Abstract
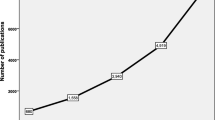
There is a large body of research on Ramadan intermittent fasting (RIF) and health in Muslim communities, that can offer insights to promote the achievement of Sustainable Development Goal 3 (SDG 3), which encompasses good health and well-being. Based on recent bibliometric evidence, we hypothesized that RIF research is highly relevant to SDG 3, particularly Targets 3.1, 3.2, 3.4, and 3.5. Therefore, this bibliometric study quantified RIF literature supporting SDG 3 and associated targets over the past seven decades and explored themes and trends. All types of research articles were extracted from the Scopus database from inception to March 2022. Microsoft Excel, Biblioshiny, and VOSviewer were used to qualitatively and quantitatively examine RIF research trends supporting SDG 3 and associated targets. We identified 1729 relevant articles. The number of publications notably increased since 1986, with a dramatic increase in 2019–2020. RIF research predominantly supported Target 3.4 (reducing risk for non-communicable diseases), with research hotspots being diabetes, diabetes medications, pregnancy, physiology, metabolic diseases, and obesity and metabolism. This target was also the most commonly supported by dedicated authors and institutions publishing on RIF, whereas other SDG 3 targets were negligibly addressed in comparison. Our comprehensive bibliometric analysis of RIF literature showed growing support for SDG 3 through positive contributions to half of the SDG 3 targets, although Target 3.4 received the most attention. We also identified knowledge gaps that may shape further research directions on RIF and promote the achievement of SDG 3 in Muslim communities.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data are contained in Supplementary Material S3.
References
Afandi, B., Hassanein, M., Roubi, S., & Nagelkerke, N. (2019). The value of continuous glucose monitoring and self-monitoring of blood glucose in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus during Ramadan fasting. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 151, 260–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2019.01.036
Al-Houqani, M., Eid, H. O., & Abu-Zidan, F. M. (2013). Sleep-related collisions in United Arab Emirates. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 50, 1052–1055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2012.08.010
Al-Jayyousi, O., Tok, E., Saniff, S. M., Wan Hasan, W. N., Janahi, N. A., & Yesuf, A. J. (2022). Re-thinking sustainable development within Islamic worldviews: A systematic literature review. Sustainability, 14(12), 7300. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127300
Al-Masaeid, H. R., Bazlamit, S. M., Al-Zedaneen, A. E., & Al-Mofleh, H. M. (2020). Impact of fasting on traffic accidents. Jordan Journal of Civil Engineering, 14(3), 431–442. (Paper has no DOI)
AlSheef, M., Alotaibi, M., Zaidi, A. R. Z., Alshamrani, A., Alhamidi, A., Zaidi, S. Z. A., Alanazi, N., Alhathlool, S., Alarfaj, O., AlHazzaa, M., Kullab, G., Alboghdadly, A., & Abu-Shaheen, A. (2020). Prevalence of cerebral venous thrombosis with the use of oral contraceptive pills during the Holy month of Ramadan. Saudi Medical Journal, 41(10), 1063–1069. https://doi.org/10.15537/smj.2020.10.25397
Amoozegar, F., Ronksley, P. E., Sauve, R., & Menon, B. K. (2015). Hormonal contraceptives and cerebral venous thrombosis risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Frontiers in Neurology, 6, 7–7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2015.00007
Aria, M., & Cuccurullo, C. (2017). bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. Journal of Informetrics, 11(4), 959–975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2017.08.007
Ariani, M., Achmad, Y., Kamarruzzaman, K., Agustina, I., Donna, B., & Wartatmo, H. (2019). Health sector preparedness during the Eid-al-Fitr homecoming across Indonesia in 2017. Prehospital and Disaster Medicine, 34(s1), s65–s65. https://doi.org/10.1017/s1049023x19001444
