Abstract
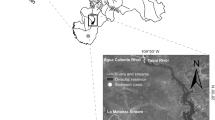
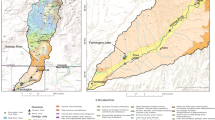
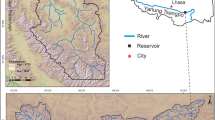
Reservoir sediments are rarely used as environmental archives because of the potential for sediment disturbance by fluctuating water levels. However, rapid rates of sedimentation, proximity to urban centres and often the existence of management records, may make them potentially important resources for reconstructing recent, anthropogenically-derived environmental change. This project assesses the potential of reservoir sedimentary records for reconstructing past atmospheric and drainage basin fluxes of heavy metals (manganese, iron, nickel, copper, zinc and lead) in the southern Pennines, UK. Five reservoirs were selected on the basis of management history and drainage basin characteristics. Multi-parameter analysis showed sediments to be replicable across the ȁ8accumulating zone’ with reasonably consistent rates of sedimentation. Water level fluctuations were not found to detrimentally affect sediment records in the deepwater area of the reservoirs. In fact, spheroidal carbonaceous particle (SCP) profiles show trends in inputs that closely reflect major changes in industrialisation, indicating the reservoir sediments to be excellent records of particulate inputs. Only lead (Pb) and zinc (Zn) were significantly enriched in the reservoir sediment in comparison to background levels. Manganese (Mn), iron (Fe) and to a limited degree, copper (Cu), appeared to be affected by post-deposition mobility. Preliminary calculations of Pb fluxes indicate that over 80% of the current Pb input to the reservoirs is from Pb deposited onto drainage basin soils in the past, rather than from direct atmospheric deposition or natural background inputs. In Howden reservoir, for example, the total Pb flux to deepwater sediment cores in 2000 was 119 mg m−2 a−1. Of this, an estimated 99 mg m−2 a−1 was from anthropogenically-derived Pb, initially deposited onto drainage basin soils and subsequently entering the reservoir via erosion and leaching processes. There is, therefore, no indication that the flux of Pb to the aquatic system is declining in response to reductions in Pb deposition. The ecotoxicological effects of the high and continuing Pb flux to these reservoirs, despite recent decreases in atmospheric deposition, is an area requiring further investigation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Abraham P.M. Allen J.A. Dunbar S.I. Dworkin (1999) ArticleTitleSediment type distribution in reservoirs: sediment source versus morphometry Environ. Geol. 38 101–110 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002540050406 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXksl2gt70%3D
N.J. Anderson S.T. Patrick P.G. Appleby F. Oldfield B. Rippey N. Richardson J. Darley R.W. Battarbee (1988) An assessment of the use of reservoir sediments in the southern Pennines for reconstructing the history and effects of atmospheric pollution Palaeoecology Research Unit, Department of Geography, University College London 72
P.G. Appleby N. Richardson P.J. Nolan (1991) ArticleTitle 241Am dating of lake sediments Hydrobiol. 214 35–42 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00050929 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXmtFais7s%3D
P.G. Appleby F. Oldfield (1978) ArticleTitleThe calculation of 210Pb dates assuming a constant rate of supply of unsupported 210Pb to the sediment Catena 5 1–8 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0341-8162(78)80002-2 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE1MXksVahurw%3D
Ashmore M.R., Fawehinmi J., Hall J., Heywood E., Hill M., Jordan C., Lofts S., Shotbolt L., Spurgeon D., Svenson C. and Tipping E. 2005. Further development of an effects based (critical loads) approach for cadmium, copper, lead and zinc. Final Report to Defra, EPG 1/3/188, 127 pp.
M. Åström (2001) ArticleTitleEffect of widespread severely acidic soils on spatial features and abundance of trace elements in streams Journal of Geochemical Exploration 73 181–191
S. Audry J. Schafer G. Blanc J-M. Jouanneau (2004) ArticleTitleFifty-year sedimentary record of heavy metal pollution (CdZn, CuPb) in the Lot River reservoirs (France) Environ. Pollut. 132 413–426 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.envpol.2004.05.025 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXmvFyltL0%3D
Baker S.J. 2001. Trace and major elements in the atmosphere at rural locations in the UK: summary of data for 1999. AEA Technology, AEAT/R/ENV/0264, 106 pp.
J.F. Boyle (2001) ArticleTitleRedox remobilization and the heavy metal record in lake-sediments: a modelling approach J. Paleolimnol. 26 423–431 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1012785525239
J.F. Boyle A.W. Mackay N.L. Rose R.J. Flower P.G. Appleby (1998) ArticleTitleSediment heavy metal record in Lake Baikal: natural and anthropogenic sources J. Paleolimnol. 20 135–150 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1008051701416
T.P Burt M.A. Donohoe A.R. Vann (1983) ArticleTitleThe effect of forestry drainage operations on upland sediment yields: the results of a storm-based study Earth Surf. Processes Landforms 8 339–346
Butcher D.P., Labadz J.C., Potter A.W.R. and White P. 1993. Reservoir sedimentation rates in the southern Pennine region, UK. In: McManus J. and Duck R.W. (eds), Geomorphology and Sedimentology of Lakes and Reservoirs. John Wiley and Sons Ltd, pp.73–92.
