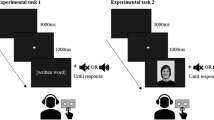
Abstract
It is unknown whether linguistic cues influence preschoolers’ recognition of facial expression when the emotion of the face is incongruent with the linguistic cues and what type of linguistic cue is influential in the modulation of facial expression. In a priming task, we presented 5-year-old children three types of linguistic information conveying happy or sad emotion (simple label, label with rich causal explanation of emotion, and label with poor causal explanation of emotion) prior to the presentation of a happy or a sad face. We asked participants to recognize emotion of facial expression and examined whether they follow linguistic information than the facial expression when the emotions of linguistic information and face were incongruent. As a result, children who were presented the label with rich causal explanation judged emotion of face according to the linguistic information, whereas children who were presented the simple label or the label with poor causal explanation followed the emotions of facial expression. This result indicated that children’s autonomic reliance on situational cues depends on the emotional causality and the concreteness of emotional state conveyed by the linguistic cues. This finding contributes to our understanding of the face inferiority effect on children’s developing notion of emotions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguert, M., Laval, V., Le Bigot, L., & Bernicot, J. (2010). Understanding expressive speech acts: the role of prosody and situational context in French-speaking 5- to 9-year-olds. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 53, 1629–1641. https://doi.org/10.1044/1092-4388(2010/08-0078).
Banerjee, M. (1997). Hidden emotions: Preschoolers’ knowledge of appearance-reality and emotion display rules. Social Cognition, 15, 107–132. https://doi.org/10.1521/soco.1997.15.2.107.
Barrett, L. F., Lindquist, K. A., & Gendron, M. (2007). Language as context for the perception of emotion. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 11, 327–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2007.06.003.
Bretherton, I., & Beeghly, M. (1982). Talking about internal states: The acquisition of an explicit theory of mind. Developmental Psychology, 18, 906–921. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.18.6.906.
Bullock, M., & Russell, J. A. (1986). Concepts of emotion in developmental psychology. In C. E. Izard & P. B. Read (Eds.), Measuring emotions in infants and children (Vol. 2, pp. 203–237). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Carroll, J. M., & Russell, J. A. (1996). Do facial expressions signal specific emotions? Judging emotion from the face in context. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 70, 205–218. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.70.2.205.
Diéguez-Risco, T., Aguado, L., Albert, J., & Hinojosa, J. A. (2013). Faces in context: Modulation of expression processing by situational information. Social Neuroscience, 8, 601–620. https://doi.org/10.1080/17470919.2013.834842.
Diéguez-Risco, T., Aguado, L., Albert, J., & Hinojosa, J. A. (2015). Judging emotional congruency: Explicit attention to situational context modulates processing of facial expressions of emotion. Biological Psychology, 112, 27–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2015.09.012.
Dunn, J., Brown, J., & Beardsall, L. (1991). Family talk about feeling states and children’s later understanding of others’ emotions. Developmental Psychology, 27, 448–455. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.27.3.448.
Egami, S. (2010). Preschool children’s understanding of others’ emotions: Focusing on a difference in emotions. Bulletin of the Faculty of Education Ehime University, 57, 27–32.
Ekman, P., Friesen, W. V., & Ellsworth, P. (2013). Emotion in the human face: Guidelines for research and an integration of findings. New York: Elsevier.
Ekman, P., & O’Sullivan, M. (1988). The role of context in interpreting facial expression: Comment on Russell and Fehr (1987). Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 117, 86–88. https://doi.org/10.1037/0096-3445.117.1.86.
Fazio, R. H., Sanbonmatsu, D. M., Powell, M. C., & Kardes, F. R. (1986). On the automatic activation of attitudes. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 50, 229–454. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.50.2.229.
Ferré, P., & Sánchez-Casas, R. (2014). Affective priming in a lexical decision task: Is there an effect of words’ concreteness? Psicológica, 35, 117–138.
Ford, J. A., & Milosky, L. M. (2003). Inferring emotional reactions in social situations differences in children with language impairment. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 46, 21–30. https://doi.org/10.1044/1092-4388(2003/002).
Foster, K. I., & Foster, J. C. (2003). DMDX: A windows display program with millisecond accuracy. Behavior Research Methods, Instruments and Computers, 35, 116–124. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03195503.
Gardner, D., Harris, P. L., Ohmoto, M., & Hamazaki, T. (1988). Japanese children’s understanding of the distinction between real and apparent emotion. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 11, 203–218. https://doi.org/10.1177/016502548801100204.