Asfahan, S., Chawla, G., & Dutt, N. (2020). Ramadan and COVID-19: A challenge amongst challenges. Turkish Thoracic Journal, 21(4), 285. https://doi.org/10.5152/TurkThoracJ.2020.20076
Auzureen, A., Aklilu, E., Khan, M., Hamdan, R. H., Sultan, A., & Soon, J. M. (2017). Microbiological quality of cooked meat products sold in Kelantan, Malaysia during Ramadhan month. International Food Research Journal, 24(1): 414–421. (Paper has no DOI)
Awad, A., Ibrahim, Y., Munir, S., Habeeballah, T., & Elmorsy, T. (2016). Characterization of street dust nearby the holy mosques in Ramadan and Hajj seasons, Saudi Arabia. Environment Asia, 9(2), 1–9. (Paper has no DOI)
BaHammam, A. S., & Almeneessier, A. S. (2020). Recent evidence on the impact of Ramadan diurnal intermittent fasting, mealtime, and circadian rhythm on cardiometabolic risk: A review. Frontiers in Nutrition, 7, 28. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2020.00028
Ben Ammar, H., Ben Massoued, R., Ben Hamadi, A., Khelifa, E., Hakiri, A., & El Hechmi, Z. (2022). Hospitalizations in psychiatry during the month of Ramadan: A study at the Tunisian mental health hospital. International Journal of Social Psychiatry, 68(2), 341–345. https://doi.org/10.1177/0020764020988888
Benchrif, A., Wheida, A., Tahri, M., Shubbar, R. M., & Biswas, B. (2021). Air quality during three covid-19 lockdown phases: AQI, PM2.5 and NO2 assessment in cities with more than 1 million inhabitants. Sustainable Cities and Society, 74, 103170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2021.103170
Beshyah, S. A. (2019). Authors’ selection of target journals and their attitudes to emerging journals: A survey from two developing regions. Sultan Qaboos University Medical Journal, 19(1), e51. https://doi.org/10.18295/squmj.2019.19.01.010
Beshyah, W. S., & Beshyah, S. A. (2019). Bibliometric analysis of the literature on Ramadan fasting and diabetes in the past three decades (1989–2018). Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 151, 313–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2019.03.023
Bragazzi, N. L., Briki, W., Khabbache, H., Rammouz, I., Mnadla, S., Demaj, T., & Zouhir, M. (2015). Ramadan fasting and infectious diseases: A systematic review. The Journal of Infection in Developing Countries, 9(11), 1186–1194. https://doi.org/10.3855/jidc.5815
Chowdhury, T. A., Waqar, S., Hussain, S., Ahmed, S. H., Syed, A., Karamat, A., Helmy, A., & Ghouri, N. (2020). COVID-19, diabetes and Ramadan. Diabetes Therapy, 11(11), 2447–2451. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-020-00887-x
De Cabo, R., & Mattson, M. P. (2019). Effects of intermittent fasting on health, aging, and disease. New England Journal of Medicine, 381(26), 2541–2551. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1905136
De Miguel Ramos, C., & Laurenti, R. (2020). Synergies and trade-offs among sustainable development goals: The case of Spain. Sustainability, 12(24), 10506. https://doi.org/10.3390/su122410506
Donthu, N., Kumar, S., Mukherjee, D., Pandey, N., & Lim, W. M. (2021). How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. Journal of Business Research, 133, 285–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.04.070
Eck van, N. J., & Waltman, L. (2021). VOSviewer Manual. In (Version 1.6.17) Stockholm Environment Institute. https://www.vosviewer.com/documentation/Manual_VOSviewer_1.6.17.pdf Accessed on 20 january, 2023.
Elling, D., Surkan, P. J., Enayati, S., & El-Khatib, Z. (2018). Sex differences and risk factors for diabetes mellitus-an international study from 193 countries. Globalization and Health, 14(1), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12992-018-0437-7
Elsevier. Scopus Content Coverage Guide. Elsevier 2020. Available online: https://www.elsevier.com/solutions/scopus/how-scopus-works/content. Accessed on 20 January 2023.
