fund. Appl. Controlled. Release. Drug. Del. 19–43 (2012)
Peppas, N.A.: Biomedical applications of hydrogels handbook. Springer. Sci. Busi. Media. 1–15 (2010)
Pourmanouchehri, Z., Jafarzadeh M., Kakaei, S., Sattarzadeh E.: Magnetic Nanocarrier Containing 68 Ga–DTPA Complex for Targeted Delivery of Doxorubicin. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 28(5), 1980–1990 (2018)
Khameneh, E.S., Amini, M.M., Kakaei, S., Khanchi, A.: Preparation of dual-modality yttrium-90 radiolabeled nanoparticles for therapeutic investigation. Radiochim. Acta. 106(11), 897–907 (2018)
Sattarzadeh, E., Amini, M.M., Kakaei, S., Khanchi, A.: 68 Ga-radiolabeled magnetic nanoparticles for PET–MRI imaging. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 317(3), 1333–1339 (2018)
SattarzadehKhameneh, E., Kakaei, S., Moharreri, M.M.: Synthesis and characterization of DTPA and DOTA modified Fe3O4@ SiO2 core-shell nanoparticles. Adv. Nanochem. 1(2), 62–65 (2019)
Sirousazar, M., et al.: Hydrogels: properties preparation characterization and biomedical applications in tissue engineering drug delivery and wound care. J. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 295–357 (2014)
Satarkar, N.S., Biswal, D., Hilt, J.Z.: Hydrogel nanocomposites: a review of applications as remote controlled biomaterials. Soft Matter 6(11), 2364–2371 (2010)
Don, T.M., et al.: Preparation of thermo-responsive acrylic hydrogels useful for the application in transdermal drug delivery systems. Mater. Chem. Phys. 107(2), 266–273 (2008)
Zhao, W., et al.: In situ synthesis of magnetic field-responsive hemicellulose hydrogels for drug delivery. Biomacromol 16(8), 2522–2528 (2015)
Ammar, N.E.B., et al.: Study of agar proportions effect on a gamma ray synthesized hydrogel. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 3(3–4), 88–100 (2016)
Tacar, O., Sriamornsak, P., Dass, C.R.: Doxorubicin: an update on anticancer molecular action toxicity and novel drug delivery systems. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 65(2), 157–170 (2013)
Kayal, S., Ramanujan, R.: Doxorubicin loaded PVA coated iron oxide nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 30(3), 484–490 (2010)
Chen, F.H., et al.: Synthesis of a novel magnetic drug delivery system composed of doxorubicin-conjugated Fe3O4 nanoparticle cores and a PEG-functionalized porous silica shell. J. Chem. Commun. 46(45), 8633–8635 (2010)
Rose, P.A., et al.: Drug embedded PVP coated magnetic nanoparticles for targeted killing of breast cancer cells. Technol. Cancer. Res. Treat. 12(5), 463–472 (2013)
Kandpal, N., et al.: Co-precipitation method of synthesis and characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 73, 87–90 (2014)
Kim, K., et al.: Formation and surface modification of fe3o4 nanoparticles by co-precipitation and sol-gel method. J. Ind. Chem. Eng. 13(7), 1137 (2007)
Do Kim, K., et al.: Formation and surface modification of Fe3O4 nanoparticles by co-precipitation and sol-gel method. J. Ind. Chem. Eng. 13(7), 1137–1141 (2007)
He, Y., et al.: Synthesis and characterization of functionalized silica-coated Fe3O4 superparamagnetic nanocrystals for biological applications. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 38(9), 1342 (2005)
Foroutan, H., Rabbani, M.: Investigation of synthesis of PVP hydrogel by irradiation. Iran. J. Radiat. Res. 5(3), 131–136 (2007)
Jafarzadeh, M., et al.: Preparation of trifluoroacetic acid-immobilized Fe3O4@ SiO2–APTES nanocatalyst for synthesis of quinolines. J. Fluor. Chem. 178, 219–224 (2015)
Akbarzadeh, A., et al.: Preparation and in vitro evaluation of doxorubicin-loaded Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles modified with biocompatible copolymers. Int. J. Nanomed. 7, 511 (2012)
Xu, L., et al.: Surface modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles as a protein delivery vehicle. J. Colloids. Surf. A. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 350(1), 8–12 (2009)
White, L., Tripp, C.: Reaction of (3-aminopropyl) dimethylethoxysilane with amine catalysts on silica surfaces. J. Colloid. Interface. Sci. 232(2), 400–407 (2000)
Heiney, P.A., et al.: Structure and growth of chromophore-functionalized (3-aminopropyl) triethoxysilane self-assembled on silicon. Langmuir 16(6), 2651–2657 (2000)
