Abstract
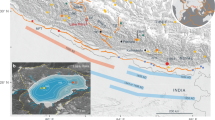
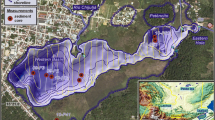
In 1999, the large surface-rupturing earthquakes of Izmit and Duzce completed a 60-year cycle that included a westward migration of nine consecutive large earthquake failures (>50 km surface rupture), which started with the 1939 Erzincan earthquake in eastern Turkey. In this study, we focused on seismic cycles and seismic risk predictability along the North Anatolian Fault (NAF). Toward the west end of the NAF (26°E–32°E, i.e. Bolu), large earthquake frequency is measured from either historic earthquake catalogs, or geologic records from isolated outcrops and marine sediment cores from the Marmara Sea. In comparison, the eastern part of the NAF zone (32°E–42°E) is less well documented by palaeo-seismologic archives. Thus, the sediment records of lake basins located on the eastern NAF zone constitute a unique opportunity for testing a new palaeo-seismologic approach. To this end, we used a diverse array of complementary methods involving: (1) a 600-km transect of fault-related lakes, (2) sedimentologic observations on cores from six lakes, and (3) a comparison between records of catastrophic sediment transfers in lakes (i.e. radionuclide chronomarkers and erosion tracers) and historic earthquake reports. Our study indicates that lakes along the NAF are sensitive geologic recorders of large surface-rupturing earthquakes (surface-wave magnitude (M s) ≥ 6.9); smaller intensities are not recorded. The most responsive lake systems exhibit increases in sediment accumulation by a factor of >40 for a >3-m strike-slip displacement (M s ≥ 7). However, based on results from the 1939 Erzincan earthquake (M s = 7.8) chronostratigraphic marker, large surface-rupturing earthquakes are detected only by certain lake records and not by others. Matching multiple lake records along the NAF provides information both on the location of a surface rupture of a paleo-earthquake as well as its magnitude. Finally, the shallow lake basins along the NAF could potentially document cycles of large seismic events for at least the late Holocene.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambraseys NN (1970) Some characteristic features of the Anatolian fault zone. Tectonophysics 9:143–165
Ambraseys NN (1971) Value of historical records of earthquakes. Nature 232:375–379
Ambraseys NN, Finkel CF (1987) Seismicity of Turkey and neighbouring regions, 1899–1915. Annales geophysicae. Series B. 5:701–725
Ambraseys NN, Finkel C (1995) The Seismicity of Turkey and adjacent areas. A historical review, 1500–1800. Eren, Istanbul, Turkey, p 240
Ambraseys NN, Jackson JA (1998) Faulting associated with historical and recent earthquakes in the eastern Mediterranean region. Geophys J Int 132:390–406
Appleby PG (1979) 210Pb dating of annually laminated lake sediments from Finland. Nature 280:53–55
Appleby PG (2001) Chronostratigraphic techniques in recent sediments. In: Last WM, Smol JP (eds) Tracking environmental change using lake sediments. Basin analysis, coring and chronological techniques, vol 1. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, pp 171–203
Appleby PG (2008) Three decades of dating recent sediments by fallout radionuclides: a review. Holocene 18:83–93
Appleby PG, Oldfield F (1978) The calculation of lead-210 dates assuming a constant rate of supply of unsupported 210Pb to the sediment. Catena 5:1–8
Armijo R, Meyer B, Hubert A, Barka A (1999) Westward propagation of the North Anatolian Fault into the northern Aegean; timing and kinematics. Geology 27:267–270
Armijo R, Pondard N, Meyer B, Uçarkus G, Mercier De Lépinay B, Malavieille J, Dominguez S, Gutscher MA, Schmidt S, Beck C, Cagatay N, Cakir Z, Imren C, Eris K, Natalin B, Özalaybey S, Tolun L, Lefèvre I, Seeber L, Gasperini L, Rangin C, Emre O, Sarikavak K (2005) Submarine fault scarps in the sea of Marmara pull-apart (North Anatolian Fault): implications for seismic hazard in Istanbul. Geochem Geophy Geosy Q06009:6–29