Faris, M. E., & Al-Holy, M. A. (2014). Implications of Ramadan intermittent fasting on maternal and fetal health and nutritional status: A review. Mediterranean Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism, 7(2), 107–118. https://doi.org/10.3233/MNM-140011
Faris, M. E., Jahrami, H., Abdelrahim, D., Bragazzi, N., & BaHammam, A. (2021). The effects of Ramadan intermittent fasting on liver function in healthy adults: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 178, 108951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2021.108951
Faris, M. E., Jahrami, H. A., Alhayki, F. A., Alkhawaja, N. A., Ali, A. M., Aljeeb, S. H., Abdulghani, I. H., & BaHammam, A. S. (2020a). Effect of diurnal fasting on sleep during Ramadan: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep and Breathing, 24(2), 771–782. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-019-01986-1
Faris, M. E., Jahrami, H. A., Alsibai, J., & Obaideen, A. (2020b). Impact of Ramadan diurnal intermittent fasting on the metabolic syndrome components in healthy, non-athletic Muslim people aged over 15 years: A systematic review and meta-analysis. British Journal of Nutrition, 123(1), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1017/S000711451900254X
Faris, M. E., Jahrami, H. A., Obaideen, A. A., & Madkour, M. I. (2019). Impact of diurnal intermittent fasting during Ramadan on inflammatory and oxidative stress markers in healthy people: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Nutrition & Intermediary Metabolism, 15, 18–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnim.2018.11.005
Faris, M. E., Kacimi, S., Al-Kurd, R. A., Fararjeh, M. A., Bustanji, Y. K., Mohammad, M. K., & Salem, M. L. (2012). Intermittent fasting during Ramadan attenuates proinflammatory cytokines and immune cells in healthy subjects. Nutrition Research, 32(12), 947–955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nutres.2012.06.021
Faris, M. E., Salem, M. L., Jahrami, H. A., Madkour, M. I., & BaHammam, A. S. (2020c). Ramadan intermittent fasting and immunity: An important topic in the era of COVID-19. Annals of Thoracic Medicine, 15(3), 125–133. https://doi.org/10.4103/atm.ATM_151_20
Fidianingsih, I., Jamil, N. A., Andriani, R. N., & Rindra, W. M. (2019). Decreased anxiety after Dawood fasting in the pre-elderly and elderly. Journal of Complementary and Integrative Medicine, 16(1), 20170172. https://doi.org/10.1515/jcim-2017-0172
Firouzbakht, M., Kiapour, A., Jamali, B., Kazeminavaei, F., Taghlilin, F., & Gorji, A. M. H. (2013). Fasting in pregnancy: A survey of beliefs and manners of Muslim women about Ramadan fasting. Annals of Tropical Medicine & Public Health, 6(5). https://doi.org/10.4103/1755-6783.133710
Germenis, A., Kokkinides, P., & Stavropoulos-Giokas, C. (1997). Non-indexed medical journals in the web: New perspectives in the medical literature. International Journal of Medical Informatics, 47(1–2), 65–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1386-5056(97)00076-2
Ghazi, H. A., Boughdady, A. M., & Elsayed, E. B. M. (2018). Effect of Ramadan fasting on physical and mental health of elderly people. World Journal of Nursing Sciences, 4(3), 56–65. https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.wjns.2018.56.65
Gilavand, A., & Fatahiasl, J. (2018). Studying effect of fasting during Ramadan on mental health of university students in Iran: A review. Journal of Research in Medical and Dental Science, 6(2), 205–209. https://doi.org/10.24896/jrmds.20186232
Habeebullah, T. M. (2013). An analysis of air pollution in Makkah-A view point of source identification. Environment Asia, 2, 11–17. (Paper has no DOI)
Hanif, S., Ali, S. N., Hassanein, M., Khunti, K., & Hanif, W. (2020). Managing people with diabetes fasting for Ramadan during the COVID-19 pandemic: A South Asian health foundation update. Diabetic Medicine, 37(7), 1094–1102. https://doi.org/10.1111/dme.14312
Hashemi, M., Baygan, A., Balouchzehi, Z., Dousti Nouri, M., & Afshari, A. (2018). Evaluation of microbial quality of traditional sweets, Zoolbia and Bamieh, during Ramadan in Mashhad, Iran. Journal of Nutrition, Fasting and Health, 6(3), 145–149. https://doi.org/10.22038/JNFH.2018.34900.1147
