Abstract
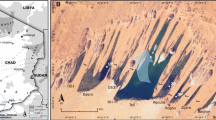
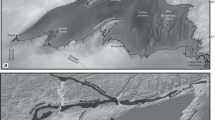
Da Qaidam and Xiao Qaidam are two of a number of lakes in northwestern China whose lake histories have been used to support the notion of a “Greatest Lakes” period in the region during marine isotope stage (MIS) 3. Reappraisal of the basins’ geomorphology, however, suggests that both lakes are highly problematic proxies for past climate. Xiao Qaidam has a low overflow threshold, only ~10–12 m above the lake surface, well below previously estimated high stands, and until about 17–23 ka BP Da Qaidam was occasionally fed by a river whose flow into the lake basin was geomorphically, rather than climatically controlled. Based on limited optically stimulated luminescence dating of shoreline and alluvial sediments it appears that highstands in the basins occurred ~100 ka BP or earlier. The two lakes are thus part of an increasing number of lake records that suggest, at least in northwestern China, (1) some lake histories may not record climate events, and (2) that the “Greatest Lakes” high stands occurred much earlier than previously recognized.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aitken MJ (1998) An Introduction to optical dating: the dating of Quaternary sediments by the use of photon-stimulated luminescence. Oxford University Press, Oxford, p 267
An ZS, Kutzbach JE, Prell WL, Porter SC (2001) Evolution of Asian monsoons and phased uplift of the Himalaya-Tibetan plateau since Late Miocene times. Nature 411:62–66
Berger GW, Mulhern PJ, Huntley DJ (1980) Isolation of silt-sized quartz from sediments. Ancient TL 11:8–9
Bowler JM, Huang Q, Chen K, Head MJ, Yuan B (1986) Radiocarbon dating of playa-lake hydrologic changes: examples from northwestern China and central Australia. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 54:241–260
Brantingham PJ, Gao X (2006) Peopling of the northern Tibetan Plateau. World Arch 38:387–414
Brantingham PJ, Ma HZ, Olsen JW, Gao X, Madsen DB, Rhode DE (2003) Speculation on the timing and nature of Late Pleistocene hunter–gatherer colonization of the Tibetan Plateau. Chin Sci Bull 48:1510–1516
Brantingham PJ, Gao X, Olsen JW, Ma H, Rhode D, Zhang H, Madsen DB (2007) A short chronology for the peopling of the Tibetan Plateau. In: Madsen DB, Chen FH, Gao X (eds) Human adaptation to climate change in Arid China. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 129–150
Chen K, Bowler JM (1986) Late Pleistocene evolution of salt lakes in the Qaidam Basin, Qinghai Province, China. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 54:87–104
Chen FH, Fan Y, Chun X, Madsen DB, Oviatt CG, Zhai H, Yang LP, Sun Y (2008a) Preliminary research on megalake Jilantai-Hetao in the arid areas of China during the Late Quaternary. Chin Sci Bull 53:1725–1739
Chen FH, Yu ZC, Yang ML, Ito E, Wang SM, Madsen DB, Huang XZ, Zhao Y, Sato T, Birks HJB, Boomer I, Chen JH, An CB, Wünnemann B (2008b) Holocene moisture evolution in arid central Asia and its out-of-phase relationship with Asian monsoon history. Quat Sci Rev 27:351–364
Colman SM, Yu SY, An Z, Shen J, Henderson ACG (2007) Late Cenozoic climate changes in China’s western interior: a review of research on Lake Qinghai and comparison with other records. Quat Sci Rev 26:2281–2300
Derevianko A, Brantingham PJ, Olsen JW, Tseveendorj D (2004) Initial upper paleolithic blade industries from the north-central Gobi Desert, Mongolia. In: Brantingham PJ, Kuhn KL, Kerry KW (eds) The early upper paleolithic beyond Western Europe. University of California Press, Berkeley, pp 207–222
Dietze E, Wünnemann B, Diekmann B, Aichner B, Hartmann K, Herzschuh U, IJmker J, Jin H, Kopsch C, Lehmkuhl F, Li S, Mischke S, Niessen F, Opitz S, Stauch G, Yang S (2010) Basin morphology and seismic stratigraphy of Lake Donggi Cona, north-eastern Tibetan Plateau, China. Quat Int 218:131–142
Fan QS, Lai ZP, Long H, Sun YJ, Liu XJ (2010) OSL chronology for lacustrine sediments recording high stands of Gahai Lake in Qaidam Basin, northeastern Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Quat Geochron 5:223–227
Fang X, Ono Y, Fukusawa H, Pan B, Li J, Guan D, Oi K, Tsukamoto S, Torii M, Mishima T (1999) Asian summer monsoon instability during the past 60,000 years: magnetic susceptibility and pedogenic evidence from the western Chinese Loess Plateau. Earth Planet Sci Let 168:219–232
Gao X, Li J, Madsen DB, Brantingham PJ, Elston RG, Bettinger RL (2002) New 14C dates for Shuidonggou and related discussions. Acta Anthropol Sin 21:211–218 (in Chinese)
