Abstract
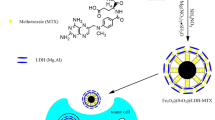
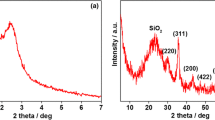
Herein, we developed the dual-function template method to fabricate hollow magnetic nano-spheres (denoted as HMFe–Si–Cn, n = 16, 18) with a mesoporous shell and hollow interior structure using alkyl chain trimethoxysilane templating. The shorter chain template directed formation of HMFe–Si–C16 with size of 119 nm, having disordered inkbottle type mesopores and saturation magnetization of 50.01 emu/g higher than that of HMFe–Si–C18 with cylindrical type mesopores. In addition, the HMFe–Cn loaded with MMC diaplays a pH and magnetic dual responsive drug release behavior. By contrast, Mitomycin C (MMC) loading efficiency of HMFe–Si–C16 was higher owing to the fact that the pore size, surface area, and pore volume of HMFe–Si–C16 were larger than those of HMFe–Si–C18. Besides, MMC loaded HMFe–Si–Cn hollow spheres showed a clear pH-dependent drug release behavior, having a higher release rate in acidic environments of pH 5.7. For the pH 5.7 and 7.4 release, the release kinetic for HMFe–Si–C16–MMC composites follows pseudo-first-order attributable to its special pore structure. With Fe(0) as a core, HMFe–Si–Cn is distinguished for higher magnetic properties, and it is more conducive to magnetic targeted treatment of cancer cells and can release drugs through external magnetic field. In addition, HMFe–Si–Cn has lower cytotoxicity and better biocompatibility. For this reason the inner cavity of HMFe–Si–C16 could be labeled with radioisotope 99Tcm to study the magnetic targeting distribution of HMFe–Si–C16 in vivo, and its cytotoxicity against in vitro HeLa cells was also studied. These results indicate the potential of HMFe–Si–C16 in the magnetic targeted drug delivery system.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Sastry, R. Fiala, R. Lipman, M. Tomasz, D.J. Patel, Solution structure of the monoalkylated mitomycin C-DNA complex. J. Mol. Biol. 247, 247–338 (1995)
A.C. Sartorelli, W.F. Hodnick, M.F. Belcourt, M. Tomasz, B. Haffty, J.J. Fischer, S. Rockwell, Mitomycin C: a prototype bioreductive agent. Oncol. Res. 6, 501–508 (1994)
M. Önol, Z. Aktaş, B. Hasanreisoğlu, Enhancement of the success rate in trabeculectomy: large-area mitomycin-C application. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 36(4), 316–322 (2008)
Y. Zhu, W.G. Lu, L.Y. Zou, J.F. Feng, Magnetic nanoparticles of Mitomycin C I. Preparation and quality evaluation. Chin. J. Pharm 37(3), 168–171 (2006)
M.E. Sharifabad, T. Mercer, T. Sen, The fabrication and characterization of stable core-shell superparamagnetic nanocomposites for potential application in drug delivery. J. Appl. Phys. 117(17), 17D139 (2015)
L. Yuan, X.R. Qi, Preparation and in vitro characterization of ATRA loaded mPEG-PLA diblock copolymeric micelles. Chin. J. New Drugs 17(3), 217–224, 227 (2008)
S. Zhou, Q. Zhong, Y. Wang et al., Chemically engineered mesoporous silica nanoparticles-based intelligent delivery systems for theranostic applications in multiple cancerous/non-cancerous diseases. Coord. Chem. Rev. 452(1), 214309 (2022)
K. Wang, J. Lu, J. Li et al., Current trends in smart mesoporous silica-based nanovehicles for photoactivated cancer therapy. J. Control Release 339(1), 445–472 (2021)
W. Lei, C. Sun, T. Jiang et al., Polydopamine-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for multi-responsive drug delivery and combined chemo-photothermal therapy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 105, 110103 (2019)
L. Zhang, T. Wang, L. Yang, C. Liu, C. Wang, H. Liu, Y.A. Wang, Z. Su, General route to multifunctional uniform yolk/mesoporous silica shell nanocapsules: a platform for simultaneous cancer-targeted imaging and magnetically guided drug delivery. Chem. Eur. J. 18(39), 12512–12521 (2012)
J. Liu, S.Z. Qiao, S.B. Hartono, G.Q. Lu, Monodisperse yolk-shell nanoparticleswith a hierarchical porous structure for delivery vehicles and nanoreactors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49(29), 4981–4985 (2010)
P.B. Santhosh, N.P. Ulrih, Multifunctional superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: promising tools in cancer theranostics. Cancer Lett. 336(1), 8–17 (2013)
M.M. Song, H. Bi, Y. Zhang, Fabrication of Fe@mSiO2 nanowires with large remanence and low cytotoxicity for targeted drug delivery. J. Appl. Phys. 111(7), 07B302 (2012)
J. Yang, F. Zhang, Y. Chen, S. Qian, P. Hu, W. Li, Y. Deng, Y. Fang, L. Han, M. Luqman, D. Zhao, Core-shell Ag@SiO2@mSiO2 mesoporous nanocarriers for metal-enhanced fluorescence. Chem. Commun. 47, 11618–11620 (2011)
C. Wu, Z.Y. Lim, C. Zhou, W.G. Wang, S. Zhou, H. Yin, Y. Zhu, A soft-templated method to synthesize sintering-resistant Au–mesoporous-silica core–shell nanocatalysts with sub-5 nm single-cores. Chem. Commun. 49, 3215e–33217 (2013)
