Abstract
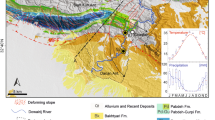
Because of differential isostatic rebound, many lakes in Canada have continued to change their extent and depth since retreat of the Laurentide Ice Sheet. Using GIS techniques, the changing configuration and bathymetry of Lake of the Woods in Ontario, Manitoba, and Minnesota were reconstructed for 12 points in time, beginning at 11,000 cal yr B.P. (∼9.6 14C ka B.P.), and were also projected 500 years into the future, based on the assumption that Lake of the Woods continued to have a positive hydrological budget throughout the Holocene. This modeling was done by first compiling a bathymetric database and merging that with subaerial data from the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM). This DEM file was then adjusted by: (1) isobase data derived from Lake Agassiz beaches prior to 9000 cal yr B.P. (∼8.1 14C ka B.P.) and (2) modeled isostatic rebound trend analysis after 9000 cal yr B.P. Just after the end of the Lake Agassiz phase of Lake of the Woods, only the northernmost part of the basin contained water. Differential rebound has resulted in increasing water depth. In the first 3000 years of independence from Lake Agassiz, the lake transgressed >50 km to the south, expanding its area from 858 to 2857 km2, and more than doubling in volume. Continued differential rebound after 6000 cal yr B.P. (∼5.2 14C ka B.P.) has further expanded the lake, although today it is deepening by only a few cm per century at the southern end. In addition, climate change in the Holocene probably played a role in lake level fluctuations. Based on our calculation of a modern hydrological budget for Lake of the Woods, reducing runoff and precipitation by 65% and increasing evaporation from the lake by 40% would end overflow and cause the level of the lake to fall below the outlets at Kenora. Because this climate change is comparable to that recorded during the mid-Holocene warming across the region, it is likely that the area covered by the lake at this time would have been less than that determined from differential isostatic rebound alone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.C. Barber A. Dyke C. Hillaire-Marcel A.E. Jennings J.T. Andrews M.W. Kerwin G. Bilodeau R. McNeely J. Southon M.D. Morehead J.M. Gagnon (1999) ArticleTitleForcing of the cold event of 8200 years ago by catastrophic drainage of Laurentide lakes Nature 400 344–348 Occurrence Handle10.1038/22504 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXkvFOgu7s%3D
L. Bengtsson J. Malm (1997) ArticleTitleUsing rainfall-runoff modeling to interpret lake level J. Paleolimnol. 18 235–248 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1007982710792
S.M. Blasco (2001) Geological history of fathom five National Marine Park over the past 15,000 years S. Parker M. Munawar (Eds) Ecology, Cultureand Conservation of a Protected Area: Fathom Five National Marine Park, CanadaEcovision World Monograph Series Backhuys Publication Leiden, Netherlands
M. Boyd G.L. Running SuffixIV K. Havholm (2003) ArticleTitlePaleoecology and geochronology of glacial Lake Hind during the Pleistocene–Holocene transition: a context for Folsom surface finds on the Canadian Prairies Geoarchaeol. Int. J. 18 583–607 Occurrence Handle10.1002/gea.10081
Boyd M., Kling H., Schnurrenberger D. and Teller J.T. 2002. Coring of West Hawk Lake meteorite impact crater: deep-water technique and initial results. International Association Great Lakes ResearchAbstracts of 35th Annual ConferenceWinnipeg, 14 pp.
W.S. Broecker J. Kennett B. Flower J.T. Teller S. Trumbore G. Bonani W. Wolfli (1989) ArticleTitleRouting of meltwater from the Laurentide Ice Sheet during the Younger Drysa cold episode Nature 341 318–321 Occurrence Handle10.1038/341318a0
A.P. Buchner L.F. Pettipas (1990) The early occupations of the Glacial Lake Agassiz basin in Manitoba; 11,500 to 7,700 B.P N.P. Lasca J. Donahue (Eds) Archaeological Geology of North America Geological Society of America BoulderColorado 51–59
P.U. Clark S.J. Marshall G.K.C. Clarke S.W. Hostetler J.M. Licciardi J.T. Teller (2001) ArticleTitleFreshwater forcing of abrupt climate change during the glaciation Science 293 283–287 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.1062517 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXlt1yhsbg%3D Occurrence Handle11452120
W.E. Dean (1993) ArticleTitlePhysical properties, mineralogy, and geochemistry of Holocene varved sediments from Elk LakeMinnesota Geol. Soc. Am. Spec. Paper 276 135–157
Encyclopedia BritannicaInc. 1999. Encyclopedia Britannica 99 CD. Multimedia Edition.
Environment Canada 2004. Water level and streamflow statistics. Website: http://www.wsc.ec.gc.ca/staflo/
InstitutionalAuthorNameFisheries and Environment Canada (1978) Hydrological Atlas of Canada Minister of Supply and Services Canada 17
Gareau P., Lewis C.F.M., Sherin A. and Macnab R. 1998. The paleo-Great Lakes, their areas and volumes from digital elevation model studies. Geological Society of America Annual Meeting, Abstracts with Programs, TorontoOntarioA-163.