Guan Y, Gao X, Wang HM, Chen FY, Pei SW, Zhang XL, Zhou ZY (2011) Spatial analysis of intra-site use at a Late Paleolithic site at Shuidonggou, northwest China. Chin Sci Bull 56:3457–3463
Han W, Fang X, Yang S, King J (2010) Differences between East Asian and Indian monsoon climate records during MIS3 attributed to differences in their driving mechanisms: evidence from the loess record of the Sichuan basin, southwestern China and other continental and marine climate records. Quat Int 218:94–103
Hartmann K, Wünnemann B, Hölz S, Kraetschell A, Zhang H (2011) Neotectonic constraints on the Gaxun Nur inland basin in north–central China, derived from remote sensing, geomorphology and geophysical analyses. In: Gloaguen R, Ratschbacher L (eds) Growth and collapse of the Tibetan Plateau. Geological Society, London, Special Pub 353, pp 221–233
Herzschuh U (2006) Palaeo-moisture evolution in monsoonal Central Asia during the last 50,000 years. Quat Sci Rev 25:163–178
Huang Q, Cai BQ, Yu JQ (1981) The 14C age and cycle of sedimentation of some saline lakes on the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Chin Sci Bull 26:66–70
Huang WW, Chen KZ, Yuan BY (1987) Paleolithics of Xiao Qaidam Lake in Qinghai Province in China. In: Proceedings of the Sino-Australian Quaternary meeting. Sciences Press, Beijing, pp 168–172 (in Chinese)
Huang Q, Ku T-L, Phillips FM (1993) Evolutionary characteristics of lakes and palaeoclimatic undulations in the Qaidam Basin, China. Chin J Oceanol Limnol 11:34–45
Jain M, Murray AS, Bøtter-Jensen L (2003) Characterization of blue-light stimulated luminescence components in different quartz samples: implications for dose measurement. Rad Meas 37:441–449
Jia Y, Shi Y, Wang S, Jiang H, Li S, Wang A, Li X (2001) Lake-expanding events in the Tibetan Plateau since 40 ka BP. Sci China, Ser D Earth Sci 44(Supplement 1):301–315
Jiang H, Mao X, Xu H, Thompson J, Wang P, Ma X (2011) Last glacial pollen record from Lanzhou (northwestern China) and possible forcing mechanisms for the MIS 3 climate change in Middle to East Asia. Quat Sci Rev 30:769–781
Lai ZP (2010) Chronology and the upper dating limit for loess samples from Luochuan section in Chinese Loess Plateau using quartz OSL SAR protocol. J Asian Earth Sci 37:176–185
Lai ZP, Brückner H (2008) Effects of feldspar contamination on equivalent dose and the shape of growth curve for OSL of silt-sized quartz extracted from Chinese loess. Geochronometria 30:49–53
Lai ZP, Wintle AG (2006) Locating the boundary between the Pleistocene and the Holocene in Chinese loess using luminescence. Holocene 16:893–899
Lai ZP, Zöller L, Fuchs M, Brückner H (2008) Alpha efficiency determination for OSL of quartz extracted from Chinese loess. Rad Meas 43:767–770
Li BY (2000) The last greatest lakes on the Xizang (Tibetan) Plateau. Acta Geograph Sin 35:174–182 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li BY, Zhu LP (2001) “Greatest lake period” and its palaeo-environment on the Tibetan Plateau. J Geograph Sci 11:34–42
Liu XJ, Lai ZP, Fan QS, Long H, Sun YJ (2010) Timing for high lake levels of Qinghai Lake in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau since the Last Interglaciation based on quartz OSL dating. Quat Geochron 5:218–222
Long H, Lai ZP, Fuchs M, Zhang JR, Li Y (2012a) Timing of Late Quaternary palaeolake evolution in Tengger Desert of northern China and its possible forcing mechanisms. Glob Planet Change 92–93:110–129
Long H, Lai ZP, Fuchs M, Zhang JR, Yang L (2012b) Palaeodunes intercalcated in loess strata from the western Chinese Loess Plateau: timing and palaeoclimatic implications. Quat Int 263:37–45
Lu HY, Liu XD, Zhang FQ, An ZS, Dodson J (1999) Astronomical calibration of loess/paleosol deposits at Luochuan, central Chinese Loess Plateau. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 154:237–246
Madsen DB, Ma H, Rhode D, Brantingham PJ, Forman SL (2008) Age constraints on the late Quaternary evolution of Qinghai Lake, Tibetan Plateau. Quat Res 69:316–325
Mischke S, Sun Z, Herzschuh U, Qiao Z, Sun N (2010) An ostracod-inferred large Middle Pleistocene freshwater lake in the presently hyper-arid Qaidam Basin (NW China). Quat Int 218:74–85
Murray AS, Wintle AG (2000) Luminescence dating of quartz using an improved single-aliquot regenerative-dose protocol. Rad Meas 32:57–73
Murray AS, Wintle AG (2003) The single aliquot regenerative dose protocol: potential for improvements in reliability. Rad Meas 37:377–381
