Abstract
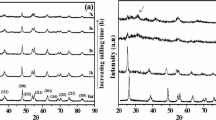
Five weight percent of Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles were prepared via ball milling route. The effect of both doping and milling on the evolution of structure and microstructure alongside with optical and magnetic properties was investigated. XRD analysis revealed the coexistence of all TiO2 phases, namely anatase, brookite, and rutile with a signature of Fe cluster; meanwhile, the phase ratio changed with milling time and the dissolution of Fe dopant within TiO2 lattice. The crystallite size varies in the range of 26–44 nm with a minimum value achieved for 10 h of milling. FTIR spectroscopy confirmed the presence of characteristic functional groups belonging to TiO2 phase. The agglomeration of Fe/TiO2 nanopowders into large clusters was observed. Raman analysis showed a variation in peak positions and broadening as function of milling time and subsequently Fe doping level. UV–Vis spectroscopy manifested an increase in the absorption accompanied with a red shift and a decrease in the band gap energy from 2.57 to 2.28 eV. A strong ferromagnetic behavior was achieved, where the saturation magnetization was found to increase considerably in the range 18.1–40.15 emu/g. The appearance of ferromagnetism was associated with the dissolution of Fe with strong magnetic moment within TiO2 host lattice as well as the presence of Fe metal for longer milling.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Álvaro, R.J., Diana, N.D., María, A.M.: Impedance analysis of TiO2 nanoparticles prepared by green chemical mechanism. Cont. Eng. Sci. 11, 737–744 (2018)
Diebold, U.: The surface science of titanium dioxide. Surf. Sci. Rep. 48(5–8), 53–229 (2003)
Hanaor, D.A.H., Triani, G., Sorrell, C.C.: Morphology and photocatalytic activity of highly oriented mixed phase titanium dioxide thin films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 205(12), 3658–3664 (2011)
Aruldoss, U., Kennedy, L.J., Vijaya, J.J., Sekaran, G.: Photocatalytic degradation of phenolic syntan using TiO2 impregnated activated carbon. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 355(1), 204–209 (2011)
Ho, C.Y., Lin, J.K., Wang, H.W.: Characteristics of boron decorated TiO2 nanoparticles for dye-sensitized solar cell photoanode. Int. J. Photoenergy. 2015, 1–8 (2015)
Löberg, J., Perez Holmberg, J., Mattisson, I., Arvidsson, A., Ahlberg, E.: Electronic properties of nanoparticles films and the effect on apatite-forming ability. Int. J. Dent. 2013, 1–14 (2013)
Devi, G.S., Hyodo, T., Shimizu, Y., Egashira, M.: Synthesis of mesoporous TiO2-based powders and their gas-sensing properties. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 87(1), 122–129 (2002)
Djerdj, I., Tonejc, A.M.: Structural investigations of nanocrystalline TiO2 samples. J. Alloys Compd. 413(1–2), 159–174 (2006)
Zhang, J., Zhou, P., Liu, J., Yu, J.: New understanding of the difference of photocatalytic activity among anatase, rutile and brookite TiO2. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16(38), 20382–20386 (2014)
Mironyuk, I., Tatarchuk, T., Naushad, M., Vasylyeva, H., Mykytyn, I.: Highly efficient adsorption of strontium ions by carbonated mesoporous TiO2. J. Mol. Liq. 285, 742–753 (2019)
Mironyuk, I., Tatarchuk, T., Vasylyeva, H., Gun'ko, V.M., Mykytyn, I.: Effects of chemosorbed arsenate groups on the mesoporous titania morphology and enhanced adsorption properties towards Sr(II) cations. J. Mol. Liq. 282, 587–597 (2019)
Scheringer, M.: Nanoecotoxicology: environmental risks of nanomaterials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 3, 322–323 (2008)
Gouda, M., Aljaafari, A.I.: Augmentation of multifunctional properties of cellulosic cotton fabric using titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Advances in Nanoparticles. 1, 29–36 (2012)
Baan, R., Straif, K., Grosse, Y., Secretan, B., El Ghissassi, F., Cogliano, V.: Carcinogenicity of carbon black, titanium dioxide, and talc. Lancet Oncol. 7, 295–296 (2006)
Han, F., Kambala, V.S.R., Srinivasan, M., Rajarathnam, D., Naidu, R.: Tailored titanium dioxide photocatalysts for the degradation of organic dyes in wastewater treatment: a review. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 359, 25–40 (2009)