E. Callender (2000) ArticleTitleGeochemical effects of rapid sedimentation in aquatic systems: minimal diagenesis and the preservation of historical metal signatures J. Paleolimnol. 23 243–260 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1008114630756
R.B. D’Agostino M.A. Stephens (1986) Goodness-of-fit Techniques Marcel Dekker New York 560
A.O. Davis J.N. Galloway D.K. Nordstrom (1982) ArticleTitleLake acidification: its effect on lead mobility in the sediment of two Aidronadack lakes Limnol. Oceanogr. 27 163–167 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL38Xht12gtb8%3D
J. Dearing (1994) Environmental Magnetic Susceptibility Chi Publishing Kenilworth 104
C.D. Evans A. Jenkins (2000) ArticleTitleSurface water acidification in the South Pennines 2. Temporal trends Environ. Pollut. 109 21–34 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXit1ygtrg%3D
J.G. Farmer L.J. Eades A.B. MacKenzie A. Kirika T.E. Bailey-Watts (1996) ArticleTitleStable lead isotope record of lead pollution in Loch Lomond Sediments since 1630 AD Environ. Sci. Technol. 30 3080–3083 Occurrence Handle10.1021/es960162o Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28Xlt1eksrY%3D
U. Förstner W. Salomons (1980) ArticleTitleTrace metal analysis on polluted sediments. Part 1: assessment of sources and intensities Environ. Technol. Lett. 1 494–505
I.D.L. Foster S.M. Charlesworth (1996) ArticleTitleHeavy metals in the hydrological cycle: trends and explanation J. Hydrol. 10 227–261
I.D.L. Foster J.A. Dearing A. Simpson A.D. Carter (1985) ArticleTitleLake catchment based studies of erosion and denudation in the Merevale catchmentWarwickshireU.K Earth Surf. Processes Landforms 10 45–68
I.D.L. Foster S.M. Charlesworth D.H. Keen (1991) ArticleTitleA comparative study of heavy metal contamination and pollution in four reservoirs in the English Midlands Hydrobiologia 214 155–162 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00050945 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXmtFChtb8%3D
I.D.L. Foster (1995) Lake and reservoir bottom sediments as a source of soil erosion and sediment transport data in the UK I.D.L. Foster A.M. Gurnell B.W. Webb (Eds) Sediment and Water Quality in River Catchments John Wiley and Sons Chichester 265–283
J.N. Galloway J.D. Thornton S.A. Norton H.L. Volchok R.A.N. McLean (1982) ArticleTitleTrace metals in atmospheric deposition: a review and assessment Atmos. Environ. 16 1677–1700 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL38XlsFSiu7Y%3D
L.C. Gottschalk (1964) Reservoir sedimentation V.T. Chow (Eds) Handbook of Applied Hydrology McGraw-Hill New York 1–33
L. Håkanson (1977) ArticleTitleThe influence of windfetchand water depth on the distribution of sediments in Lake Vanern, Sweden Can. J. Earth Sci. 14 397–412
S.M. Hutchinson (1995) ArticleTitleUse of magnetic and radiometric measurements to investigate erosion and sedimentation in a British upland catchment Earth Surf. Processes Landforms 20 293–314
B.R. Jones R.E. Laslett (1994) Methods for analysis of trace metals in marine and other samples Aquatic Environment Protection: Analytical Methods Series NumberInSeriesVol 11 Ministry of AgricultureFarming and Fisheries, Directorate of Fisheries Research Lowestoft 29
J.A. Lee J.H. Tallis (1973) ArticleTitleRegional and historical aspects of lead pollution in Britain Nature 245 216–218 Occurrence Handle10.1038/245216a0 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE2cXjtVamtQ%3D%3D
J. Lees I. Foster D. Jones P. Owens D. Walling G. Leeks (1997) Sediment yields in a changing environment: a historical reconstruction using reservoir bottom-sediments in three contrasting small catchments North York Moors UK 169–179
E.A. Livett J.A. Lee J.H. Tallis (1979) ArticleTitleLeadzinc and copper analysis of British blanket peats J. Ecol. 67 865–891 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3cXktlWjtr0%3D
E.A. Livett (1988) Geochemical monitoring M. Begon A.H. Fitter E.D. Ford A. MacFadyen (Eds) Advances in Ecological Research NumberInSeriesVol. 18. Academic Press London 65–174
F.J.H. Mackereth (1969) ArticleTitleA short core sampler for sub-aqueous deposits Limnol. Oceanogr. 14 145–151
J.D. McKee T.P. Wilson D.T. Long (1989a) ArticleTitlePore water profiles and early diagenesis of Mn, Cu and Pb in sediments from large lakes J. Great Lakes Res. 15 68–83 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1MXks1emt78%3D
J.D. McKee T.P. Wilson D.T. Long (1989b) ArticleTitleGeochemical partitioning of PbZn, CuFe and Mn across the sediment-water interface in large lakes J. Great Lakes Res. 15 46–58 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1MXks1emt74%3D