S.W. Hostetler P.J. Bartlein P.U. Clark E.E. Small A.M. Solomon (2000) ArticleTitleSimulated interactions of proglacial Lake Agassiz with the Laurentide ice sheet 11,000 years ago Nature 405 334–337 Occurrence Handle10.1038/35012581 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXjs1KltLc%3D Occurrence Handle10830959
F.S. Hu H.E. Wright SuffixJr. E. Ito K. Lease (1997) ArticleTitleClimatic effects of Glacial Lake Agassiz in the midwestern United States during the last deglaciation Geology 25 207–210 Occurrence Handle10.1130/0091-7613(1997)025<0207:CEOGLA>2.3.CO;2 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXit12ktL0%3D
W.M. Last J.T. Teller (2002) ArticleTitlePaleolimnology of Lake Manitoba: the lithostratigraphic evidence Géogr. Phys. Quatern. 56 135–154
D.W. Leverington J.D. Mann J.T. Teller (2000) ArticleTitleChanges in the bathymetry and volume of glacial lake Agassiz between 11,000 and 9300 14C Yr BP Quatern. Res. 54 174–181 Occurrence Handle10.1006/qres.2000.2157
D.W. Leverington J.D. Mann J.T. Teller (2002a) ArticleTitleChanges in the bathymetry and volume of glacial lake Agassiz between 9200 and 7700 14C Yr BP Quatern. Res. 57 244–252 Occurrence Handle10.1006/qres.2001.2311
D.W. Leverington J.T. Teller J.D. Mann (2002b) ArticleTitleA GIS method for reconstruction of late Quaternary landscapes from isobase data and modern topography Comput. Sci. 28 631–639
C.F.M. Lewis P. Gareau (2001) Evaluationg Glacio-isostatic Uplift from Tilted Shoreline Data to Reconstruct the Paleo-bathymetry and Topography of the Great Lakes Basin Canadian Geophysical Union OttawaON
Lewis C.F.M. and Thorleifson L.H. 2003. Empirical modeling of regional glacio-isostatic warping for evaluating drainage system development in Red River valley and Lake Winnipeg basin. In: Brooks G.R., George S.S., Lewis C.F.M., Medioli B.E., Nielsen E., Simpson S. and Thorleifson L.H. 2003 Geoscientific insights into Red River flood hazards in Manitoba. The final report of the Red River flood project. Natural Resources Canada.
Lewis C.F.M., Blasco S.M. and Coakley J.P. 2002. Severe Dry Climate Impact on the Laurentian Great Lakes Indicated by Early to Middle Holocene Lake Closure. Internat. Assoc. Great Lakes ResearchWinnipeg. Abstracts 45th Annual Conference72 pp.
C.F.M. Lewis D.L. Forbes B.J. Todd E. Nielsen L.H. Thorleifson P.J. Henderson I. McMatin T.W. Anderson R.N. Betcher W.M. Buhay S.M. Burbidge C.J. Schröder-Adams J.W. King K. Moran C. Gibson C.A. Jarrett H.J. Kling W.L. Lockhart W.M. Last G.L.D. Matile J. Risberg C.G. Rodrigues A.M. Telka R.E. Vance (2001) ArticleTitleUplift-driven expansion delayed by middle Holocene desiccation in Lake Winnipeg, ManitobaCanada Geology 29 743–746 Occurrence Handle10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0743:UDEDBM>2.0.CO;2
Licciardi J.M., Teller J.T. and Clark P.U. 1999. Freshwater routing by the Laurentide Ice Sheet during the last deglaciation. In: Clark P., Webb R.S. and Keigwin L.D. (eds), Mechanisms of Global Climate Change at Millennial Time Scales. American Geophysical Union Monograph 112: 171–202.
B.V. Liengme (1997) A Guide to Microsoft Excel for Scientists and Engineers Arnold/John W. Wiley & Sons, Inc. London/New York
LWCB (Lake of the Woods Control Board) 2002. Managing the Water Resources of the Winnipeg River Drainage Basin. LWCB Brochurepp. 7–20.
V. Macins (1972) The Fisheries of Lake of the Woods Sport Fisheries BranchMinistry of Natural Resources Ontario 1–5
J.D. Mann D.W. Leverington J. Rayburn J.T. Teller (1999) ArticleTitleThe volume and paleobathymetry of glacial Lake Agassiz J. Paleolimnol. 22 71–80 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1008090015161
Matile G.L.D., Thorleifson L.H. and Lewis C.F.W. 2000. A model for postglacial expansion of Lake Winnipeg based on postglacial uplift. In: Todd B.J., Lewis C.F.M., Forbes D.L., Thorleifson L.H. and Erik N.1996 Lake Winnipeg Project: Cruise Report and Scientific Results. Geological Survey of Canada Open File 3470.