Hassanein, M., Abuelkheir, S., Alsayyah, F., Twair, M., Abdelgadir, E., Basheir, A., Rashid, F., Al Saeed, M., Eltayb, F., & Abdellatif, M. (2021a). Evaluation of optimum diabetes care on glycemic control of patients with gestational diabetes during Ramadan fasting. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 173, 108669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2021.108669
Hassanein, M., Alamoudi, R. M., Kallash, M. A., Aljohani, N. J., Alfadhli, E. M., Tony, L. E., Khogeer, G. S., Alfadhly, A. F., Khater, A. E., Ahmedani, M. Y., Buyukbese, M. A., Shaltout, I., Belkhadir, J., Hafidh, K., Chowdhury, T. A., Hussein, Z., & Elbarbary, N. S. (2021b). Ramadan fasting in people with type 1 diabetes during COVID-19 pandemic: The DaR global survey. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 172, 108626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108626
Ho, L., Alonso, A., Forio, M. A. E., Vanclooster, M., & Goethals, P. L. (2020). Water research in support of the Sustainable Development Goal 6: A case study in Belgium. Journal of Cleaner Production, 277, 124082. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124082
Hoddy, K. K., Marlatt, K. L., Çetinkaya, H., & Ravussin, E. (2020). Intermittent fasting and metabolic health: From religious fast to time-restricted feeding. Obesity, 28(S1), S29–S37. https://doi.org/10.1002/oby.22829
Jaleel, M. A., Raza, S. A., Fathima, F. N., & Jaleel, B. N. F. (2011). Ramadan and diabetes: As-saum (the fasting). Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism, 15(4), 268. https://doi.org/10.4103/2230-8210.85578
Kalantari, A., Kamsin, A., Kamaruddin, H. S., Ebrahim, N. A., Gani, A., Ebrahimi, A., & Shamshirband, S. (2017). A bibliometric approach to tracking big data research trends. Journal of Big Data, 4(1), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-017-0088-1
Koushali, A. N., Hajiamini, Z., Ebadi, A., Bayat, N., & Khamseh, F. (2013). Effect of Ramadan fasting on emotional reactions in nurses. Iranian Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Research, 18(3), 232. (Paper has no DOI)
Kridli, S. A.-O. (2011). Health beliefs and practices of Muslim women during Ramadan. MCN: The American Journal of Maternal/Child Nursing, 36(4), 216–221. https://doi.org/10.1097/NMC.0b013e3182177177
Lekagul, A., Chattong, A., Rueangsom, P., Waleewong, O., & Tangcharoensathien, V. (2022). Multi-dimensional impacts of coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic on Sustainable Development Goal achievement. Globalization and Health, 18(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12992-022-00861-1
LeMieux, M., Al-Jawadi, A., Wang, S., & Moustaid-Moussa, N. (2013). Metabolic profiling in nutrition and metabolic disorders. Advances in Nutrition, 4(5), 548–550. https://doi.org/10.3945/an.113.004267
Lorenz, M., Aisch, G., & Kokkelink, D. (2012). Datawrapper: Create Charts and Maps [Software]. Datawrapper. Retrieved 21/01/2022 from www.datawrapper.de/
Mahanani, M. R., Abderbwih, E., Wendt, A. S., Deckert, A., Antia, K., Horstick, O., Dambach, P., Kohler, S., & Winkler, V. (2021). Long-term outcomes of in utero Ramadan exposure: A systematic literature review. Nutrients, 13(12), 4511. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124511
Martín-Martín, A., Thelwall, M., Orduna-Malea, E., & Delgado López-Cózar, E. (2021). Google Scholar, Microsoft Academic, Scopus, Dimensions, Web of Science, and OpenCitations’ COCI: A multidisciplinary comparison of coverage via citations. Scientometrics, 126(1), 871–906. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-020-03792-z
Mashat, B. H. (2010). The microbiological quality of Sabil (free) drinking water in Makkah Al-Mukarramah during Ramadan 2007. Journal of King Abdulaziz University, 21, 87Á100. https://doi.org/10.4197/met.21-2.7
Mirsane, S. A., & Shafagh, S. (2016). A narrative review on fasting of pregnant women in the holy month of Ramadan. Journal of Fasting and Health, 4(2), 53–56. (Paper has no DOI)
Nasrallah, M., & Seroji, A. (2008). Particulates in the atmosphere of Makkah and Mina valley during Ramadhan and Hajj season of 1424 and 1425 H (2004–2005). Arab Gulf Journal of Scientific Research, 26, 199–206. https://doi.org/10.2495/AIR110301