U. Ochsenbein W. Davison J. Hilton E.Y. Haworth (1983) ArticleTitleThe geochemical record of major cations and trace metals in a productive lake Archiv für Hydrobiologie 98 463–488 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2cXls1Ggsw%3D%3D
F. Oldfield (1977) ArticleTitleLakes and their drainage basins as units of sediment-based ecological study Prog. Phys. Geog. 1 460–504
F. Oldfield R. Wu (2000) ArticleTitleThe magnetic properties of the recent sediments of Brothers WaterNW England J. Paleolimnol. 23 165–174 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1008049419623
W.H. Patrick SuffixJr M. Verloo (1998) ArticleTitleDistribution of soluble heavy metals between ionic and complexed forms in a saturated sediment as affected by pH and redox conditions WaterSci. Technol. 37 165–172 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXktFemsLc%3D
N. Rose (1994) ArticleTitleA note on further refinements to a procedure for the extraction of carbonaceous fly-ash particles from sediments J. Paleolimnol. 11 201–204 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00686866
N.L. Rose S. Harlock P.G. Appleby R.W. Battarbee (1995) ArticleTitleDating of recent lake sediments in the United Kingdom and Ireland using spheroidal carbonaceous particle (SCP) concentration profiles Holocene 5 328–335
N.L. Rose P.G. Appleby (2005) ArticleTitleRegional applications of lake sediment dating by spheroidal carbonaceous particle analysis 1: United Kingdom J. Paleolimnol. 34 349–361 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10933-005-4925-4
D.L. Rowell (1994) Soil Science. Methods and Applications Prentice Hall Harlow 360
L. Shotbolt S.M. Hutchinson A.D. Thomas (2001) ArticleTitleEstablishing sediment stratigraphy in reservoirs in the southern Pennines J. Hydrol. Sci. 46 701–715 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXovVGisrc%3D
Shotbolt L. 2002. The use of southern Pennine reservoir sediments as records of atmospheric heavy metal deposition. Unpublished Ph.D. thesis. University of Salford, 374 pp.
I.F. Small S. Rowan R.W. Duck (2003) ArticleTitleLong-term sediment yield in Crombie Reservoir catchmentAngus; and its regional significance within the Midland Valley of Scotland Hydrol. Sci. 48 619–635
J.H. Tallis (1973) ArticleTitleStudies on Southern Pennine peats: V. Direct observation on peat erosion and peat hydrology at Featherbed Moss, Derbyshire J. Ecol. 61 1–22
Tipping E. and Smith E.J. 2000. Assessment of acidification reversal in surface waters of the Pennines. Centre for Ecology and Hydrology, Report for the Department of Trade and Industry, N/01/00058/REP, 27 pp.
K.K. Turekian K.H. Wedepohl (1961) ArticleTitleDistribution of the elements in some major units of the earth's crust Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 72 175–192 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaF3MXltlCrtA%3D%3D
P.C. Metre ParticleVan E. Callender (1997) ArticleTitleWater-quality trends in White Creek Basin from 1912–1994 identified using sediment cores from White Rock Lake reservoir Dallas, Texas. J. Paleolimnol. 17 239–249
J.R. White C.T. Driscoll (1987) ArticleTitleZinc cycling in an Adirondack Lake Environ. Sci. and Technol. 21 211–216 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2sXjvVSjtQ%3D%3D
L. Willies J. Maskall (1995) The historical and archaeological “spin-off” from heavy metal environmental research in the Peak District. Archaelogical Sciences A. Sinclair E. Slater J. Gowlett (Eds) Proceedings of a Conference at Liverpool University Oxbow Monograph Oxford 328–332
L. Willies H. Parker (1999) Peak District Mining and Quarrying Tempus Publishing Limited Gloucestershire
H.B. Xue R. Gachter L. Sigg (1997) ArticleTitleComparison of Cu and Zn cycling in eutrophic lakes with oxic and anoxic hypolimnion Aquatic Sciences 59 176–189 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s000270050083 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXntlyqu7c%3D
D.E. Yeloff J.C. Labadz C.O. Hunt (2005) ArticleTitleThe suitability of a south Pennine (UK) reservoir as an archive of recent environmental change J. Paleolimnol 34 339–348 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10933-005-5013-5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shotbolt, L., Hutchinson, S.M. & Thomas, A.D. Sediment Stratigraphy and Heavy Metal Fluxes to Reservoirs in the Southern Pennine Uplands, UK. J Paleolimnol 35, 305–322 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-005-1594-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-005-1594-2