Abstract
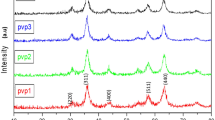
In this paper, we elucidate several specific magnetic properties of Fe 3 O 4nanoparticles synthesized by coprecipitation method. The characterizations by X-ray diffraction technique (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) showed the particles to be of spinel structure and spherical shapes whose diameter could be controlled in the range from 14 to 22 nm simply by adjusting the precursor salts concentration and coprecipitation temperature. Magnetic properties of the Fe 3 O 4 nanoparticles measured by using vibration sample magnetometer (VSM) indicated the saturation magnetization and blocking temperature to increase with the particles size. Fe 3 O 4 nanoparticles with crystal size smaller than 22 nm exhibits superparamagnetic behavior at room temperatures. Characteristic magnetic parameters of the particles including saturation magnetization, effective anisotropy constant, and magnetocrystalline anisotropy constant have been determined. The observed decrease of saturation magnetization was explained on the base of core-shell model. A simple analysis indicated that the shell thickness decreases with an increase in particle size.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caruntu, D., Caruntu, G., O’Connor, C.J.: Magnetic properties of variable-sized Fe 3 O 4 nanoparticles synthesized from non-aqueous homogeneous solutions of polyols. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 40, 5801–5809 (2007)
Mahmoudi, M., Mahmoudi, S., Sant, S., Wang, B., Laurent, S., Sen, T.: Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs): development, surface modification and applications in chemotherapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 63, 24–46 (2011)
Kwon, S.G., Piao, Y., Park, J., Angappane, S., Jo, Y., Hwang, N.-M., Park, J.-G., Hyeon, T.: Kinetics of monodisperse iron oxide nanocrystal formation by “heating-up” process. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 12571–12584 (2007)
Goya, G.F., Berquo, T.S., Fonseca, F.C.: Static and dynamic magnetic properties of spherical magnetite nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 94, 3520–3528 (2003)
Linh, P.H., Thach, P.V., Tuan, N.A., Thuan, N.C., Manh, D.H., Phuc, N.X., Hong, L.V.: Magnetic fluid based on Fe 3 O 4 nanoparticles: preparation and hyperthermia application. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 187, 012069 (2009)
Cullity, B.D.: Elements of X-Ray Diffraction, vol. 2nd ed., p. 356.Addison-Wesley, Reading (1978)
Morales, M.P., Veintemillas-Verdaguer, S., Montero, M.I., Serna, C.J., Roig, A., Casas, L.l., Martínez, B., Sandiumenge, F.: Surface and internal spin canting in γ-Fe 2 O 3 nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 11, 3058–3064 (1999)
Lima Jr. E., Brandl, A.L., Arelaro, A.D., Goy, G.F.: Spin disorder and magnetic anisotropy in Fe 3 O 4 nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 99, 083908 (2006)
Yang, H., Wang, Z., Song, L., Zhao, M., Wang, J., Luo, H.: A study on the coercivity and the magnetic anisotropy of the lithium ferrite nanocrystallite. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 29, 2574–2578 (1996)
Bate, G., Craik, D.J. (ed.): Magnetic Oxides. Wiley, London (1975)
Dunlop, D.J.: Superparamagnetic and single-domain threshold sizes in magnetite. J. Geophys. Res. 78, 1780–1792 (1973)
Sarkar, D., Mandal, M.: Static and dynamic magnetic characterization of DNA-templated chain-like magnetite nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 116, 3227–3234 (2012)
Gangopadhyay, S., Hadjipanayis, G.C., Dale, B., Sorensen, C.M., Klabunde, K.J., Papaefthymiou, V., Kostikas, A.: Magnetic properties of ultrafine iron particles. Phys. Rev. B 45, 9778 (1992)
Manh, D.H., Phong, P.T., Thanh, T.D., Nam, D.N.H., Hong, L.V., Phuc, N.X.: Size effects and interactions in La 0.7Ca 0.3MnO 3 nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 1373–1377 (2011)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Vietnam National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED) under grant number 103.02-2011.31, Institutes of Materials Science and National Key Laboratory for Electronic Material and Devices, Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Linh, P.H., Manh, D.H., Phong, P.T. et al. Magnetic Properties of Fe 3 O 4 Nanoparticles Synthesized by Coprecipitation Method. J Supercond Nov Magn 27, 2111–2115 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-014-2561-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-014-2561-9