Abstract
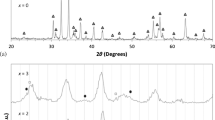
In this research, nano-sized powders of strontium hexaferrite were synthesized by sol-gel auto-combustion route using stoichiometric ratio of Fe/Sr. The effect cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) addition on microstructure and magnetic properties of hexaferrite have been studied. The samples were characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), dynamic light scattering (DLS), vibration sample magnetometer (VSM), field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM), and transmission electron microscope (TEM) techniques. The results revealed that CTAB addition causes a noticeable reduction in the amount of residual α-Fe2O3 phase, since presence of CTAB in the sol facilitates the entrance of Sr2+ ions into the reactions of hexaferrite formation. Also, the morphology of the particles was affected by CTAB addition. Irregular-shaped nanoparticles were synthesized without CTAB additions, while platelet-shaped nanoparticles were obtained by CTAB addition. The mechanism of strontium hexaferrite nanopowder formation has been explained. Magnetic measurements in the sample calcined at 800 °C for 1 h represented that CTAB addition increased the coercivity force (i H c) from 4.9 to 5.2 kOe and maximum magnetization (M max) from 48.4 to 60.4 emu/g, respectively.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhanyong, W., Liuming Z., Jieli, L., Huichun, Q., Yuli, Z., Yongzheng, F., Minglin, J., Jiayue, X.: Microwave-assisted synthesis of SrFe12O19 hexaferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 2782–2785 (2010)
Xia, A., Zuo, C., Chen, L., Jin, C., Lv, Y.: Hexagonal SrFe12O19 ferrites: hydrothermal synthesis and their sintering properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater 332, 186–191 (2013)
Wang, Y., Li, Q., Zhang, C., Li, B.: Effect of Fe/Sr mole ratios on the formation and magnetic properties of SrFe12O19 microtubules prepared by sol–gel method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 3368–3372 (2009)
Singh, P., Babbar, V.K., Razdan, A., Srivastava, S.L., Agrawal, V.K., Goel, T.C.: Dielectric constant, magnetic permeability and microwave absorption studies of hot-pressed Ba-CoTi hexaferrite composites in X-band. J. Mater. Sci. 41, 7190–7196 (2006)
Kuo, H.M., Hsui, Te-Fa., Tuo, Y.S., Yuan, C.L.: Microwave adsorption of core–shell structured Sr(MnTi)xFe 12−2xO19/PANI composites. J. Mater. Sci 47, 2264–2270 (2012)
Jacobo, S.E., Blesa, M.A., Domingo-Pascual, C., Rodpigguez-Clemente, R.: Synthesis of ultrafine particles of barium ferrite by chemical coprecipitation. J. Mater. Sci 32, 1025–1028 (1997)
Calleja, A., Tijero, E., Martinez, B., Pinol, S., Sandiumenge, F., Obradors, X.: Hexaferrite particles by coprecipitation and lyophilization. J. Magn. Magn. Mater 196–197, 293–294 (1999)
Barb, D., Diamandescu, L., Rusi, A.: Preparation of barium hexaferrite by a hydrothermal method: structure and magnetic properties. J. Mater. Sci 21, 1118–1122 (1986)
Ataie, A., Harris, I.R., Ponton, C.B.: Magnetic properties of hydrothermally synthesized strontium hexaferrite as a function of synthesis conditions. J. Mater. Sci 30, 1429–1433 (1995)
Elvin, G., Parkin, I.P.P., Bui, Q.T., Barquin, L.F., Pankhurst, Q.A., Komarov, A.V., Morozov, Y.G.: Self-propagating high-temperature synthesis of SrFe12O19 from reactions of strontium superoxide, iron metal and iron oxide powders. J. Mater. Sci. Lett 16, 1237–1239 (1997)
Ding, J., Miao, W.F., McCormick, P.G., Street, R.: High-coercivity ferrite magnets prepared by mechanical alloying. J. alloys comp. 281, 32–36 (1998)
Ketov, S.V., Yagodkin, Yu.D., Lebed, A.L., Chernopyatova, Yu. V., Khlopkov, K.: Structure and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline SrFe12O19 alloy produced by high-energy ball milling and annealing. J. Magn. Magn. Mater 300, e479–e481 (2006)
Surig, C., Hempel, K.A., Bonnenborg, D.: Hexaferrite particles prepared by sol-gel technique. IEEE Trans. Magn. 30, 4092–4094 (1994)
Srivastava, A., Singh, P., Gupta, M.P.: Barium ferrite: preparation by liquid mix technique and its characterization. J. Mater. Sci. 22, 1489–1494 (1987)
Pullar, R.C., Taylor, M.D., Bhattacharya, A.K.: Novel aqueous sol–gel preparation and characterization of barium M ferrite BaFe12O19 fibers. J. Mater. Sci. 32, 349–352 (1997)
Alamolhoda, S., Seyyed Ebrahimi, S.A., Badiei, A.: Optimization of the Fe/Sr ratio in processing of ultrafine strontium hexaferrite powders by a sol–gel auto combustion method. Phys. Met. Metall. 102, S71–S73 (2006)
Sivakumar, M., Gedanken, A., Zhong, W., Du, Y.W., Bhattacharya, D., Yeshurun, Y., Felner, I.: Nanophase formation of strontium hexaferrite fine powder by the sonochemical method using Fe(CO)5. J. Magn. Magn. Mater 268, 95–104 (2004)