Mills, A., Hodgen, S., Lee, S.K.: Self-cleaning titania films: an overview of direct, lateral and remote photo-oxidation processes. Res. Chem. Intermed. 31(4), 295–308 (2005)
Weir, A., Westerhoff, P., Fabricius, L., Hristovski, K., Von Goetz, N.: Titanium dioxide nanoparticles in food and personal care products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 46, 2242–2250 (2012)
Di Paola, A., Ikeda, S., Marcì, G., Ohtani, B., & Palmisano, L. (2001). Transition metal doped TiO2: physical properties and photocatalytic behavior. Int. J. Photoenergy, 3(4), 171–176
Nasralla, N., Yeganeh, M., Astuti, Y., Piticharoenphun, S., Shahtahmasebi, N., Kompanyb, A., Karimipour, M., Mendisd, B.G., Pooltone, N.R.J., Šiller, L.: Structural and spectroscopic study of Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel method. Scientia Iranica F. 20(3), 1018–1022 (2013)
Vigil, E., Gonzáles, B., Zumeta, I., Domingo, C., Doménech, X., Ayllón, J.A.: Preparation of photoelectrodes with spectral response in the visible without applied bias based on photochemically deposited copper oxide inside a porous titanium dioxide film. Thin Solid Films. 489(1–2), 50–55 (2005)
Othman, S.H., Rashid, S.A., Mohd Ghazi, T.I., Abdullah, N.: Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles produced via MOCVD: synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic activity. J. Nanomater. 2011, 8, (2011)
Chanda, A., Rout, K., Vasundhara, M., Joshi, S.R., Singh, J.: Structural and magnetic study of undoped and cobalt doped TiO2 nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 8(20), 10939–10947 (2018)
Desireé, M., Navas, J., Sánchez-Coronilla, A., Alcántara, R., Fernández-Lorenzo, C., Martín-Calleja, J.: Highly Al-doped TiO2 nanoparticles produced by ball mill method: structural and electronic characterization. Mater. Res. Bull. 70, 704–711 (2015)
Avciata, O., Benli, Y., Gorduk, S., Koyun, O.: Ag doped TiO2 nanoparticles prepared by hydrothermal method and coating of the nanoparticles on the ceramic pellets for photocatalytic study: surface properties and photoactivity. Journal of Engineering Technology and Applied Sciences. 1(1), 34–50 (2016)
Zhang, Y., Shen, Y., Gu, F., Wu, M., Xie, Y., Zhang, J.: Influence of Fe ionsin characteristics and optical properties of mesoporous titanium oxide thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 256(1), 85–89 (2009)
Ali, T., Tripathi, P., Azam, A., Raza, W., Ahmed, A.S., Ahmed, A., Muneer, M.: Photocatalytic performance of Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles under visible-light irradiation. Mater. Res. Express. 4, 015022 (2017)
Prinz, G. A. (2001). Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science. 282.5394. 1660 282, 1660 (1998). Google Scholar Crossref, CAS
Wolf, S.A., Awschalom, D.D., Buhrman, R.A., Daughton, J.M., Von Molnar, S., Roukes, M.L., Treger, D.M.: Spintronics: a spin-based electronics vision for the future. Science. 294(5546), 1488–1495 (2001)
Ohno, H.: Making nonmagnetic semiconductors ferromagnetic. Science. 281(5379), 951–956 (1998)
Dietl, T., Ohno, H., Matsukura, F., Cibert, J., Ferrand, E.D.: Zener model description of ferromagnetism in zinc-blende magnetic semiconductors. Science. 287(5455), 1019–1022 (2000)
Choudhury, B., Choudhury, A.: Structural, optical and ferromagnetic properties of Cr doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. B. 178(11), 794–800 (2013)
Santara, B., Pal, B., Giri, P.K.: Signature of strong ferromagnetism and optical properties of Co doped TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 110(11), 114322 (2011)
Santara, B., Giri, P.K., Dhara, S., Imakita, K., Fujii, M.: Oxygen vacancy-mediated enhanced ferromagnetism in undoped and Fe-doped TiO2 nanoribbons. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 47(23), 235304 (2014)
Atsumoto, Y., Murakami, M., Shono, T., Hasegawa, T., Fukumura, T., Kawasaki, M., Koinuma, H.: Room-temperature ferromagnetism in transparent transition metal-doped titanium dioxide. Science. 291(5505), 854–856 (2001)
Wang, Q., Liu, X., Wei, X., Dai, J., Li, W.: Ferromagnetic property of co and Ni doped TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Nanomater. 1–5 (2015)