Arnaud F, Magand O, Chapron E, Bertrand S, Boës X, Mélières MA (2006) Radionuclide profiles (210Pb, 137Cs, 241Am) as a help for dating recent sediments in highly active geodynamic settings (Lakes Puyehue and Icalma, Chilean Lake District). Sci Total Environ 366:837–850
Avsar U, Hubert-Ferrari A, Fagel N, Boës X, and Schmidt S (2009) Paleolimnological and sedimentological traces of the 1943 (Ms = 7.3) Earthquake in the sediments of Ladik Lake, Samsun/Turkey EGU, European Geosciences Union General Assembly 2009. Vienna, Austria, April 2009
Barka AA (1992) The North Anatolian fault zone. Annales Tectonicae 6:164–195
Barka AA (1996) Slip distribution along the North Anatolian fault associated with the large earthquakes of the period 1939 to 1967. B Seismol Soc Am 86:1238–1254
Barka AA (1999) The 17 August 1999 Izmit Earthquake. Science 285:1858–1859
Barka AA (2000) Tectonic evolution of the Niksar and Tasova-Erbaa pull-apart basins, North Anatolian Fault Zone: their significance for the motion of the Anatolian block. Tectonophysics 322:243–264
Barka AA, Kadinski-Cade K (1988) Strike-slip fault geometry in Turkey and its influence on earthquake activity. Tectonics 7:663–684
Beck C, Mercier de Lépinay B, Schneider JL, Cremer M, Çağatay N, Wendenbaum E, Boutareaud S, Ménot G, Schmidt S, Weber O, Eris K, Armijo R, Meyer B, Pondard N, Gutscher MA, Turon JL, Labeyrie L, Cortijo E, Gallet Y, Bouquerel H, Gorur N, Gervais A, Castera MH, Londeix L, de Rességuier A, Jaouen A (2007) Late Quaternary co-seismic sedimentation in the sea of Marmara’s deep basins. Sediment Geol 199:65–89
Carrillo E, Beck C, Audemard MF, Moreno E, Ollarves R (2008) Disentangling Late Quaternary climatic and seismo-tectonic controls on Lake Mucubaji sedimentation (Mérida Andes, Venezuela). Paleogeogr Paleoclim Paleoecol 259:284–300
Carroll JL, Lerche I, Abraham JD, Cisar DJ (1995) Model-determined sediment ages from 210Pb profiles in un-mixed sediments. Nucl Geophys 9:553–565
Ergin K, Guclu U, Uz Z (1967) A catalogue of earthquakes for Turkey and surrounding area. Publ. Techn. Univ. Istanbul, Turkey, p 169
Eyidogan H, Güçlü U, Utku Z, Degirmenci E (1991). Türkiye Büyük Depremleri Makro-Sismik Rehberi (1900–1988), ITÜ MF Jeofizik Mühendisligi Bölümü Yayınları s 200
Hartleb RD, Dolan JF, Akyüz HS, Yerli B (2003) A 2000-year-long paleoseismologic record of earthquakes along the central North Anatolian Fault, from trenches at Alayurt, Turkey. B Seismol Soc Am 93:1935–1954
Hartleb RD, Dolan JF, Kozaci O, Akyüz HS, Seitz GG (2006) A 2500-year-long paleoseismologic record of large, infrequent earthquakes on the North Anatolian fault at Çukurçimen, Turkey. GSA Bulletin 118:823–840
Hitchcock C, Altunel E, Barka A, Bachhuber J, Lettis W, Helms J, Lindvall S (2003) Timing of late holocene earthquakes on the Eastern Düzce Fault and implications for slip transfer between the southern and northern strands of the North Anatolian Fault System, Bolu, Turkey. Turk J. Earth Sci 12:119–136
Hubert-Ferrari A, King G, Manighetti I, Armijo R, Meyer B, Tapponnier P (2003) Long-term elasticity in the continental lithosphere; modelling the Aden Ridge propagation and the Anatolian extrusion process. Geophys J Int 153:111–132
Inouchi Y, Kinugasa Y, Kumon F, Nakano S, Yasumatsu S, Shiki T (1996) Turbidites as records of intense palaeoearthquakes in Lake Biwa, Japan. Sediment Geol 104:117–125
Ken-Tor R, Agnon A, Enzel Y, Stein M, Marco S, Negendank JFW (2001) High-resolution geological record of historic earthquakes in the Dead Sea basin. J Geophys Res 106:2221–2234
Leroy S, Kazancı N, Ileri O, Kibar M, Emre O, McGee E, Griffiths HI (2002) Abrupt environmental changes within a late Holocene lacustrine sequence south of the Marmara Sea (Lake Manyas, N-W Turkey): possible links with seismic events. Mar Geol 190:531–552
