Abstract
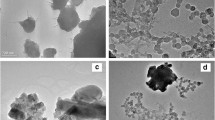
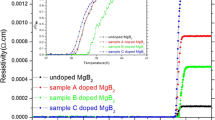
The effects of the amount of hexylbenzene additive (C12H18) on the structural, thermal, and magnetic properties of MgB2 superconductor are examined in this study. Pure and hexylbenzene-doped MgB2 bulk samples were produced with in situ solid-state reaction method. X-ray diffraction patterns of MgB2 doped with MgB2 and hexylbenzene at different ratios were determined to have MgB2 as the main phase and consisted of a small amount of MgO. Pure and different ratios of hexylbenzene-doped Mg and B starting powders were heat-treated by a differential scanning calorimeter between room temperature and 800 °C. It was determined from the differential scanning calorimetry curves obtained that the first exothermic peak pointed the MgB2 phase emerging with a solid–solid (Mg–B) reaction, and this temperature shifted towards the low temperatures as the hexylbenzene addition rates increased. It was observed that there was dependency to the applied field in all samples from the ac susceptibility measurements as a function of the temperature in pure and hexylbenzene-doped MgB2 superconductor materials, and shift towards the lower temperatures in T c, superconducting transition temperature, with increasing content. It was observed that the changes occurred in in-phase (\(\chi ^{\prime })\) and out-off-phase (\(\chi ^{\prime \prime }\)) components of ac susceptibility both weakened the MgB2 phase structure of hexylbenzene content and, as a result of this, led to changes in the pinning mechanism.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nagamatsu, J., Nakagawa, N., Muranaka, T., Zenitani, Y., Akimitsu, J.: Nature 410, 63 (2001)
Dou, S.X., Soltanian, S., Horvat, J., Wang, X.L., Zhou, S.H., Ionescu, M., Liu, H.K., Munroe, P., Tomsic, M.: Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 3419–3421 (2002)
Kumakura, H., Kitaguchi, H., Matsumoto, A., Hatekayama, H.: Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 3669–3671 (2004)
Sumption, M.D., Bhatia, M., Dou, S.X., Rindfliesch, M., Tomsic, M., Arda, L., Ozdemir, M., Hascicek, Y., Collings, E.W.: Supercond. Sci. Technol. 17, 1180–1184 (2004)
Wilke, R.H.T., Bud’ko, S.L., Canfield, P.C., Finnemore, D.K., Suplinskas, R.J., Hannahs, S.T.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 217003 (2004)
Yeoh, W.K., Kim, J.H., Horvat, J., Xu, X., Qin, M.J., Dou, S.X., Jiang, C.H., Nakane, T., Kumakura, H., Munroe, P.: Supercond. Sci. Technol. 19, 596–599 (2006)
Kim, J.H., Yeoh, W.K., Qin, M.J., Xu, X., Dou, S.X.: J. Appl. Phys. 100, 013908 (2006)
Yamada, H., Hirakawa, M., Kumakura, H., Kitaguchi, H.: Supercond. Sci. Technol. 19, 175–177 (2006)
Babaoğlu Meral, G., Serap, S., Özlem, Ç., Hasan, A., Ercan, E., Md, H., Shahriar, A., Ekrem, Y., Ali, G.: J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324(21), 3455–3459 (2012)
Kim, J.H., Zhou, S., Hossain, M.S.A., Pan, A.V., Dou, S.X.: Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 142505 (2006)
Hossain, M.S.A., Kim, J.H., Xu, X., Wang, X.L., Rindfleisch, M., Tomsic, M., Sumption, M.D., Collings, E.W., Dou, S.X.: Supercond. Sci. Technol. 20, L51–L54 (2007)
Ağl, H., Çiçek, Ö., Ertekin, E., Motaman, A., Hossain, M.S.A., Dou, S.X., Gencer, A.: J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 26(5), 1525–1529 (2013)
Kazakov, S.M., Puzniak, R., Rogacki, K., Mironov, A.V., Zhigadlo, N.D., Jun, J., Soltmann, C. h., Batlogg, B., Karpinski, J.: Phys. Rev. B 71, 024533 (2005)
Senkowicz, B.J., Giencke, J.E., Patnaik, S., Eom, C.B., Hellstrom, E.E., Larbalestier, D.C.: Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 202502 (2005)
Bean, C.P.: Rev. Mod. Phys. 36, 31–39 (1964)
Kimishima, Y., Takami, S., Okuda, T., Uehara, M., Kuramoto, T., Sugiyama, Y.: Phys. C 281-285, 463–465 (2007)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Research Fund of Hakkari University, Hakkari, Turkey, under grant contract no. MF2014BAP2, and by the Republic of Turkey, Ministry of Development, under the project number 2010K120520.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ağıl, H., Aksu, E., Aktürk, S. et al. The Effects of Structural, Thermal, and Magnetic Properties of Hexylbenzene-Doped MgB2 Superconductor. J Supercond Nov Magn 30, 1727–1736 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-017-3982-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-017-3982-z