Abstract
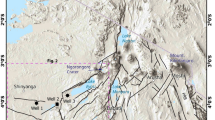
As part of English Nature’s Lakes Flagship Project to address adverse environmental impacts on selected, important lakes, a proposal has been made to dredge Aqualate Mere. The site has experienced rapid, ‘recent’ sedimentation thought to be derived from a nearby canal. The aim of this study has been to determine the recent sedimentation history of the site in order to assess the possibility of the disposal to land of its sediments and the efficacy of this form of lake restoration. A predominantly clayey silt layer was found across the lake beneath which darker, organic-rich sediments were noted. This transition may represent the input of canal-derived sediments, although it may reflect other environmental changes at this time. The radiometric dating technique employed was unable to date this sediment boundary. A further change in the characteristics of the upper part of the clayey silt layer may represent an additional influence of the canal. Heavy metal levels were modest, whereas nutrient levels were relatively high and some pesticides were detected. Topsoil erosion supplying nutrients and other compounds associated with agriculture have been an important source of the lower layers of the clayey silt sediments in particular. The highest levels of most pollutants were found in the finer sediments in the uppermost (post-1950s) part of the sediment profile. These sediments appear to reflect a change in the characteristics of the sediments of the canal, which was associated with a change in the nature of its water supply. The key geochemical properties of the sediments should not preclude the land-based disposal of dredged materials under current UK regulations for waste management. Accurate estimation of sediment quantities was limited, as the interface between the ‘recent’ and underlying sediments was not positively identified at all sample points.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ADAS 2003. Land Spread Clears Way. ADAS Environment News and Views: Spring 2003 (online). Available: http://www.adas.co.uk/envnews/Spring2003/landspread.htm. Accessed on: 19.12.03.
B.J. Alloway (1995) Cadmium B.J. Alloway (Eds) Heavy Metals in Soils Blackie Academic and Professional London 122–151
P.G. Appleby (2001) Chronostratigraphic techniques in recent sediments W.M. Last J.P. Smol (Eds) Basin Analysis, Coring and Chronological Techniques, Tracking Environmental Change Using Lake Sediments, Vol. 1 Kluwer Academic Dordrecht 171–203
P.G. Appleby P.J. Nolan D.W. Gifford M.J. Godfrey F. Oldfield N.J. Anderson R.W. Battarbee (1986) ArticleTitle210Pb dating by low background gamma counting Hydrobiologia 141 21–27
P.G. Appleby F. Oldfield (1978) ArticleTitleThe calculation of 210Pb dates assuming a constant rate of supply of unsupported 210Pb to the sediment Catena 5 1–8
P.G. Appleby N. Richardson P.J. Nolan (1992) ArticleTitleSelf absorption corrections for well-type germanium detectors Nucl. Inst. Meth. B 71 228–233
F.C. Archer I.H. Hodgson (1987) ArticleTitleTotal and extractable trace element contents of soils in England and Wales J. Soil Sci. 38 421–431
Aspinwall and Co. 1995. NRA (Severn Trent Region) hydrogeological assessment of sites of special scientific interest. Final Report: Aqualate MereSJ 770 205, Staffordshire. Unpublished Report (Ref: NA5006B). Aspinwall and Co., Shrewsbury, 10 pp.
M.T. Auer N.A. Johnson M.R. Penn S.W. Effler (1996) ArticleTitlePollutant sources, depositional environmentand the surficial sediments of Onondaga LakeNew York J. Environ. Qual. 25 46–55
D.E. Baker J.P. Senft (1995) Copper B.J. Alloway (Eds) Heavy Metals in Soils Blackie Academic and Professional London 179–205
P.W. Beales (1980) ArticleTitleThe late Devensian and Flandrian vegetational history of Crose MereShropshire New Phytol. 85 133–161
M.L. Berrow G.A. Reaves (1984) Background levels of trace elements in soils Proc. Int. Conf. Environ. Contamination CEC Consultants Ltd Edinburgh 333–340
H.J.B. Birks H.H. Birks (1980) Sampling and description of organic sediments H.J.B. Birks H.H. Birks (Eds) Quaternary Palaeoecology Edward Arnold London 37–45
J. Bloesch (1995) ArticleTitleMechanisms, measurements and importance of sediment resuspension in lakes Mar. Freshwat. Res. 46 295–304
S. Bruk (1985) Methods of computing sedimentation in lakes and reservoirs. A contribution to the International Hydrological ProgrammeIHP-2 Project A.2.6.1 UNESCO Paris
A.S. Cohen (2003) Paleolimnology. The History and Evolution of Lake Sediments Oxford University Press Oxford 500
B.E. Davies (1995) Lead B.J. Alloway (Eds) Heavy Metals in Soils Blackie Academic and Professional London 206–223
J.A. Dearing (1994) Environmental Magnetic Susceptibility: using the Bartington MS2 System Chi Publishing Kenilworth 104
J.A. Dearing (1999) Magnetic susceptibility J. Walden F. Oldfield J. Smith (Eds) Environmental Magnetism: A Practical Guide. Technical Guide 6 Quaternary Research Association London 35–62
DEFRA and Environment Agency 2002a. Soil Guideline Values for Cadmium Contamination. R&D Publication SGV3. Environment Agency, Bristol, 15 pp.
