Abstract
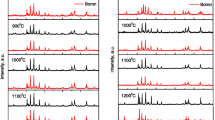
Barium hexaferrite (BaFe12O19) ceramics were obtained by combination of polyol-synthesized precursors subsequently consolidated by spark plasma sintering (SPS) at a low temperature (800 ∘C). X-ray powder diffraction studies showed the influence of the experimental parameters to produce a virtually single- or multiphase material. The room temperature magnetic properties exhibited interesting variety of properties, including exchange coupling (spring magnet) between hexaferrite and other magnetic phases. The saturation magnetization and coercive field, at room temperature, are in the 34–70 emu/g and 4.1–5.0 kOe ranges, respectively. The combination of strong coercive field and magnetization resulted in a maximum energy product [(BH)max] = 10.9 kJ/m3 for the sample with the highest BaFe12O19 content.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pullar, R.C.: Hexagonal ferrites: a review of the synthesis, properties and applications of hexaferrite ceramics. Prog. Mater. Sci. 57(7), 1191–1334 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.pmatsci.2012.04.001
Haq, A., Anis-ur-Rehman, M.: Effect of Pb on structural and magnetic properties of Ba-hexaferrite. Physica B 407, 822–826 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.physb.2011.11.038
Ghzaiel, T.B., Dhaoui, W., Pasko, A., Mazaleyrat, F.: Effect of non-magnetic and magnetic trivalent ion substitutions on BaM-ferrite properties synthesized by hydrothermal method. J. Alloys Compd. 671, 245–253 (2016). doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.02.071
González-Carreño, T., Morales, M.P., Serna, C.J.: Barium ferrite nanoparticles prepared directly by aerosol pyrolysis. Mater. Lett. 43(3), 97–101 (2000). doi:10.1016/S0167-577X(99)00238-4
Xu, P., Han, X., Wang, M.: Synthesis and magnetic properties of BaFe12O19 hexaferrite nanoparticles by a reverse microemulsion technique. J. Phys. Chem. C 111(16), 5866–5870 (2007)
Drofenik, M., Ban, I., Makovec, D., žnidaršič, A., Jagličić, Z., Hanžel, D., Lisjak, D.: The hydrothermal synthesis of super-paramagnetic barium hexaferrite particles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 127, 415–419 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2011.02.037
Orrù, R., Licheri, R., Locci, A.M., Cincotti, A., Cao, G.: Consolidation/synthesis of materials by electric current activated/ assisted sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng., R 63(4), 127–287 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.mser.2008.09.003
Kneller, E.F., Hawig, R.: The exchange-spring magnet: a new principle for permanent magnets. IEEE Trans. Mag. 27(4), 3588–3600 (1991). doi:10.1109/20.102931
Beji, Z., Smiri, L.S., Yaacoub, N., Greneche, J.M., Menguy, N., Ammar, S., Fievet, F.: Annealing effect on the magnetic properties of polyol-made Ni-Zn ferrite nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 22(4), 1350–1366 (2010). doi:10.1021/cm901969c
Gaudisson, T., Acevedo, U., Nowak, S., Yaacoub, N., Greneche, J.M., Ammar, S., Valenzuela, R.: Combining soft chemistry and spark plasma sintering to produce highly dense and finely grained soft ferrimagnetic Y3Fe5O12 (YIG) ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96(10), 3094–3099 (2013). doi:10.1111/jace.12452
Stingaciu, M., et al.: Magnetic properties of ball-milled SrFe12O19 particles consolidated by Spark-Plasma Sintering. Sci. Rep. 5, 14112 (2015). doi:10.1038/srep14112
Valenzuela, R., Gaudisson, T., Ammar, S.: Severe reduction of Ni-Zn ferrites during consolidation by spark plasma sintering (SPS). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 400, 311–314 (2016). doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.07.044
Shepherd, P., Mallick, K.K., Green, R.J.: Magnetic and structural properties of M-type barium hexaferrite prepared by co-precipitation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 311(2), 683–692 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2006.08.046
Franceschin, G., Flores-Martínez, N., Vázquez-Victorio, G., Ammar, S., Valenzuela, R.: Sintering and reactive sintering by spark plasma sintering (SPS). In: Shishkovsky, I.V. (ed.) Sintering. Intechopen (In Press)
Acevedo, U., Gaudisson, T., Ortega-Zempoalteca, R., Nowak, S., Ammar, S., Valenzuela, R.: Magnetic properties of ferrite-titanate nanostructured composites synthesized by the polyol method and consolidated by spark plasma sintering. J. Appl. Phys. 113, 17B519 (2013). doi:10.1063/1.4798604
Valenzuela, R.: Magnetic Ceramics, p. 129. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vázquez-Victorio, G., Flores-Martínez, N., Franceschin, G. et al. Low-Temperature Short-Time SPS Processes to Produce Fine-Grained High-Coercivity Barium Hexaferrite Ceramics from Polyol Nanoparticles. J Supercond Nov Magn 31, 347–351 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-017-4219-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-017-4219-x