Abstract
We reconstructed the Holocene climate in the study area using data from a BZ section in the Baiyangdian paleo-lake. Samples were analyzed for multiple proxies for climate conditions, including grain size, magnetic susceptibility (MS), and carbonate content, which were combined with accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) 14C data. The results show that from 10.0 to 6.3 kyr BP, the study area experienced an interval of increasing precipitation and rising water level at Lake Baiyangdian. For a very short period, ~ 8.4 kyr BP, the extent of the lake reached the sampling point. The climate during this stage was relatively humid. The water level dropped abruptly at 6.5 kyr BP as a result of a weak monsoon event. From 6.3 to 2.9 kyr BP the climate became humid once again. The continuous lacustrine sediment of the strata indicated that the water level of Lake Baiyangdian expanded rapidly during this period and reached the sampling point. After 2.9 kyr BP, the climate in the region changed again from humid to dry. The abrupt increase in MS after ~1 kyr BP (993 AD) is consistent with records of human activities in local chronicles, which indicates that the environment in the study area was influenced by human activities. Through a comparison of the BZ section and the East Asian summer monsoon (EASM) records, we found that precipitation in the study area was controlled by the EASM. A series of cold Holocene events were clearly recorded by the sediment in the BZ section, and these events are synchronous with the North Atlantic ice-rafting events (IRD). The connection between the characteristics of the BZ section and the EASM and IRD indicate that climate evolution in the study area was strongly affected by EASM and IRD.

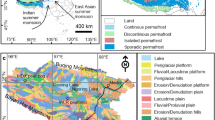
(modified from Google Earth; the water system distribution is modified from Shi 2012)







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Backwell L, Steininger C, Neveling J, Abdala F, Pereira L, Mayer E, Rossouw L, de la Peña P, Brink J (2018) Holocene large mammal mass death assemblage from South Africa. Quat Int 495:49–63
Baoding local Chronicles office (2018) Baoding yearbook. China literature and history press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Bond G, Showers W, Cheseby M, Lotti R, Almasi P, DeMenocal P, Priore P, Cullen H, Hajdas I, Bonani G (1997) A pervasive millennial-scale cycle in North Atlantic holocene and glacial climates. Science 278:1257–1266
Bond G, Kromer B, Beer J, Muscheler R, Evans MN, Showers W, Hoffmann S, Lotti-Bond R, Hajdas I, Bonani G (2001) Persistent solar influence on North Atlantic climate during the holocene. Science 294:2130–2136
Briner JP (2016) Ice streams waned as ice sheets shrank. Nature (London) 530(7590):287–288
Calvo JP, Jones BF, Bustillo M, Fort R, Alonso Zarza AM, Kendall C (1995) Sedimentology and geochemistry of carbonates from lacustrine sequences in the Madrid Basin, central Spain. Chem Geol 123:173–191
Chen S, Liu J (2018) Evolution of integrated lake status since the last deglaciation: a high-resolution sedimentary record from Lake Gonghai, Shanxi, China. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 496:175–182
Chen P, Zhou Q (1989) Paleoclimatic significance of cold water carbonate in sediment: a case study of two borehole profiles in caohai, guizhou. Guizhou Geol 6:347–356 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chen J, Wan G, Wang F, Huang R, Zhang F (2002) Carbon environmental record of modern lake sediment. Sci China (series D: Earth Sci) 1:73–80 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chen F, Xu Q, Chen J (2015) East Asian summer monsoon precipitation variability since the last deglaciation. Sci Rep 11186
Chen T, Yang Z, Liu R, Wang L, Bi Z, Yang Q (2017) Particle size characteristics and sedimentary environment analysis of zk-1 borehole in baiyangdian since late pleistocene. J Hebei Univ Geosci 40:1–7 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Cui J, Zhou S, Chang H (2009) The Holocene warm-humid phases in The North China Plain as recorded by multi-proxy records. Chin J Oceanol Limnol 27:147–161
Daggers L, Plew MG, Edwards A, Evans S, Trayler RB (2018) Assessing the early holocene environment of Northwestern Guyana: An Isotopic Analysis Of Human And Faunal Remains. Lat Am Antiq 29:279–292
Dariusz WS, Mariusz P (2016) 1976–2010 changes of lake water level in Poland (English). J Geogr Sci 26:83–101