Ghobeiti Hasab, M., Seyyed Ebrahimi, S.A., Badiei, A.: Comparison of the effects of cationic, anionic and nonionic surfactants on the properties of Sr-hexaferrite nanopowder synthesized by a sol–gel auto-combustion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 316, e13—e15 (2007)
Ghobeiti Hasab, M., Seyyed Ebrahimi, S.A., Badiei, A.: An investigation on physical properties of strontium hexaferrite nanopowder synthesized by a sol–gel auto-combustion process with addition of cationic surfactant. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 27, 3637–3640 (2007)
Rietveld, H.M.: A profile refinement method for nuclear and magnetic structures. J. Appl. Cryst. 2, 65–71 (1969)
Martell, E., Smith, R.M.: Critical stability constants, Vol. 3. Springer, New York (1977)
Topallar, H., Karadag, B.: Mechanism of micelle formation in sodium dodecyl sulfate and cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. J. Surfactants Deterg. 1, 49–51 (1998)
Dean, J.A.: Lange’s handbook of chemistry. 15 th edn. Mc Graw Hill, New York (1999)
Alamolhoda, S., Seyyed Ebrahimi, S.A., Badiei, A.: A study on the formation of strontium hexaferrite nanopowder by a sol–gel auto-combustion method in the presence of surfactant. J. Magn. Magn. Mater 303, 69–72 (2006)
Chen, D.Y., Meng, Y.Y., Zeng, D.C., Liu, Z.W., Yu, H.Y., Zhong, X.C.: CTAB-assisted low-temperature synthesis of SrFe12O19 ultrathin hexagonal platelets and its formation mechanism. Mater. Lett. 76, 84–86 (2012)
Singh, I., Bedi, R.K.: Surfactant-assisted synthesis, characterizations, and room temperature ammonia sensing mechanism of nanocrystalline CuO. Solid State Sci. 13, 2011–2018 (2011)
Pu, Z., Cao, M., Yang, J., Huang, K., Hu, C.: Controlled synthesis and growth mechanism of hematite nanorhombohedra, nanorods and nanocubes. Nanotechnology 17, 799–804 (2006)
Zhang, H., Shen, C., Chen, S., Xu, Z., Liu, F., Li, J., Gao, H.: Morphologies and microstructures of nano-sized Cu2O particles using a cetyltrimethylammonium template. Nanotechnology 16, 267–272 (2005)
Kang, S.K., Chah, S., Yun, C.Y., Yi, J.: Aspect ratio controlled synthesis of gold nanorods. Korean J. Chem. Eng 20, 1145–1148 (2003)
Mula, S., Mondal, K., Ghosh, S., Pabi, S.K.: Structure and mechanical properties of Al–Ni–Ti amorphous powder consolidated by pressure-less, pressure-assisted and spark plasma sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 527, 3757–3763 (2010)
Lin, C.S., Hwang, C.C., Huang, T.H., Wang, G.P., Peng, C.H.: Fine powders of SrFe12O19 with SrTiO3 additive prepared via a quasi-dry combustion synthesis route. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 139, 24–36 (2007)
Saravanan, P., Arvindha Babu, D., Chandrasekaran, V.: Microstructure, phase evolution and magnetic properties of melt-spun SmCo6.8− xSn x Zr 0.2 (x = 0, 0.1 and 0.3) ribbons. Intermetallics 19, 651–656 (2011)
Dzyaloshinsky, I.: A thermodynamic theory of weak ferromagnetism of antiferromagnetics. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 4, 241–255 (1958)
Bødker, F., Hansen, M.F., Koch, C.B., Lefmann, K., Mørup, S.: Magnetic properties of hematite nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 61, 6826–6838 (2000)
Moulson, A.J., Herbert, J.M.: Electroceramics Materials. Properties. Applications 2nd edn. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester (2003)
Spaldin, N.A.: Magnetic Materials, Fundamentals and Applications 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, New York (2010)
Pullar, R.C.: Hexagonal ferrites: a review of the synthesis, properties and applications of hexaferrite ceramics. Prog. Mater. Sci 57, 1191–1334 (2012)
Zi, Z.F., Sun, Y.P., Zhu, X.B., Yang, Z.R., Dai, J.M., Song, W.H.: Structural and magnetic properties of SrFe12O19 hexaferrite synthesized by a modified chemical co-precipitation method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320, 2746–2751 (2008)
Nga, T.T.V., Duong, N.P., Loan, T.T., Hien, T.D.: Key step in the synthesis of ultrafine strontium ferrite powders (SrFe12O19) by sol–gel method. J. Alloys Comp. 610, 630–634 (2014)
Xu, Y.F., Ma, Y.Q., Xu, S.T., Zan, F.L., Zheng, G.H., Dai, Z.X.: Effects of vacancy and exchange-coupling between grains on magnetic properties of SrFe12O19 and α-Fe2O3 composites. Mater. Res. Bull. (2014). doi:10.1016/j.materresbull.2014.05.017
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mirkazemi, S.M., Alamolhoda, S. & Ghiami, Z. Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of SrFe 12 O 19 Nano-sized Powders Prepared by Sol-Gel Auto-combustion Method with CTAB Surfactant. J Supercond Nov Magn 28, 1543–1549 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-014-2872-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-014-2872-x