Marco S, Stein M, Agnon A, Ron H (1996) Long-term earthquake clustering: a 50,000-year paleoseismic record in the Dead Sea Graben. J Geophys Res 101:6179–6191
McHugh CMG, Seeber L, Cormier MH, Dutton J, Cagatay N, Polonia A, Ryan WBF, Gorur N (2006) Submarine earthquake geology along the North Anatolia Fault in the Marmara Sea, Turkey: a model for transform basin sedimentation. Earth Planet Sc Lett 248:661–684
Migowski C, Agnon A, Bookman R, Negendank JFW, Stein M (2004) Recurrence pattern of Holocene earthquakes along the Dead Sea transform revealed by varve-counting and radiocarbon dating of lacustrine sediments. Earth Planet Sc Lett 222:301–314
Pantosti D, Pucci S, Palyvos N, De Martini PM, D’Addezio G, Collins PEF, Zabci C (2008) Paleoearthquakes of the Düzce fault (North Anatolian Fault Zone): insights for large surface faulting earthquake recurrence. J Geophys Res 113:1–20
Polonia A, Gasperini L, Amorosi A, Bonatti E, Bortoluzzi G, Çagatay N, Capotondi L, Cormier MH, Gorur N, McHugh C, Seeber L (2004) Holocene slip rate of the North Anatolian Fault beneath the Sea of Marmara. Earth Planet Sc Lett 227:411–426
Reilinger RE, McClusky SC, Oral MB, King W, Toksöz MN (1997) Global positioning, system measurements of present-day crustal movements in the Arabian-Africa-Eurasia plate collision zone. J Geophys Res 102:9983–9999
Sengor AMC (2005) The North Anatolian Fault: a new look. Annu Rev Earth Pl Sc 33:37–112
Shiki T, Kumon F, Inouchi Y, Kontani Y, Sakamoto T, Tateishi M, Matsubara H, Fukuyama K (2000) Sedimentary features of the seismo-turbidites, Lake Biwa, Japan. Sediment geol 135:37–50
Stein RS, Barka AA, Dieterich JH (1997) Progressive failure on the North Anatolian fault since 1939 by earthquake stress triggering. Geophys J Int 128:594–604
Sugai T, Awata Y, Toda S, Emre Ö, Dogan A, Ozalp S, Haraguchi T, Kinoshita H, Takada K, Yamaguchi M (2001) Paleoseismic investigation of the 1999 Düzce earthquake fault at Lake Efteni, North Anatolian fault system, Turkey. Annual Report on Active Fault and Paleoearthquake Researches No. 1. Active Fault Research Center, Japan, pp 339–351
Tan O, Tapirdamaz MC, Yoruk A (2007) The earthquake catalogues for Turkey. Turk J of Earth Sci 17:405–418
Turekian KK, Cochran JK (1978) Determination of marine chronologies using natural radionuclides. In: Riley JP, Chester R (eds) Chemical oceanography, vol 7. Academic Press, New York, pp 313–360
Westaway R (1994) Present-day kinematics of the Middle-East and Eastern Mediterranean. J Geophys Res 99:12071–12090
Acknowledgments
This study was carried out within the framework of the EC FP6 Marie Curie Excellence Grant project titled Understanding the irregularity of seismic cycles: A case study in Turkey. We are grateful to the European Commission, Human Resources and Mobility for funding. The Fulbright commission is acknowledged for providing a grant to XB for studies at the University of Rhode Island. We thank the Eastern Mediterranean Centre for Oceanography and Limnology (EMCOL) at the Technical University of Istanbul for providing laboratory facilities, for assisting in summer field campaigns, and for XRF elemental analysis. Special thanks are due to the EMCOL personnel and students: Celal Somuncuoğlu, Emre Damci, Dursun Acar, and Sena Akcer. We acknowledge the contribution of Ulas Avsar (University of Gent), David Garcia (ROB), and Sevgi Altinok (University of Eskisehir). We also thank Roger Kelly, Scott Stachelhaus, Danielle Cares and Chip Heil of the Graduate School of Oceanography, University of Rhode Island, for assistance in radionuclide analysis and analysis of physical sediment properties. Finally, thanks are due to Chantal Tribolo for consultation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boës, X., Moran, S.B., King, J. et al. Records of large earthquakes in lake sediments along the North Anatolian Fault, Turkey. J Paleolimnol 43, 901–920 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-009-9376-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-009-9376-x