Nithyaa, N., Jaya, N.V.: Structural, optical, and magnetic properties of Gd-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 31, 4117–4126 (2018)
Sun, J., Zhang, J.X., Fu, Y.Y., Hu, G.X.: Microstructural evolution of an Al67Mn8Ti24Nb1 alloy during mechanical milling and subsequent annealing process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 329, 703–707 (2002)
Hang, D.L., Mukhtar, A., Kong, C., Munroe, P.: Synthesis and thermal stability of Cu-(2.5-10) vol.% Al2O3nanocomposite powders by high energy mechanical milling. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 144(1), 012028 (2009)
Yadav, T.P., Mukhopadhyay, N.K., Tiwari, R.S., Srivastava, O.N.: Studies on Al–Ni–Fe decagonal quasicrystalline alloy prepared by mechanical alloying. Philos. Mag. 87(18–21), 3117–3125 (2007)
Lutterotti, L. (2016). Microstructure Analysis by MAUD.http://maud.radiographema.com/
Rietveld, H.: A profile refinement method for nuclear and magnetic structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2(2), 65–71 (1969)
Li, J.G., Ishigaki, T., Sun, X.: Anatase, brookite, and rutile nanocrystals via redox reactions under mild hydrothermal conditions: phase-selective synthesis and physicochemical properties. J. Phys. Chem. C. 111(13), 4969–4976 (2007)
Bose, P., Pradhan, S.K., Sen, S.: Rietveld analysis of polymorphic transformations of ball milled anatase TiO2. Mater. Chem. Phys. 80(1), 73–81 (2003)
Begin-Colin, S., Girot, T., Le Caër, G., Mocellin, A.: Kinetics and mechanisms of phase transformations induced by ball-milling in anatase TiO2. J. Solid State Chem. 149(1), 41–48 (2000)
Garza-Arévalo, J.I., García-Montes, I., Reyes, M.H., Guzmán-Mar, J.L., Rodríguez-González, V., Reyes, L.H.: Fe doped TiO2 photocatalyst for the removal of As (III) under visible radiation and its potential application on the treatment of As-contaminated groundwater. Mater. Res. Bull. 73, 145–152 (2016)
Choudhury, B., Verma, R., Choudhury, A.: Oxygen defect assisted paramagnetic to ferromagnetic conversion in Fe doped TiO2 nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 4(55), 29314–29323 (2014)
Palaniandy, S., Jamil, N.H.: Influence of milling conditions on the mechanochemical synthesis of CaTiO3 nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 476(1–2), 894–902 (2009)
Carneiro, J.O., Azevedo, S., Fernandes, F., Freitas, E., Pereira, M., Tavares, C.J., Teixeira, V.: Synthesis of iron-doped TiO2 nanoparticles by ball-milling process: the influence of process parameters on the structural, optical, magnetic, and photocatalytic properties. J. Mater. Sci. 49(21), 7476–7488 (2014)
Deiana, C., Minella, M., Tabacchi, G., Maurino, V., Fois, E., Martra, G.: Shape-controlled TiO2 nanoparticles and TiO2 P25 interacting with CO and H2O2 molecular probes: a synergic approach for surface structure recognition and physico-chemical understanding. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15(1), 307–315 (2013)
Jun, D., Qi, W., Shan, Z., Xin, G., Jiao, L., Haizhi, G., Wenlong, Z., Hailong, P., Jianguo, Z.: Effect of hydroxyl groups onhydrophilic and photocatalytic activities of rare earth doped titanium dioxide thin films. J. Rare Earths. 33(2), 148–153 (2015)
Ganesh, I., Kumar, P.P., Gupta, A.K., Sekhar, P.S., Radha, K., Padmanabham, G., Sundararajan, G.: Preparation and characterization of Fe-doped TiO2 powders for solar light response and photocatalytic applications. Processing and Application of Ceramics. 6(1), 21–36 (2012)
Khan, H., Swati, I.K.: Fe3+-doped anatase TiO2 with d–d transition, oxygen vacancies and Ti3+ centers: synthesis, characterization, UV–vis photocatalytic and mechanistic studies. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 55(23), 6619–6633 (2016)
Zielińska, B., Borowiak-Palen, E., Kalenczuk, R.J.: A study on the synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity of TiO2 derived nanostructures. Mater. Sci.-Pol. 28(3), 625–637 (2010)
Van Minh, N., Long, D.H., Khoi, N.T., Jung, Y., Kim, S.J., Yang, I.S.: Raman studies of Ti1-x FexO2 nanoparticles. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 7(2), 177–180 (2008)
Tompsett, G.A., Bowmaker, G.A., Cooney, R.P., Metson, J.B., Rodgers, K.A., Seakins, J.M.: The Raman spectrum of brookite, TiO2 (Pbca, Z = 8). J. Raman Spectrosc. 26, 57–62 (1995)