Ning Y, Liu W, An Z (2009) A 130-ka reconstruction of precipitation on the Chinese Loess Plateau from organic carbon isotopes. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 270:59–64
Owen LA, Finkel RC, Ma H, Barnard PL (2006) Late Quaternary landscape evolution in the Kunlun Mountains and Qaidam Basin, northern Tibet: a framework for examining the links between glaciation, lake level changes and alluvial fan formation. Quat Int 154–155:73–86
Prescott JR, Hutton JT (1994) Cosmic ray contributions to dose rates for luminescence and ESR dating: large depths and long-term time variations. Rad Meas 23:497–500
Rhode D, Ma H, Madsen DB, Brantingham PJ, Forman SL, Olsen JW (2010) Paleoenvironmental and archaeological investigations at Qinghai Lake, western China: geomorphic and chronometric evidence of lake level history. Quat Int 218:9–44
Roberts RM (2007) Assessing the effectiveness of the double-SAR protocol in isolating a luminescence signal dominated by quartz. Rad Meas 42:1627–1636
Shi Y, Yu G, Liu X, Li B, Yao T (2001) Reconstruction of the 30–40 ka BP enhanced Indian monsoon climate based on geological records from the Tibetan Plateau. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 160:69–83
Sun YJ, Lai ZP, Long H, Liu XJ, Fan QS (2010) Quartz OSL dating of archaeological sites in Xiao Qaidam Lake of the NE Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau and its implications for palaeoenvironmental changes. Quat Geochron 5:360–364
Tian L, Masson-Delmotte V, Stievenard M, Yao T, Jouzel J (2001) Tibetan Plateau summer monsoon northward extent revealed by measurements of water stable isotopes. J Geophys Res 106:28081–28088
Vandenberghe J, Renssen H, van Huissteden K, Nugteren G, Konert M, Lu H, Dodonov A, Buylaert JP (2006) Penetration of Atlantic westerly winds into central and East Asia. Quat Sci Rev 25:2380–2389
Wang E, Xu FY, Zhou JX, Wan J, Burchfiel BC (2006) Eastward migration of the Qaidam basin and its implications for Cenozoic evolution of the Altyn Tagh fault and associated river systems. Geol Soc Am Bull 118:349–365
Wei X, Jiang J (1994) The evolution of the Quaternary salt lakes in the Qaidam Basin. Acta Geol Sin 7:71–82
Wünnemann B, Hartmann K, Janssen M, Zhang HC (2007) Responses of Chinese desert lakes to climate instability during the past 45,000 years. In: Madsen DB, Chen FH, Gao X (eds) Late Quaternary climate change and human adaptation in Arid China. Elsevier, Amsterdam, Developments in Quaternary Science 9, pp 11–24
Yang X, Scuderi LA (2010) Hydrological and climatic changes in deserts of China since the late Pleistocene. Quat Res 73:1–9
Yang B, Wang J, Shi Y, Braeuning A (2004) Evidence for a warm-humid climate in arid northwestern China during 40–30 ka BP. Quat Sci Rev 23:2537–2548
Yang X, Scuderi LA, Paillou C, Liu Z, Li H, Ren X (2011) Quaternary environmental changes in the drylands of China—a critical review. Quat Sci Rev 30:3219–3233
Yin A, Wang LC, Zhou SP, Chen XH, Gehrels GE, McRivette MW (2008) Cenozoic tectonic evolution of Qaidam basin and its surrounding regions (Part 1): the southern Qilian Shan-Nan Shan thrust belt and northern Qaidam basin. Geol Soc Am Bull 120:813–846
Yu G, Harrison SP, Xue B (2001) Lake status records from China: data base documentation. Max Planck Institute for Biogeochemistry, Technical Report #4. Jena
Zhang JR, Lai ZP, Jia YL (2012) Luminescence chronology for late Quaternary Lake levels of enclosed Huangqihai Lake in East Asian monsoon marginal area in northern China. Quat Geochron 10:123–128
Zheng MP, Xiang J, Wei XJ, Zheng Y (1989) Saline lakes on the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau. Beijing Scientific and Technical Publishing House, Beijing, pp 306–329 (in Chinese)
Zheng M, Meng Y, Wei L (2000) Evidence of the pan-lake stage in the period of 40–28 ka B.P. on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Geol Sinica 74:266–272
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by P.R.C. 973 project (2010CB950202), U.S. National Science Foundation grants 0214870 and 084145, and a Chinese Academy of Science One-Hundred Talent Project (A0961) granted to ZPL. We thank Zhang Biao, E Chongyi, Steffen Mischke, David Page, Evelyn Seelinger, and two anonymous reviewers for assistance with this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madsen, D.B., Lai, Z., Sun, Y. et al. Late Quaternary Qaidam lake histories and implications for an MIS 3 “Greatest Lakes” period in northwest China. J Paleolimnol 51, 161–177 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-012-9662-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-012-9662-x