Nur, I., Talukder, M., Das, T. R., Asaduzzaman, M., & Munshi, S. (2021). Microbiological status of some street iftar items collected from chalk bazar in Dhaka city, Bangladesh. Food Research, 5, 236–240. https://doi.org/10.26656/fr.2017.5(3).617
Obaideen, K., Shihab, K. H. A., Madkour, M. I., & Faris, M. E. (2022). Seven decades of Ramadan intermittent fasting research: Bibliometrics analysis, global trends, and future directions. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews, 16(8), 102566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2022.102566
Oliveira de, O. J., Da Silva, F. F., Juliani, F., Barbosa, L. C. F. M., & Nunhes, T. V. (2019). Bibliometric method for mapping the state-of-the-art and identifying research gaps and trends in literature: An essential instrument to support the development of scientific projects. In Scientometrics Recent Advances. IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.85856
Oosterwijk, V. N., Molenaar, J. M., van Bilsen, L. A., & Kiefte-de Jong, J. C. (2021). Ramadan fasting during pregnancy and health outcomes in offspring: A systematic review. Nutrients, 13(10), 3450. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103450
Parkhurst, J. O., & Whiteside, A. (2010). Innovative responses for preventing HIV transmission: The protective value of population-wide interruptions of risk activity. Southern African Journal of HIV Medicine, 11(1), 19–21. https://doi.org/10.4102/sajhivmed.v11i1.240
Patterson, R. E., & Sears, D. D. (2017). Metabolic effects of intermittent fasting. Annual Review of Nutrition, 37, 371–393. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-nutr-071816-064634
Pradella, F., & van Ewijk, R. (2018). As long as the breath lasts: In utero exposure to Ramadan and the occurrence of wheezing in adulthood. American Journal of Epidemiology, 187(10), 2100–2108. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwy132
Rahman, M. M., Islam, M. K., Al-Shayeb, A., & Arifuzzaman, M. (2022). Towards sustainable road safety in Saudi Arabia: Exploring traffic accident causes associated with driving behavior using a Bayesian belief network. Sustainability, 14(10), 6315. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14106315
Ramahi, I., Seidenberg, A. B., Kennedy, R. D., & Rees, V. W. (2012). Secondhand smoke emission levels in enclosed public places during Ramadan. European Journal of Public Health, 23(5), 789–791. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurpub/cks119
Rezaeigolestani, M., Hashemi, M., & Nematy, M. (2017). Risk Factors of Food-Borne Bacterial Diseases in Ramadan. Journal of Fasting & Health, 5(4), 138–143. https://doi.org/10.22038/jfh.2017.28193.1106
Robinson, T., & Raisler, J. (2005). D.“Each One Is a Doctor for Herself”. Ethnicity and Disease, 15, 99–103. (Paper has no DOI)
Roehner, B. M. (2014). Is the month of Ramadan marked by a reduction in the number of suicides? arXiv preprint:1401.3525. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1401.3525
Roky, R., Houti, I., Moussamih, S., Qotbi, S., & Aadil, N. (2004). Physiological and chronobiological changes during Ramadan intermittent fasting. Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism, 48(4), 296–303. https://doi.org/10.1159/000081076
Sachs, J., Kroll, C., Lafortune, G., Fuller, G., & Woelm, F. (2021). The Decade of Action for the Sustainable Development Goals: Sustainable Development Report 2021. Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/9781009106559
Salti, I., Bénard, E., Detournay, B., Bianchi-Biscay, M., Le Brigand, C., Voinet, C., Jabbar, A., & Group, E. S. (2004). A population-based study of diabetes and its characteristics during the fasting month of Ramadan in 13 countries: Results of the epidemiology of diabetes and Ramadan 1422/2001 (EPIDIAR) study. Diabetes Care, 27(10), 2306–2311. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.27.10.2306
Sasannejad, P., Mellat Ardekani, A., Velayati, A., Shoeibi, A., Saeidi, M., Foroughipour, M., & Azarpazhooh, M. R. (2012). Cerebral vein thrombosis in women using short course oral contraceptive consumption. Iranian Journal of Reproductive Medicine, 10(6), 537–542. (Paper has no DOI)