Ding D, Li G, Xu J, Ding D, Li Q, Wang L, Wang H, Zhang Y (2017) Evolution of the Asian monsoon during the holocene 24:114–123 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Dong J, Shen C, Kong X, Wu C, Hu H, Ren H, Wang Y (2018) Rapid retreat of the East Asian summer monsoon in the middle Holocene and a millennial weak monsoon interval at 9 ka in northern China. J Asian Earth Sci 151:31–39
Duan Z, Liu Q, Yang X, Gao X, Su Y (2014) Magnetism of the Huguangyan Maar Lake sediment, Southeast China and its paleoenvironmental implications. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 395:158–167
Flemming B (2007) The influence of grain-size analysis methods and sediment mixing on curve shapes and textural parameters: Implications for sediment trend analysis. Sediment Geol 202:425–435
Folk L, Robert C, Ward W (1957) Brazos River Bar: a Study in the Significance of Grain Size Parameters. J Sediment Petrol 27:3–26
Fu C (2009) Review and prospect of environmental magnetism in paleoclimatic environment research. J Earth Sci Environ 31:312–322 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Fusco DA, McDowell MC, Prideaux GJ (2016) Late-Holocene mammal fauna from southern Australia reveals rapid species declines post-European settlement: implications for conservation biology. Holocene 26:699–708
Goldsmith Y, Broecker WS, Xu H, Polissar PJ, DeMenocal PB, Porat N, Lan J, Cheng P, Zhou W, An Z (2017) Northward extent of East Asian monsoon covaries with intensity on orbital and millennial timescales. Proc Acad Sci USA 114:1817–1821
Guo C, Li Y, Cheng Y, Yu D, Zhang C (2012) Carbonate content and pollen preservation in sediment from different locations of boye ze. Arid Area Study 29:1089–1093 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Guo B, Peng T, Feng Z, Li J, Li X, Li M, Ma Z, Song C, Zhang J, Zhang S, Hui Z (2019) Pedogenic components of Xijin loess from the western Chinese Loess Plateau with implications for the Quaternary climate change. J Asian Earth Sci 170:128–137
Gupta AK, Thomas E (2003) Initiation of Northern Hemisphere glaciation and strengthening of the northeast Indian monsoon: Ocean Drilling Program Site 758, eastern equatorial Indian Ocean. Geology 31:47
Haug GH (2001) Southward migration of the intertropical convergence zone through the holocene. Science 293:1304–1308
He N, Zhu X (1992) Paleoenvronment changes since 30,000 a B. P. and effects of human activities in the Baiyangdian area. Mar Geol Quat Geol 1992(02):79–88 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hu S, Su M, Erwin Appel JL (2000) Environmental mechanism of magnetic susceptibility changes of lacustrine sediment from Lake Hulun, China. Sci China Ser D Earth Sci 43:534–540
Hu S, Deng C, Stephenson A, Apple EV (2001) A study of gyroremanent magnetization GRM and rotational remanence magnetization (RRM) carried by greigite from lake sediments. Chin Sci Bull 17:1491–1494 (in Chinese)
Hu S, Liu C, Zheng H, Wang Z, Yu J (2012) Impacts of climate change and human activities on runoff in Baiyangdian water source area (in English). J Geogr Sci 22:895–905
Jia F, Lu R, Liu X, Zhao C, Lv Z, Gao S (2018) Palaeoenvironmental implications of a Holocene sequence of lacustrine-peat sediment from the desert-loess transitional zone in Northern China. J Asian Earth Sci 156:167–173
Jiang Q, Ji J, Shen J, Matsumoto R, Tong G, Qian P, Ren X, Yan D (2013) Holocene vegetational and climatic variation in westerly-dominated areas of Central Asia inferred from the Sayram Lake in northern Xinjiang, China. Sci China Earth Sci 56:339–353
Jin G, Liu D (2001) Climate events of middle holocene cooling and ancient cultural changes in north China. Chin Sci Bull 20:1725–1730 (in Chinese)
Klus A, Prange M, Varma V, Tremblay LB, Schulz M (2018) Abrupt cold events in the North Atlantic Ocean in a transient Holocene simulation. Clim Past 14:1165–1178
Kodama KP, Lyons JC, Siver PA et al (1997) A mineral magnetic and scaled-chrysophyte paleolimnological study of two Northeastern Pennsylvania lakes: records of fly ash deposition, land-use change, and paleorainfall variation. J Paleolimnol 17:173–189
Koutavas A, Joanides S (2012) El Niño-Southern oscillation extrema in the Holocene and last glacial maximum. Paleoceanography 27:PA4208
Kotlia BS, Wünnemann B (2019) Holocene climate and civilization. Quat Int 507:1–3
Le Roux JP, Rojas EM (2007) sediment transport patterns determined from grain size parameters: overview and state of the art. Sediment Geol 202:473–488