Saif, B., et al.: Synthesis and characterization of Fe3O4 coated on APTES as carriers for morin-anticancer drug. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 6(04), 267 (2015)
Khosroshahi, M., Ghazanfari, L.: Amino surface modification of Fe3O4/SiO2 nanoparticles for bioengineering applications. J. Surf. Eng. 27(8), 508–573 (2011)
Lukins, R.E.: Vibrating sample magnetometer 2D and 3D magnetization effects associated with different initial magnetization states. AIP. Adv. 7(5), 056801 (2017)
Mahdavinia, G.R., Etemadi, H.: In situ synthesis of magnetic CaraPVA IPN nanocomposite hydrogels and controlled drug release. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 45, 250–260 (2014)
Arsalani, N., Fattahi, H., Nazarpoor, M.: Synthesis and characterization of PVP-functionalized superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles as an MRI contrast agent. Express. Polym. Lett. 4(6), 329–338 (2010)
Lu, C.H., et al.: Design and synthesis of Fe3O4@SiO2 core-shell nanomaterials. Integr. Ferroelectr. 182(1), 46–52 (2017)
Eid, M., et al.: Radiation synthesis and characterization of poly (vinyl alcohol)/poly (N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone) based hydrogels containing silver nanoparticles. J. Polym. Res. 19(3), 9835 (2012)
Vimala, K., et al.: Controlled silver nanoparticles synthesis in semi-hydrogel networks of poly (acrylamide) and carbohydrates: a rational methodology for antibacterial application. Carbohydr. Polym. 75(3), 463–471 (2009)
Jayakumar, O.D., et al.: Water dispersible Fe3O4 nanoparticles carrying doxorubicin for cancer therapy. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 9(11), 6344–6348 (2009)
Ghaffari, M., Ehsani, M., Khonakdar, H.A.: Morphology rheological and protective properties of epoxy/nano-glassflake systems. Prog. Org. Coat. 77(1), 124–130 (2014)
Abdurrahmanoglu, S., Okay, O.: Rheological behavior of polymer–clay nanocomposite hydrogels: Effect of nanoscale interactions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 116(4), 2328–2335 (2010)
Killion, J.A., et al.: Hydrogel/bioactive glass composites for bone regeneration applications: Synthesis and characterisation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 33(7), 4203–4212 (2013)
Hosseini, H., Tenhu, H., Hietala, S.: Rheological properties of thermoresponsive nanocomposite hydrogels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 133(11) (2016)
Rescignano, N., et al.: Preparation of alginate hydrogels containing silver nanoparticles: a facile approach for antibacterial applications. J. Polym. Int. 65(8), 921–926 (2016)
Durán-Valencia, C., et al.: Development of enhanced nanocomposite preformed particle gels for conformance control in high-temperature and high-salinity oil reservoirs. Polym. J. 46(5), 277 (2014)
Demeter, M., et al.: Network structure studies on γ–irradiated collagen–PVP superabsorbent hydrogels. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 131, 51–59 (2017)
Jovanović, Ž., et al.: Bioreactor validation and biocompatibility of Ag/poly (N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone) hydrogel nanocomposites. Colloid. Surf. B. 105, 230–235 (2013)
Jovanović, Ž., et al.: Structural and optical characteristics of silver/poly (N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone) nanosystems synthesized by γ-irradiation. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 81(11), 1720–1728 (2012)
Elbaz, N.M., et al.: Core-shell silver/polymeric nanoparticles-based combinatorial therapy against breast cancer in-vitro. Sci. Rep. 6, 30729 (2016)
Roy, N., Saha, N.: PVP-based hydrogels: synthesis properties and applications. J. Hydrogel. Synth. Character. Appl. 227–252 (2012)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Radiation Application Research School, Foundation of Nuclear Science and Technology Research Institute and Golestan University for supporting this research work. We are also grateful to Dr. Naser Zarsav for his valuable comments and thoroughly editing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ehteshamzadeh, T., Kakaei, S., Ghaffari, M. et al. Doxorubicin Embedded Polyvinylpyrrolidone-Coated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles for Targeted Drug Delivery System. J Supercond Nov Magn 34, 3345–3360 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-021-05952-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-021-05952-5