Schoeps, A., van Ewijk, R., Kynast-Wolf, G., Nebié, E., Zabré, P., Sié, A., & Gabrysch, S. (2018). Ramadan exposure in utero and child mortality in Burkina Faso: Analysis of a population-based cohort including 41,025 children. American Journal of Epidemiology, 187(10), 2085–2092. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwy091
Shalihin, N., Firdaus, F., Yulia, Y., & Wardi, U. (2020). Ramadan and strengthening of the social capital of Indonesian Muslim communities. HTS Theological Studies, 76(3). https://doi.org/10.4102/hts.v76i3.6241
Smith, S. L., Shiffman, J., Shawar, Y. R., & Shroff, Z. C. (2021). The rise and fall of global health issues: An arenas model applied to the COVID-19 pandemic shock. Globalization and Health, 17(1), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12992-021-00691-7
Somanje, A. N., Mohan, G., Lopes, J., Mensah, A., Gordon, C., Zhou, X., Moinuddin, M., Saito, O., & Takeuchi, K. (2020). Challenges and potential solutions for sustainable urban-rural linkages in a Ghanaian context. Sustainability, 12(2), 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12020507
Song, G., Wu, J., & Wang, S. (2021). Text mining in management research: A bibliometric analysis. Security and Communication Networks, 2021, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/2270276
Sulphey, M. M. (2022). A meta-analytic literature study on the relationship between workplace spirituality and sustainability. Journal of Religion and Health, 61(6), 4674–4695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10943-022-01629-y
Taheri, S., Chagoury, O., Tourette, M., Skaroni, I., Othman, M., Bashir, M., Dukhan, K., Al Mohannadi, D., Hassan, D., & Ghadban, W. (2020). Managing diabetes in Qatar during the COVID-19 pandemic. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, 8(6), 473–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30154-6
Tahir, M., Macassa, G., Akbar, A., Naseer, R., Zia, A., & Khan, S. (2013). Road traffic crashes in Ramadan: An observational study. Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, 19, s147–151. https://doi.org/10.26719/2013.19.Supp3.S147
Taktak, S., Kumral, B., Unsal, A., Ozdes, T., Aliustaoglu, S., Yazici, Y. A., & Celik, S. (2016). Evidence for an association between suicide and religion: A 33-year retrospective autopsy analysis of suicide by hanging during the month of Ramadan in Istanbul. Australian Journal of Forensic Sciences, 48(2), 121–131. https://doi.org/10.1080/00450618.2015.1034775
Talabis, M., McPherson, R., Miyamoto, I., Martin, J., & Kaye, D. (2015). Analytics defined. Information Security Analytics, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-800207-0.00001-0
Tang, D., Tang, Q., Huang, W., Zhang, Y., Tian, Y., & Fu, X. (2023). Fasting: From physiology to pathology. Advanced Science, 10(9), 2204487. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202204487
Teng, N. I. M. F., Shahar, S., Manaf, Z. A., Das, S. K., Taha, C. S. C., & Ngah, W. Z. W. (2011). Efficacy of fasting calorie restriction on quality of life among aging men. Physiology and Behavior, 104(5), 1059–1064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2011.07.007
Teng, N. I. M. F., Shahar, S., Rajab, N. F., Manaf, Z. A., Johari, M. H., & Ngah, W. Z. W. (2013). Improvement of metabolic parameters in healthy older adult men following a fasting calorie restriction intervention. The Aging Male, 16(4), 177–183. https://doi.org/10.3109/13685538.2013.832191
Tocco, J. U. (2017). The Islamification of antiretroviral therapy: Reconciling HIV treatment and religion in Northern Nigeria. Social Science & Medicine, 190, 75–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2017.08.017
Todd, E. C. (2017). Foodborne disease in the Middle East. Water, Energy & Food Sustainability in the Middle East, 389–440. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48920-9_17
Trepanowski, J. F., & Bloomer, R. J. (2010). The impact of religious fasting on human health. Nutrition Journal, 9(1), 57. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-9-57