Li Y, Wang N, Cheng H, Long H, Zhao Q (2009) Holocene environmental change in the marginal area of the Asian monsoon: a record from Zhuye Lake, NW China. Boreas 38:349–361
Li S, Wuennemann B, Xia L, Yu S (2009) A preliminary study on holocene water level change events and their causes in zgetang fault sedimentary records on the qinghai-tibet plateau. Front Geosci 16:162–167 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li Y, Wang NA, Li Z, Zhou X, Zhang C (2012) Holocene climate cycles in northwest margin of Asian monsoon. Chin Geogr Sci 22:450–461
Li S, Guo W, Yin Y, Jin X, Tang W (2015) Environmental changes inferred from lacustrine sediment and historical literature: a record from Gaoyou Lake, eastern China. Quatern Int 380–381:350–357
Li X, Wang M, Hou J (2018) Centennial-scale climate variability during the past 2000 years derived from lacustrine sediment on the western Tibetan Plateau. Quat Int 510:65–75
Li M, Zhang S, Xu Q, Xiao J, Wen R (2019) Spatial patterns of vegetation and climate in the North China Plain during the Last Glacial Maximum and Holocene climatic optimum. Sci China Earth Sci 62:1279–1287. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-018-9264-2
Li C, Li B, Li Y, Chen B, Xu Q, Zhang W, Liu W, Ding G (2020) Variation of summer monsoon intensity in the North China Plain and its response to abrupt climatic events during the early-middle Holocene. Quat Int 550:66–73
Liu D, Zheng M, Guo Z (1998) Origin and development of Asian monsoon system and its time coupling with polar ice sheet and regional tectonic movement. Quat Stud 1998(03):194–204 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu X, Shen J, Wang Su, Zhang En, Cai Y (2003) Paleoclimate records of lacustrine autogenic carbonate deposits in qinghai lake since 16ka. Chin J Geol 9:38–46 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu J, Chen F, Chen J, Xia D, Xu Q, Wang Z, Li Y (2011) Humid Medieval Warm Period recorded by magnetic characteristics of sediments from Gonghai Lake, Shanxi, North China. Chin Sci Bull 56:2464–2474
Liu G, Yin Y, Liu H, Hao Q (2013) Quantifying regional vegetation cover variability in North China during the Holocene: implications for climate feedback. PloS One 8:e71681
Lu L, Shi Z (2010) Analysis for sediment grain size parameters of connotations and calculation method. Environ Sci Manag 35:54–60 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ma Q, Zhu L, Lü X, Wang J, Ju J, Kasper T, Daut G, Haberzettl T (2019) Late glacial and Holocene vegetation and climate variations at Lake Tangra Yumco, central Tibetan Plateau. Glob Planet Chang 174:16–25
Mao H, He J, Uuml CL, Liang Y, Liu H, Wang F (2011) Characteristics of organic carbon forms in the sediment of Wuliangsuhai and Daihai Lakes. Environ Sci 3:658–666
Makwana N, Prizomwala SP, Chauhan G, Phartiyal B, Thakkar MG (2018) Late Holocene palaeo-environmental change in the Banni Plains, Kachchh, Western India. Quat Int 507:197–205
Melles M, Brigham-Grette J, Minyuk PS, Nowaczyk NR, Wennrich V, DeConto RM, Anderson PM, Andreev AA, Coletti A, Cook TL, Haltia-Hovi E (2012) 2.8 Million years of arctic climate change from lake Elgygytgyn, NE Russia. Science 337:315–320
Mischke S, Zhang C (2010) Holocene cold events on the Tibetan Plateau. Glob Planet Change 72:155–163
Oh H, Shin H (2016) Climatic classification over asia during the middle holocene climatic optimum based on PMIP models. J Earth Sci-China 27:123–129
Pei L, Zhang D, Li J, Fei J (2019) Proxy-based temperature reconstruction in China for the Holocene(Article). Quat Int 521:168–174
Rao Z, Jia G, Li Y, Chen F, Chen J, Xu Q (2016) Asynchronous evolution of the isotopic composition and amount of precipitation in north China during the Holocene revealed by a record of compound-specific carbon and hydrogen isotopes of long-chain n-alkanes from an alpine lake. Earth Planet Sci Lett 446:68–76
Revelles J, Cho S, Iriarte E, Burjachs F, van Geel B, Palomo A, Piqué R, Peña-Chocarro L, Terradas X (2015) Mid-Holocene vegetation history and Neolithic land-use in the Lake Banyoles area (Girona, Spain). Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 435:70–85
Sabatier P, Dezileau L, Colin C, Briqueu L, Bouchette F, Martinez P, Siani G, Raynal O, Von Grafenstein U (2012) 7000 years of paleostorm activity in the NW Mediterranean Sea in response to Holocene climate events. Quat Res 77:1–11