Gnepp, J. (1983). Children’s social sensitivity: Inferring emotions from conflicting cues. Developmental Psychology, 19(6), 805–814. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.19.6.805.
Gnepp, J., Klayman, J., & Trabasso, T. (1982). A hierarchy of information sources for inferring emotional reactions. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 33(1), 111–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-0965(82)90009-1.
Gnepp, J., McKee, E., & Domanic, J. A. (1987). Children’s use of situational information to infer emotion: Understanding emotionally equivocal situations. Developmental Psychology, 23(1), 114–123. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.23.1.114.
Gross, D., & Harris, P. L. (1988). False beliefs about emotion: Children’s understanding of misleading emotional displays. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 11, 475–488. https://doi.org/10.1177/016502548801100406.
Halberstadt, J. B., & Niedenthal, P. M. (2001). Effects of emotion concepts on perceptual memory for emotional expressions. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 81, 587–598. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.81.4.587.
Harris, P. L. (2008). Children’s understanding of emotion. In M. Lewis, J. M. Haviland-Jones, & L. Barrett (Eds.), Handbook of emotions (3rd ed., pp. 70–83). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Harris, P. L., Donnelly, K., Guz, G. R., & Pitt-Watson, R. (1986). Children’s understanding of the distinction between real and apparent emotion. Child Development, 57, 895–909. https://doi.org/10.2307/1130366.
Hayashi, M. (2004). Discourse within a sentence: An exploration of postpositions in Japanese as an interactional resource. Language in Society, 33(3), 343–376. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0047404504043027.
Hillier, A., & Allinson, L. (2002). Beyond expectations. Autism, understanding embarrassment, and the relationship with theory of mind. Autism. The International Journal of Research and Practice, 6, 299–314. https://doi.org/10.1177/1362361302006003007.
Hoffner, C., & Badzinski, D. M. (1989). Children’s integration of facial and situational cues to emotion. Child development. https://doi.org/10.2307/1130986.
Josephs, I. E. (1994). Display rule behavior and understanding in preschool children. Journal of Nonverbal Behavior, 18, 301–326. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02172291.
Joshi, M. S., & MacLean, M. (1994). Indian and English children’s understanding of the distinction between real and apparent emotion. Child Development, 65, 1372–1384. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8624.1994.tb00822.x.
Kikuchi, T. (2004). Development of young children’s understanding of their own facial expressions. The Japanese Journal of DevelopmentalPsychology, 15, 207–216. https://doi.org/10.5926/jjep1953.54.1_90.
Kim, H., Somerville, L. H., Johnstone, T., Polis, S., Alexander, A. L., Shin, L. M., et al. (2004). Contextual modulation of amygdala responsivity to surprised faces. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 16, 1730–1745. https://doi.org/10.1162/0898929042947865.
Klauer, K. C., & Musch, J. (2003). Affective priming: Findings and theories. In J. Musch & K. C. Klauer (Eds.), The psychology of evaluation: Affective processes in cognition and emotion (pp. 7–49). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Lieberman, M. D., Eisenberger, N. I., Crockett, M. J., Tom, S. M., Pfeifer, J. H., & Way, B. M. (2007). Putting feelings into words affect labeling disrupts amygdala activity in response to affective stimuli. Psychological Science, 8, 421–428. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9280.2007.01916.x.
Lindquist, K. A., & Gendron, M. (2013). What’s in a word? Language constructs emotion perception. Emotion Review, 5(1), 66–71. https://doi.org/10.1177/1754073912451351.
Lupyan, G. (2012). Linguistically modulated perception and cognition: the label-feedback hypothesis. Frontiers in Psychology. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2012.00054.
Morton, J. B., & Trehub, S. E. (2001). Children’s understanding of emotion in speech. Child Development, 72, 834–843. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8624.00318.
Pons, F., Harris, P. L., & de Rosnay, M. (2004). Emotion comprehension between 3 and 11 years: Developmental periods and hierarchical organization. European Journal of Developmental Psychology, 1, 127–152. https://doi.org/10.1080/17405620344000022.
Reichenbach, L., & Masters, J. C. (1983). Children’s use of expressive and contextual cues in judgments of emotion. Child Development. https://doi.org/10.2307/1129903.
Ridgeway, D., Waters, E., & Kuczaj, S. A. (1985). Acquisition of emotion-descriptive language: Receptive and productive vocabulary norms for ages 18 months to 6 years. Developmental Psychology, 21, 901–908. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.21.5.901.
Roberson, D., & Davidoff, J. (2000). The categorical perception of colors and facial expressions: The effect of verbal interference. Memory and Cognition, 28, 977–986. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03209345.