T. Ohhashi, T. Tsuruoka, K. Inoue et al., An integrated function system using metal nanoparticle@ mesoporous silica@ metal-organic framework hybrids. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 245, 04–108 (2017)
T. Liu, Novel hierarchically structured nanocomposites for biomedical applications[D]. Curtin University, (2017)
W. Zhao, H. Chen, Y. Li, L. Li, M. Lang, J. Shi, Uniform rattle-type hollow magnetic mesoporous spheres as drug delivery carriers and their sustained-release property. Adv. Funct. Mater. 18(18), 2780–2788 (2008)
J. Zhang, C.Q. Lan, M. Post, B. Simard, Y. Deslandes, T.H. Hsieh, Design of nanoparticles as drug carriers for cancer therapy. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 3(3–4), 147–158 (2006)
Y.X. Yang, H.P. Ying, J.G. Shao, A study on effect of different template chain length on synthesis of mesoporous silica in acidic condition. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 90(11), 3460–3467 (2007)
J.J. Yuan, X. Zhang, H. Qian, A novel approach to fabrication of superparamagnetite hollow silica/magnetic composite spheres. J. Magn. Mag. Mater. 322(15), 2172–2176 (2010)
S.Q. Shah, M.R. Khan, S.M. Ali, Radiosynthesis of 99mTc(CO)3-clinafloxacin dithiocarbamate and its biological evaluation as a potential Staphylococcus aureus infection radiotracer. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 45, 248–254 (2011)
Y. Chen, H. Chen, L. Guo, Q. He, F. Chen, J. Zhou, J. Feng, J. Shi, Hollow/rattle-type mesoporous nanostructures by structural difference-based selective etching strategy. ACS Nano 4(1), 529–539 (2010)
J.M. Yan, Q. Zhang, J.C. Gao, Adsorption and coacervation (Beijing Science Press, Beijing, 1986), p. 115
K.S.W. Sing, R.T. Williams, Physisorption hysteresis loops and the characterization of nanoporous materials. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 22(10), 773–782 (2004)
W.D. Xiang, Y.X. Yang, J.L. Zheng, Synthesis of mesoporous silica using cationic surfactant templating in different inorganic acid source. Mater. Sci.-Poland 28(3), 709–730 (2010)
K. Morishige, M. Tateishi, F. Hirose, K. Aramaki, Change in desorption mechanism from pore blocking to cavitation with temperature for nitrogen in ordered silica with cagelike pores. Langmuir 22(22), 9220–9224 (2006)
J.B. Zhang, Y.X. Yang, J.L. Zheng, Chin, Synthesis of mesoporous silica with a three-dimensional hexagonal ordered structure using cationic and amphoteric mixed surfactants. J. Inorg. Chem. 27(9), 1817–1829 (2011)
K. Morishige, N. Tateishi, Adsorption hysteresis in ink-bottle pore. J. Chem. Phys. 119(4), 2301–2306 (2003)
R. Bhaskar, S.R.S. Murthy, B.D. Miglani, K. Viswanathan, Novel method to evaluate diffusion controlled release of drug from resinate. Int. J. Pharm. 28(1), 59–66 (1986)
L. Xu, J. Dai, J. Pan, X. Li, P. Huo, Y. Yan, X. Zou, R. Zhang, Performance of rattle-type magnetic mesoporous silica spheres in the adsorption of single and binary antibiotics. Chem. Eng. J. 174, 221–230 (2011)
Y. Hua, Z. Zhi, Q. Zhao, C. Wu, P. Zhao, H. Jiang, T. Jiang, S. Wang, 3D cubic mesoporous silica microsphere as a carrier for poorly soluble drug carvedilol. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 147(1), 94–101 (2012)
J.X. Zhang, Q. Zhang, A.D. Huang, Determination of biodistribution of galactose polyhydroxyethylglutamine in mice with isotope 99mTc labeling. J. Instrum. Anal. 22(3), 69–71 (2003)
M.C.F. Passos, C.F. Ramos, M. Bernardo-Filho, D.M.M. De Mattos, E.G. Moura, The effect of protein or energy restriction on the biodistribution of Na99TcmO4 in Wistar rats. Nucl. Med. Commun. 21(11), 1059–1062 (2000)
X. Xie, S. Deng, Comparative study on observing vascular crisis of rabbits with replanted limb by Na99TcmO4 trace imaging. Nucl. Tech. 11, 011 (2005)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (20577010, 20971043), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, and the Open Project Program of State Key Laboratory of Inorganic Synthesis and Preparative Chemistry, Jilin University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZC: Methodology, Software, Investigation, Validation. YY: Conceptualization, Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing Supervision, Writing—review & editing, Funding acquisition. HL: bioexperiment. HY: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing—review & editing. CN: Supervision, Writing—review & editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, Z., Li, H., Yang, Y. et al. Effects of different pore structures on loading and sustained-release of mitomycin C by hollow mesoporous Fe(0)@mSiO2. J Porous Mater 29, 1489–1505 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-022-01271-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-022-01271-9