Abstract
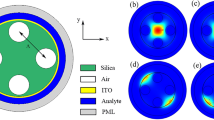
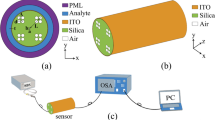
In this paper, we propose a high-sensitivity two-core dual-polarization photonic-crystal-fiber surfaceplasmon-resonance (PCF-SPR) sensor based on Indium Tin oxide (ITO). ITO is a conductor material with adjustable photoelectric properties and low losses in the infrared range, and the two-core structure could better direct the incident light to the metal surface to enhance the coupling. According to numerical simulation results, the maximum wavelength sensitivities are 17,000 nm/RIU and 25,500 nm/RIU in the x-polarization mode and y-polarization mode. The maximum resolution of the x-polarization mode and y-polarization mode of the sensor can reach 5.88·10−6 RIU and 3.92·10−6 RIU, respectively, and the liquid refractive index detection range is 1.32 – 1.39. Taking into account the simple structure and excellent sensing performance, the sensor has wide application prospect and can accurately detect the refractive index of liquids, such as blood plasma, hemoglobin, etc.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. F. Abdulrazak, Md. B. Hossain, Md. S. Islam, et al., Opt. Quantum Electron., 54, 58 (2022); DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-021-03441-6
D. Vijayalakshmi, C. T. Manimegalai, N. Ayyanar, et al., Opt. Quantum Electron., 53, 454 (2021); DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-021-03092-7
W. Liu, C. Hu, L. Zhou, et al., Phys. E: Low-Dimensional Systems and Nanostructures, 138, 115106 (2022); DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2021.115106
Q. Wang, H. Song, and A. Zhu, IEEE Trans. Instrum. Measurement, 70, 02007 (2021); DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2020.3039627
E. Kretschmann and H. Raether, Z. Naturforsch. A, 23, 2135 (1968); DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/zna-1968-1247
I. Danlard, I. O. Mensah, E. K. Akowuah, et al., Optik, 258, 168893 (2022); DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2022.168893
A. A. Revathi and D. Rajeswari, J. Opt., 2, 163 (2020); DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-020-00600-y
S. Jain, K. Choudhary, and S. Kumar, Opt. Fiber Technol., 73, 103030 (2022); DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yofte.2022.103030
M. R. Islam, M. A. Jamil, Md. S. Zaman, et al., Optik, 221, 165311 (2020); DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.165311
Y. Liu and H. Chen, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 54, 325103 (2021); DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/abfce7
C. Liu, Y. Zhang, X. Li, et al., Opt. Fiber Technol., 72, 102975 (2022); DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yofte.2022.102975
Md. N. Sakib, Mb. B. Hossainb, K. F. Al-tabatabaie, et al., Results Phys., 15, 102788 (2019); DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2019.102788
C. Li, B. Song, Y. Guo, et al., IEEE Sensors J., 11, 5893 (2020); DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2020.2972031
C. Liu, J. Wang, F. Wang, et al., Opt. Commun., 464, 125496 (2020); DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2020.125496
S. Yao, Y. Yu, S. Qin, et al., Opt. Express, 9, 16405 (2022); DOI: https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.456924
G. Soghra, B. Jamal, and M. Bahar, Optik, 260, 169026 (2022); DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2022.169026
Q. Liu, Y. Jiang, Y. Sun, et al., Appl. Opt., 60, 1761 (2021); DOI: https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.419518
H. Talukder, M. H. K. Anik, M. I. A. Isti, et al., Eur. Phys. J. Plus, 137, 1262 (2022); DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-03484-y
Md. A. Mollah and Md. S. Islam, IEEE Sensors J., 3, 2813 (2020); DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2020.3023975
R. Nasirifar, M. Danaie, and A. Dideban, Optik, 250, 168051 (2022); DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.168051
A. K. Shakya and S. Singh, Measurement, 188, 110513 (2022); DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2021.110513
J. N. Jabir and N. A. Areebi, Opt. Quantum Electron., 54, 626 (2022); DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-022-03950-y
D. Rajeswari and A. A. Revathi, Optik, 258, 168897 (2022); DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2022.168897
S. Singh and Y. K. Prajapati, Optik, 235, 166657 (2021); DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.166657
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, N., Pan, H., Zhang, A. et al. High-Sensitivity Two-Core Dual-Polarization Photonic-Crystal-Fiber Surface-Plasmon-Resonance Sensor Based on Indium Tin Oxid. J Russ Laser Res 44, 375–383 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10946-023-10144-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10946-023-10144-8