Abstract
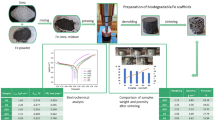
This study describes production of highly porous 17-4 PH stainless steel for biomedical implant applications by space holder-sintering technique. 17-4 PH stainless steel powders were mixed with space holder and then compacted. For designing pore properties, both spherical and irregular shaped carbamide with different particle size ranges were used as space holder and removed by water leaching. Porous 17-4 PH steel specimens were sintered at 1,260 °C for 40 min. Boron was used as a liquid phase sintering additive. In addition, sintered specimens were aged in order to increase mechanical properties. Specimens were austenitized at 1,050 °C and then quenched. Quenched specimens were aged at times of 1–6 h at temperatures between 450 and 570 °C. The pore size and shape of the 17-4 PH stainless steel foams replicated the initial size and shape of the carbamide particles. This suggests that pore properties can be designed by using proper size, shape and content of space holder.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.F. Ashby, A.G. Evans, N.A. Fleck, L.J. Gibson, J.W. Hutchinson, H.N.G. Wadley, Metal Foams: A Design Guide (Elsevier, Boston, 2000)
M. Bram, C. Stiller, H.P. Buckramed, D. Stöver, H. Bauer, High-porosity titanium, stainless steel and superalloy parts. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2, 196–199 (2000)
J. Banhart, Manufacture, characterisation and application of cellular metals and metal foams. Prog. Mater. Sci. 46(6), 559–632 (2001)
L.J. Gibson, M.F. Ashby, Cellular Solids–Structures and Properties, 2nd edn. (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1997)
N. Wenjuan, B. Chenguang, Q. GuiBao, W. Qiang, Processing and properties of porous titanium using space holder technique. Mat. Sci. Eng. A 506, 148–151 (2009)
H.I. Bakan, A novel water leaching and sintering process for manufacturing highly porous stainless steel. Scripta Mater. 55, 203–206 (2006)
C.E. Wen, C.E. Mabuchi, M. Yamada, Y. Shimojima, K. Chino, Y. Asahina, Processing of biocompatible porous Ti and Mg. Scripta Mater. 45, 1147–1153 (2001)
H.O. Gulsoy, R.M. German, Sintered foams from precipitation hardened stainless steel powder. Powder Metall. 51(4) (2008)
Y.Y. Zhao, D.X. Sun, A novel sintering-dissolution process for manufacturing Al foams. Scripta Mater. 44, 105–110 (2001)
H.P. Degisher, B. Kriszt, Handbook of Cellular Metals (Wiley, Weinheim, 2002), pp. 313–315
Z. Esen, S. Bor, Processing of titanium foams using magnesium spacer particles. Scripta Mater. 56, 341–344 (2007)
N. Michailidis, F. Stergioudi, A. Tsoukniadas, E. Pavlidou, Compressive response of Al-foams produced via a powder sintering process based on a leachable space-holder material. Mat. Sci. Eng. A 528, 1662–1867 (2011)
C.T. Schade, P.D. Stears, A. Lawley, R.D. Doherty, Precipitation hardening PM stainless steels. Int. J. Powder Metall. 43(4) (2007)
H. Mirzadeh, A. Najafizadeh, Aging kinetics of 17–4 PH stainless steel. Mater. Chem. Phys. 116, 119–124 (2009)
M. Murayama, Y. Katayama, K. Hono, A microstructural evolution in a 17-4 PH stainless steel after aging at 400 °C. Metall. Mater. Trans. 30, 345–353 (1999)
J. Wang, H. Zou, L. Cong, Y. Peng, S. Qiu, B. Shen, The microstructure evolution of type 17–4 PH stainless steel during long-term aging at 350 °C. Nucl. Eng. Des. 236, 2531–2536 (2006)
H.P. Ren, H.Y. Wang, Z.C. Liu, Cu precipitation dynamics in Fe-Cu alloy. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 96, 0-12206 (2008)
B. Rivolta, R. Gerosa, On the non-isothermal precipitation of copper-rich phase in 17–4 PH stainless steel using dilatometric techniques. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 102, 857–862 (2010)
L.J. Gibson, Biomechanics of cellular solids. J. Biomech. 38, 377–399 (2005)
V.K. Balla, S. Bodgak, S. Bose, A. Bandyopadhyay, Porous tantalum structures for bone implants: fabrication, mechanical and in vitro biological properties. Acta Biomater. 6, 3349–3359 (2010)
H.J. Rack, J.I. Qazi, Titanium alloys for biomedical applications. Mat. Sci. Eng. C 26, 1269–1277 (2006)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit of Istanbul University, Project number T-1430. It was partially based on a Ph.D. thesis pursued by Ilven Mutlu.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mutlu, I., Oktay, E. Production and aging of highly porous 17-4 PH stainless steel. J Porous Mater 19, 433–440 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-011-9491-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-011-9491-8