Alexandrescu, R., Morjan, I., Scarisoreanu, M., Birjega, R., Popovici, E., Soare, I., Prodan, G.: Structural investigations on TiO2 and Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles synthesized by laser pyrolysis. Thin Solid Films. 515(24), 8438–8445 (2007)
Wu, Q., Zheng, Q., van de Krol, R.: Creating oxygen vacancies as a novel strategy to form tetrahedrally coordinated Ti4+ in Fe/TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C. 116(12), 7219–7226 (2012)
Khoshnevisan, B., Marami, M.B., Farahmandjou, M.: Fe3+-doped anatase TiO2 study prepared by new sol-gel precursors. ChinesePhysicsLetters. 35(2), 027501 (2018)
Marami, M.B., Farahmandjou, M., Khoshnevisan, B.: Sol–gel synthesis of Fe-doped TiO2 nanocrystals. J. Electron. Mater. 47(7), 3741–3748 (2018)
Vargas, X.M., Marin, J.M., Restrepo, G.: Characterization and photocatalytic evaluation (UV-visible) of Fe-doped TiO2 systems calcined at different temperatures. J. Adv. Oxid. Technol. 18(1), 129–138 (2015)
Fabbiyola, S., Sailaja, V., Kennedy, L.J., Bououdina, M., Vijaya, J.J.: Optical and magnetic properties of Ni-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 694, 522–531 (2017)
Khatoon, S., Wani, I.A., Ahmed, J., Magdaleno, T., Al-Hartomy, O.A., Ahmad, T.: Effect of high manganese substitution at ZnO host lattice using solvothermal method: structural characterization and properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 138(2–3), 519–528 (2013)
Ghosh, S., Khan, G.G., Mandal, K., Samanta, A., Nambissan, P.M.G.: Evolution of vacancy-type defects, phase transition, and intrinsic ferromagnetism during annealing of nanocrystalline TiO2 studied by positron annihilation spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C. 117(16), 8458–8467 (2013)
Assadi, M.H.N., Hanaor, D.A.: Theoretical study on copper’s energetics and magnetism in TiO2 polymorphs. J. Appl. Phys. 113(23), 233913 (2013)
Hou, Q., Zhao, C., Guo, S., Mao, F., Zhang, Y.: Effect on electron structure and magneto-optic property of heavy W-doped anatase TiO2. PLoS One. 10(5), e0122620 (2015)
Patel, S.K.S., Gajbhiye, N.S.: Intrinsic room-temperature ferromagnetism of V-doped TiO2 (B) nanotubes synthesized by the hydrothermal method. Solid State Commun. 151(20), 1500–1503 (2011)
Amade, R., Heitjans, P., Indris, S., Finger, M., Haeger, A., Hesse, D.: Defect formation during high-energy ball milling in TiO2 and its relation to the photocatalytic activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 207(2–3), 231–235 (2009)
Pongwan, P., Inceesungvorn, B., Wetchakun, K., Phanichphant, S., Wetchakun, N.: Highly efficient visible-light-induced photocatalytic activity of Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Eng. J. 16(3), 143–152 (2012)
Ismail, M. A ., Memo, N. k., Hedhili, M. N., Anjum, D. H., Bhunia, M., & Suk Ho Chung, S. H. Rhodamine-B dye photodegradation on Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles synthesized by flame spray pyrolysis. Nineteenth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC19 Sharm El Sheikh, 21–23 April 2016
Zhang, H., Xu, Y., Yang, W., Lin, R.: Structural and magnetic evolution of Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles synthesized by sol-gel method. J. Electroceram. 38(1), 104–110 (2017)
Zahid, R., Manzoor, M., Rafiq, A., Ikram, M., Nafees, M., Butt, A.R., Ali, S.: Influence of iron doping on structural, optical and magnetic properties of TiO2 nanoparticles. Electron. Mater. Lett. 14(5), 587–593 (2018)
Wang, Y., Zhang, R., Li, J., Li, L., Lin, S.: First-principles study on transition metal-doped anatase TiO2. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 9(1), 46 (2014)
Wu, H.C., Li, S.H., Lin, S.W.: Effect of Fe concentration on Fe-doped anatase TiO2 from GGA. Int. J. Photoenergy. 1–6 (2012)
Mallia, G., Harrison, N.M.: Magnetic moment and coupling mechanism of iron-doped rutile TiO2 from first principles. Phys. Rev. B. 75(16), 165201 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kissoum, Y., Mekki, D.E., Bououdina, M. et al. Dependence of Fe Doping and Milling on TiO2 Phase Transformation: Optical and Magnetic Studies. J Supercond Nov Magn 33, 427–440 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-019-05169-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-019-05169-7