I. McMartin (2000) ArticleTitlePaleogeography of Lake Agassiz and regional post-glacial uplift history the Flin Flon region, central Manitoba and Saskatchewan J. Paleolimnol. 24 293–315 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1008127123310
E. Nielsen (1998) ArticleTitleLake Winnipeg coastal submergence over the last three centuries J. Paleolimnol. 19 335–342 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1007946402547
W.R. Peltier (1994) ArticleTitleIce age paleotopography Science 265 195–201
W.R. Peltier (1998) ArticleTitlePostglacial variations in the level of the sea: implications for climate dynamics and solid-earth geophysics Rev. Geophys. 36 603–689 Occurrence Handle10.1029/98RG02638
Pettipas L.F. and Buchner A.P. 1983. Paleo-indian prehistory of the glacial Lake Agassiz region in Manitoba11500 to 6500 B.P. In: Teller J.T. and Clayton L.Glacial Lake Agassiz. Geological Association of Canada Special Paper 26: 421–451.
S.C. Porter D.J. Sauchyn D.L. Delorme (1999) ArticleTitleThe ostracode record from Harris Lakesouthwestern Saskatchewan: 9200 years of local environmental change J. Paleolimnol. 21 35–44 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1008031105186
A. Schwalb W.E. Dean (1998) ArticleTitleStable isotopes and sediments from Pickerel LakeSouth DakotaUSA: a 12 ky record of environmental changes J. Paleolimnol. 20 15–30 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1007971226750
Teller J.T. 1987. Proglacial lakes and the southern margin of the Laurentide Ice Sheet. In: Ruddiman W.F. and Wright H.E. eds., North America and Adjacent Oceans during the Last Deglaciation. Decade of North American Geology K-3: 39–69.
J.T. Teller (2001) ArticleTitleFormation of large beaches in an area of rapid differential isostatic rebound: the three outlet control of Lake Agassiz Quatern. Sci. Rev. 20 1649–1659 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0277-3791(01)00007-5
Teller J.T. 2004. Controls, history, outbursts, and impact of large late-Quaternary proglacial lakes in North America: Chapter 3. In: Gilespie A., Porter S. and Atwater B. (eds), The Quaternary Period in the United States. INQUA Anniversary Volume. Elsevier, pp. 45–61.
Teller J.T. and Clayton L. 1983. An introduction to glacial Lake Agassiz. In: Teller J.T. and Clayton L. eds., Glacial Lake Agassiz. Geological Association of CanadaSpecial Paper 26: 3–5.
J.T. Teller W.M. Last (1982) ArticleTitlePedogenic horizons in post-glacial sediment of Lake ManitobaCanada Earth Surf. Proc. Land. 7 367–397 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL38XltFaqsrc%3D
J.T. Teller D.W. Leverington (2004) ArticleTitleGlacial Lake Agassiz: a 5000-year history of change and its relationship to delta 18O record of Greenland Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 116 729–742 Occurrence Handle10.1130/B25316.1 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXktlamtbc%3D
Teller J.T. and Thorleifson L.H. 1983. The Lake Agassiz-Lake Superior connection. In: Teller J.T. and Clayton L. eds., Glacial Lake Agassiz. Geological Association of Canada Special Paper 26: 261–290.
J.T. Teller D.W. Leverington J.D. Mann (2002) ArticleTitleFreshwater outbursts to the oceans from glacial Lake Agassiz and their role in climate change during the last deglaciation Quatern. Sci. Rev. 21 879–887 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0277-3791(01)00145-7
J.T. Teller J. Risberg G. Matile S. Zoltai (2000) ArticleTitlePostglacial history and paleoecology of WampumManitobaa former lagoon in the Lake Agassiz basin GSA Bull. 112 943–958
B.L. Valero-Garcés K.R. Laird S.C. Fritz K. Kelts E. Ito E.C. Grimm (1997) ArticleTitleHolocene climate in the Northern Great Plains inferred from sediment stratigraphy, stable isotopes, carbonate geochemistry, diatoms, and pollen at Moon LakeNorth Dakota Quatern. Res. 48 359–369
H.E. Wright SuffixJr. I. Stefanova J. Tian T.A. Brown F.S. Hu (2004) ArticleTitleA chronological framework for the Holocene vegetational history of central Minnesota: the Steel Lake pollen record Quatern. Sci. Rev. 23 611–626
J. Xia B.J. Haskell D.R. Engstrom E. Ito (1997) ArticleTitleHolocene climate reconstructions from tandem trace-element and stable-isotope composition of ostracodes from Coldwater lakeNorth DakotaU.S.A J. Paleolimnol. 17 85–100
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Z., Teller, J. Modeling the history of Lake of the Woods since 11,000 cal yr B.P. using GIS. J Paleolimnol 33, 483–497 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-005-0813-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-005-0813-1