Van Eck, N., & Waltman, L. (2010). Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics, 84(2), 523–538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3
Vilaplana T.G., Leeman D., Balogun K., Ngui S.L., Phipps E., Khan W.M., Team I., Balasegaram S. (2021). Hepatitis A outbreak associated with consumption of dates England and Wales, January 2021 to April 2021. Eurosurveillance, 26(20), 2100432. https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.20.2100432
Visioli, F., Mucignat-Caretta, C., Anile, F., & Panaite, S. A. (2022). Traditional and medical applications of fasting. Nutrients, 14(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030433
Visser, M., Van Eck, N. J., & Waltman, L. (2021). Large-scale comparison of bibliographic data sources: Scopus, Web of Science, Dimensions, Crossref, and Microsoft Academic. Quantitative Science Studies, 2(1), 20–41. https://doi.org/10.1162/qss_a_00112
Wallin, J. A. (2005). Bibliometric methods: Pitfalls and possibilities. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology, 97(5), 261–275. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-7843.2005.pto_139.x
Weitz, N., Carlsen, H., & Trimmer, C. (2019). SDG Synergies. An approach for coherent 2030 Agenda implementation. Stockholm Environment Institute. http://www.jstor.org/stable/resrep22999 , Accessed on 20 january 2023.
Wells, A., McClave, R., Cotter, E. W., Pruski, T., Nix, D., & Snelling, A. M. (2022). Engaging faith-based organizations to promote health through health ministries in Washington, DC. Journal of Religion and Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10943-022-01651-0
WorldPolulationReview. (2022, January 21, 2022). Muslim Population by Country 2022. https://worldpopulationreview.com/country-rankings/muslim-population-by-country Accessed on January , 2023.
Young, S., Patterson, L., Wolff, M., Greer, Y., & Wynne, N. (2015). Empowerment, leadership, and sustainability in a faith-based partnership to improve health. Journal of Religion and Health, 54(6), 2086–2098. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10943-014-9911-6
Zaina, A., Tarabeih, W., Abid, A., & Kassem, S. (2021). COVID-19 pandemic and Ramadan fasting among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. The Israel Medical Association Journal: IMAJ, 23(4), 203–207. (Paper has no DOI)
Zamir, R., Islam, A., Rahman, A., Ahmed, S., & Omar Faruque, M. (2018). Microbiological quality assessment of popular fresh date samples available in local outlets of Dhaka city, Bangladesh. International Journal of Food Science, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7840296
Zhou, X., Moinuddin, M., & LI, Y. (2021). SDG Interlinkages Analysis & Visualisation Tool (Version 4.0). Institute for Global Environmental Strategies (IGES). https://sdginterlinkages.iges.jp Accessed on January, 2023.
Zimmet, P., Alberti, K., Stern, N., Bilu, C., El-Osta, A., Einat, H., & Kronfeld-Schor, N. (2019). The Circadian syndrome: Is the metabolic syndrome and much more! Journal of Internal Medicine, 286(2), 181–191. https://doi.org/10.1111/joim.12924
Acknowledgements
Deep thanks are due to the librarian Mr. Nadeem Rafiq and the library staff, Central Library of the University of Sharjah, for their continuous support in providing the full-text articles requested.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.O., M.F., and K.A. contributed to conceptualization, investigation, and writing (original draft). K.O. and K.A. contributed to methodology, formal analysis, validation, data curation, and visualization. K.O. made software. M.F. contributed to supervision. M.F. and K.O. done resources and project administration. M.A., M.M., R.A., H.K., Y.M., and D.A. helped in writing (review and editing).
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that this research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
AbuShihab, K., Obaideen, K., Alameddine, M. et al. Reflection on Ramadan Fasting Research Related to Sustainable Development Goal 3 (Good Health and Well-Being): A Bibliometric Analysis. J Relig Health (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10943-023-01955-9
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10943-023-01955-9