Shen J (2012) Spatiotemporal variations of Chinese lakes and their driving mechanisms since the Last Glacial Maximum: a review and synthesis of lacustirne sediment archives. Chin Sci Bull. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-012-5510-7 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Shen J, Jiang J, Wu J (2004) Climate and environmental changes recorded in the sediment of anguli basin. Geogr Sci 24:346–351 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Shen G, Ding G, Yang X, Zhang R, Li Y, Li B (2018) Holocene climatic and environmental change in The Baiyangdian area. Quat Sci 38(3):756–768 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Shi C (2012) Research on the changes of henan system in the qing dynasty in the historical period – also on the evolution relationship with baiyangdian lake group. A review of Chinese history and geography 27:50–59 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Shuman B, Bravo J, Kaye J (2001) Late quaternary water-level variations and vegetation history at Crooked Pond, Southeastern Massachusetts. Quat Res (Orlando) 56(3):401–410
Snowball I, Sandgren P, Petterson G (1999) The mineral magnetic properties of an annually laminated holocene lake-sediment sequence in Northern Sweden. Holocene 9(3):353–362
Snowball I, Zillen L, Gaillard MJ (2002) Rapid early holocene environmental changes in Northern Sweden based on studies of two varved lake-sediment sequences. Holocene 12(1):7–16
Song C, Ke L, Pan H, Zhan S, Liu K, Ma R (2018) Long-term surface water changes and driving cause in Xiongan, China: from dense Landsat time series images and synthetic analysis. Sci Bull 63:708–716
Steinman BA, Nelson DB, Abbott MB, Stansell ND, Finkenbinder MS, Finney BP (2019) Lake sediment records of Holocene hydroclimate and impacts of the Mount Mazama eruption, north-central Washington, USA. Quat Sci Rev 204:17–36
Sun Q, Wang S, Zhou J, Chen Z, Shen J, Xie X, Wu F, Chen P (2010) sediment geochemistry of Lake Daihai, north-central China: implications for catchment weathering and climate change during the Holocene. J Paleolimnol 43:75–87
Tian F, Wang Y, Liu J, Tang W, Jiang N (2017) Late Holocene climate change inferred from a lacustrine sedimentary sequence in southern Inner Mongolia, China. Quat Int 452:22–32
Wang H (1983) Expansion and contraction of Baiyangdian in the past ten thousand years. Geogr Res 3:8–18 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang X (2014) Applicability of biofilm monitoring method to water combined pollution in Baiyangdian basin. J Agro-Environ Sci 33:1802–1809 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang Y, Cheng H, Edwards RL, HeY Kong X, An Z, Wu J, Kelly MJ, Dykoski CA, Li X (2005) The holocene Asian monsoon: links to solar changes and North Atlantic climate. Science 308:854–857
Wang J, Li H, Deng W, Guo X, Li S, Zhang J (2012) Paleoenvironmental significance of magnetization rate and grain size of sediment in gashunnuer lake, Inner Mongolia. Chin Desert 32:661–668 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang Y, Chi Z, Min L, Dong J, Yao P (2015) Sedimentary characteristics and stratigraphic division of holocene series in Baiyang Dian, Hebei Provence. Acta Geol Sin 36(5):575–582 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wentworth CK (1922) A scale of grade and class terms for clastic sediment. J Geol 30:377–392
Wiersma AP, Renssen H (2006) Model–data comparison for the 8.2 ka BP event: confirmation of a forcing mechanism by catastrophic drainage of Laurentide Lakes. Quat Sci Rev 25:63–88
Williamson CE, Saros JE, Schindler DW (2009) Climate change: sentinels of change. Science 323:887–888
Woodbridge J, Roberts N, Fyfe R (2018) Pan-Mediterranean Holocene vegetation and land-cover dynamics from synthesized pollen data. J Biogeogr 45:2159–2174
Xiao B, Sun F, Yao X, Hu K, Kidron GJ (2019) Seasonal variations in infiltrability of moss-dominated biocrusts on aeolian sand and loess soil in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Hydrol Process 33:2449–2463
Xie S, Evershed RP, Huang X, Zhu Z, Pancost RD, Meyers PA, Gong L, Hu C, Huang J, Zhang S, Gu Y, Zhu J (2013) Concordant monsoon-driven postglacial hydrological changes in peat and stalagmite records and their impacts on prehistoric cultures in central China. Geology 41:827–830