DEFRA and Environment Agency 2002b. Soil Guideline Values for Chromium Contamination. R&D Publication SGV4. Environment Agency, Bristol, 15 pp.
DEFRA and Environment Agency 2002c. Soil Guideline Values for Inorganic Mercury Contamination. R&D Publication SGV5. Environment Agency, Bristol, 16 pp.
DEFRA and Environment Agency 2002d. Soil Guideline Values for Nickel Contamination. R&D Publication SGV7. Environment Agency, Bristol, 15 pp.
Douglas I. 2000. The Tern Catchment. LOCAR Task Force Report (online). NERC. Available: http://www.nerc.ac.uk/funding/thematics/locar (MS file of Task Force Report (see sections 3 and 4)). Accessed on: 19.12.03.
English Nature 2002. Conservation of Lakes in England. English NaturePeterboroughA5 leaflet.
D. Engstrom H.E. Wright SuffixJr. (1984) Chemical stratigraphy of lake sediments E. Haworth J. Lund (Eds) Lake Sediments and Environmental History University of Minnesota Press Minneapolis 11–67
Environment Agency, in preparation. Information on land quality in England including background levels of organic and inorganic contaminants. R&D Technical Report P291. Environment Agency, Bristol.
Environmental Impacts Team 1994. Geological site documentation/management brief. Aqualate Mere SSSI, Staffordshire SJ72, English NaturePeterborough.
I.D.L. Foster J.A Dearing (1987) ArticleTitleLake-catchments and environmental chemistry: a comparative study of contemporary and historical catchment processes in midland England GeoJournal 14 285–297
R.M. Harrison (1996) Eutrophication R.M. Harrison (Eds) Pollution: Causes, Effects and Control The Royal Society of Chemistry Cambridge 72–75
R.W. Hemphill M.E. Bramley (1989) Protection of River and Canal banks. A Guide to Selection and Design CIRIA. Water Engineering Report Butterworths London 200
P.E. Hester R.M. Harrison (Eds) (1996) Agricultural Chemical and the Environment. Issues in Environmental Science and Technology 5 The Royal Society of Chemistry Cambridge 127
J. Hilton J.P. Lishman P.V. Allen (1986) ArticleTitleThe dominant processes of sediment distribution in a small, eutrophic, monomictic lake Limnol. Oceanogr. 31 125–133
S.M. Hutchinson (2003) ArticleTitleEnvironmental archives of heavy metal pollution or contaminated land? A case study of former water powered industrial sites in South YorkshireUK J. Phys. IV AFrance 107 645–648
M.A. Kamrin (Eds) (1997) Pesticide Profiles: Toxicity, Environmental Impact and Fate CRC Press New York 676
L. Keikens (1995) Zinc B.J. Alloway (Eds) Heavy Metals in Soils Blackie Academic and Professional London 284–305
W.M. Last J.P. Smol (2001) Glossary, acronyms and abbreviations W.M. Last J.P. Smol (Eds) Physical and Geochemical Methods, Tracking Environmental Change Using Lake Sediments, Vol. 2 Kluwer Academic Dordrecht 441–492
MAFF/WOAD 1998. The Soil Code – Code of Good Agricultural Practice (revised). HMSO, Norwich65 pp.