Russell, J. A., & Widen, S. C. (2002). A label superiority effect in children’s categorization of facial expressions. Social Development, 11, 30–52. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-9507.00185.
Schwarz, K. A., Wieser, M. J., Gerdes, A. B., Mühlberger, A., & Pauli, P. (2013). Why are you looking like that? How the context influences evaluation and processing of human faces. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 8, 438–445. https://doi.org/10.1093/scan/nss013.
Spackman, M. P., Fujiki, M., & Brinton, B. (2006). Understanding emotions in context: the effects of language impairment on children’s ability to infer emotional reactions. International Journal of Language and Communication Disorders, 41, 173–188. https://doi.org/10.1080/13682820500224091.
Theurel, A., Witt, A., Malsert, J., Lejeune, F., Fiorentini, C., Barisnikov, K., et al. (2016). The integration of visual context information in facial emotion recognition in 5- to 15-year-olds. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 150, 252–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jecp.2016.06.004.
Trauner, D. A., Ballantyne, A., Chase, C., & Tallal, P. (1993). Comprehension and expression of affect in language-impaired children. Journal of Psycholinguistic Research, 22, 445–452. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01074346.
Trope, Y. (1986). Identification and inferential processes in dispositional attribution. Psychological Review, 93, 239–257. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.93.3.239.
Wang, Z., Lü, W., Zhang, H., & Surina, A. (2014). Free-labeling facial expressions and emotional situations in children aged 3–7 years: Developmental trajectory and a face inferiority effect. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 38(6), 487–498. https://doi.org/10.1177/0165025414531462.
Widen, S. C., & Russell, J. A. (2004). The relative power of an emotion’s facial expression, label, and behavioral consequence to evoke preschoolers’ knowledge of its cause. Cognitive Development, 19, 111–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogdev.2003.11.004.
Widen, S. C., & Russell, J. A. (2010). Differentiation in preschooler’s categories of emotion. Emotion, 10, 651. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0019005.
Wiggers, M., & van Lieshout, C. F. (1985). Development of recognition of emotions: Children’s reliance on situational and facial expressive cues. Developmental Psychology, 21(2), 338–349. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.21.2.338.
Xu, F., & Kushnir, T. (2013). Infants are rational constructivist learners. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 22(1), 28–32. https://doi.org/10.1177/0963721412469396.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a Grant to S.I. from Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (25245067, 25240020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix 1: Definitions and Examples of the Linguistic Cue in the Priming Task
Appendix 1: Definitions and Examples of the Linguistic Cue in the Priming Task
Type of linguistic cue | Definition | Emotional valence of linguistic cue | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
Label | Sentences included a subject and an emotional adjective only | Happy (‘ureshii’) | ‘Risachan-wa-ureshii’ (Risa is happy.) |
Sad (‘kanashii’) | ‘Hirokikun-wa-kanashii’ (Hiroki is sad.) | ||
Label + WOC | Sentences included a subject, emotional adjective, and situational information that had a low causal relationship with the emotional adjective | Happy (‘ureshii’) | ‘Doa-wo-akete-Hirokikun-wa-ureshii’ (Hiroki is happy because he opened the door.) ‘Nikki-wo-kaite-Meichan-wa-ureshii’ (Mei is happy because she wrote a diary.) |
Sad (‘kanashii’) | ‘Basu-ni-notte-Risachan-wa-kanashii’ (Risa is sad because she took a bus.) ‘Yama-ni-nobotte-Toorukun-wa-kanashii’ (Tooru is sad because he climbed the mountain.) | ||
Label + WC | Sentences included a subject, emotional adjective, and situational information that had a high causal relationship with the emotional adjective | Happy (‘ureshii’) | ‘Otanjyoubi-purezento-wo-moratte-Risachan-wa-ureshii’ (Risa is happy because she received a birthday gift.) ‘Kadogeimu-ni-katte-Takikun-wa-ureshii’ (Taki is happy because he won at a card game.) |
Sad (‘kanashii’) | ‘Katteiru-koinu-wo-nakusite-Aoichan-wa-kanashii’ (Aoi is sad because she lost her puppy.) ‘Ojiisan-ga-shinjyatte-Tarokun-wa-kanashii’ (Taro is sad because his grandfather died.) |
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, Yh., Itakura, S. Causal Information Over Facial Expression: Modulation of Facial Expression Processing by Congruency and Causal Factor of the Linguistic Cues in 5-Year-Old Japanese Children. J Psycholinguist Res 48, 987–1004 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10936-019-09643-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10936-019-09643-0