Xu Q, Wu C (1986) A preliminary understanding of the environmental evolution in Baiyangdian area during the holocene. Geogr Land Stud 1986(03):51–56 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xu QH, Chen F, Zhang S, Cao X, Li J, Li Y, Li M, Chen J, Liu J, Wang ZL (2016) Vegetation succession and East Asian Summer Monsoon changes since the last deglaciation inferred from high-resolution pollen record in Lake Gonghai, Shanxi Province, China. The Holocene 27:835–846
Xu J, Shi X, Liu S, Liu J, Shan X, Dong Z (2018) Late holocene east Asian monsoon high-resolution sedimentary record: evidence from the inland shelf argillaceous area of the east China sea. Prog Mar Sci 36:216–228 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang J (2004) Discussion on the spatial and temporal pattern of the evolution of Dali and last glacial glaciers in diancang mountain, Ph.D., Peking University (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang J, Xu X, Hu Y, Yuan H, Xiao G (2016) Paleovegetation evolution and its response to the climate change since Middle Pleistocene in the North China plain. Geol Bull China 35(10):1745–1751 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang X, Ye P, Cai M, Chang P, You B (2017) Variation of lake water level recorded by grain size of sediments from Hetao Paleolake since 150ka. Geol Bull China 36(6):1043–1050 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang X, Zhang R, Wang R, Mao X, Meng H, Chen L (2018) Palynological records of environmental changes in the late holocene of Wenanwa wetland in hebei province. Acta Micropalaeontol 35:65–73 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yao J, Chen Y, Zhao Y, Yu X (2018) Hydroclimatic changes of Lake Bosten in Northwest China during the last decades. Sci Rep-UK 8:9113–9118
Yuan J, Cao G, Chongyi E, Yuan Y, Wu C, Yu M, Yang R (2017) Characteristics of Loess magnetic susceptibility and its influencing factors analysis in Hebei Country. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 94:12114
Zan J, Fang X, Zhang W, Zhang D, Yan M (2018) A new record of late Pliocene-early Pleistocene aeolian loess–red clay deposits from the western Chinese Loess Plateau and its palaeoenvironmental implications. Quat Sci Rev 186:17–26
Zeng C (2009) Environmental record of spontaneous carbonate content in lakes. Ocean Limnol Bull 2009(1):67–72 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang P, Dai J (2017) Comparison of grain size parameters of several sediment graphical methods and moment metho2d and their significance. Chin J Geol 41:239–244 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang P, Song C, Gao H, Zhang H (2008) The significance and establishment of discriminant function with grain size of stable lacustrine sediment and Eolian loess. Acta Sedimentol Sin 26:501–507 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang J, Chen F, Holmes JA, Li H, Li S, Guo X, Wang J, Lü Y, Zhao Y, Qiang M (2011) Holocene monsoon climate documented by oxygen and carbon isotopes from lake sediment and peat bogs in China: a review and synthesis. Quat Sci Rev 30:1973–1987
Zhang S, Zhang S, Yang Z, Cioppa MT, Liu J, Liu Q, Wang X, Eichhorn HS, Qiao Y, Chen F, Shao Z, Gagnon JE, Huo J, Sheng M (2018a) A high-resolution Holocene record of the East Asian summer monsoon variability in sediment from Mountain Ganhai Lake, North China. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 508:17–34
Zhang E, Chang J, Sun W, Cao Y, Langdon P, Cheng J (2018b) Potential forcings of summer temperature variability of the southeastern Tibetan Plateau in the past 12 ka. J Asian Earth Sci 159:34–41
Zhu X, He N (1988) Discussion on the sedimentary environment and the reasons of drying up in baiyangdian. Geogr Geogr Inf Sci 1998(2):50–54 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zolitschka B (1998) A 14,000 year sediment yield record from western Germany based on annually laminated lake sediment. Geomorphology 22:1–17
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Geological Survey Projects of China (Grant Nos. DD20189629, DD20190370). We would like to thank editors and reviewers for their constructive suggestions. We would also like to thank professor Jie Cheng for his guidance. We thank LetPub (www.letpub.com) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ni, Ht., Wang, Y., Tian, F. et al. Holocene climate evolution: information from the Lacustrine–Fluvial sediment in North China. J Paleolimnol 68, 71–89 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-021-00190-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-021-00190-0