C.P. Mainstone W. Parr M. Day (2000) Phosphorous and River Ecology. Trackling Sewage Inputs English Nature Peterborough 46
S.P. McGrath P.J. Loveland (1992) The Soil Geochemical Atlas of England and Wales Blackie London 101
A.M. Moir I.E. Thornton (1989) ArticleTitleLead and cadmium in urban allotment and garden soils and vegetables in the UK Environ. Geochem. Health 11 113–120
P.J. Mulholland J.W. Elwood (1982) ArticleTitleThe role of lake and reservoir sediments as sinks in the perturbed global carbon cycle Tellus 34 490–499
F. Oldfield (1999) The rock magnetic identification of magnetic mineral and magnetic grain size assemblages J. Walden F. Oldfield J. Smith (Eds) Environmental Magnetism: A Practical Guide. Technical Guide 6 Quaternary Research Association London 98–112
P. O’Neill (1995) Arsenic B.J. Alloway (Eds) Heavy Metals in Soils Blackie Academic and Professional London 105–121
Parker B. 2003. Water supply and sewage (online). Wolverhampton History and Heritage Society. Available: http://localhistory.scit.wlv.ac.uk/articles/water/Sewage.htm. Accessed on: 19.12.03.
C.S. Reynolds (1979) ArticleTitleThe limnology of the eutrophic meres of the Shropshire–Cheshire Plain Field Studies 5 93–173
C.S. Reynolds C. Sinker (1976) ArticleTitleThe Meres: Britain’s eutrophic lakes New Sci. 71 IssueID1007 10–12
D.W. Schnurrenberg J. Russell K. Kelts (2003) ArticleTitleClassification of lacustrine sediments based on sedimentary components J. Paleolimnol. 29 141–154
Shotbolt L.S. 2002. The use of southern Pennine reservoir sediments as records of atmospheric heavy metal deposition. Ph.D. thesis. University of Salford, 350pp.
Shotbolt L.S., Hutchinson S.M. and Thomas A.D. 2000. Heavy metal deposition onto the southern Pennines, UK: obtaining an historical record from reservoir sediment. IAHS Symposium on the Role of Erosion and Sediment Transport in Nutrient and Contaminant TransferJuly 2000, WaterlooCanada.
L. Shotbolt S.M. Hutchinson A.D. Thomas (2001) ArticleTitleEstablishing sediment stratigraphy in reservoirs in the southern Pennines J. Hydrol. Sci. 46 701–715
C.A. Sinker (1962) ArticleTitleThe North Shropshire meres and mosses: a background for ecologists Field Studies 1 101–138
P.G. Sly (1973) ArticleTitleThe significance of sediment deposits in large lakes and their energy relationships Proc. Symp. Hydrol. Lakes. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 109 383–396
J.P. Smol (2002) Pollution of Lakes and Rivers. A Paleoenvironmental Perspective Arnold London 280
Soil Survey of England and Wales 1984. Soils and their uses in Midland and Western England. Soil Survey England Wales Bull. 12.
E. Steinnes (1995) Mercury B.J. Alloway (Eds) Heavy Metals in Soils Blackie Academic and Professional London 245–259
J.H. Tallis (1973) ArticleTitleThe terrestrialization of lake basins in north Cheshirewith special reference to the development of a ‘Schwingmoor’ structure J. Ecol. 61 537–567
R. Thompson F. Oldfield (1986) Environmental Magnetism Allen and Unwin London 227
M. Thomas D. Petit L. Lamberts (1984) ArticleTitlePond sediments as historical record of heavy metals fallout WaterAir Soil Pollut. 23 51–59
C.D.S. Tomlin (Eds) (1997) The Pesticide Manual. A World Compendium British Crop Protection Council Bracknell 1606
J. Troels-Smith (1955) ArticleTitleCharacterisation of unconsolidated sediments Danmarks Geologiske Undersogelse Series 4 IssueID3 38–73
S.N. Twigger C.J. Haslam (1991) ArticleTitleEnvironmental Change in Shropshire during the last 13,000 years Field Studies 7 743–758
UKAS 2004. UK Accreditation Service (online). UK Accreditation Service. Available: http://www.ukas.com. Accessed on: 2.07.04.
P.C. Van Metre E. Callender (1997) ArticleTitleWater-quality trends in White Creek Basin from 1912–1994 identified using sediment cores from White Rock Lake reservoirDallas, Texas J. Paleolimnol. 17 239–249
J. Walden F. Oldfield J. Smith (Eds) (1999) Environmental Magnetism: A Practical Guide. Technical Guide 6 Quaternary Research Association London 243
Waste Management Licensing Regulations 1994. Statutory Instrument 1994/1056.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hutchinson, S.M. The recent sedimentation history of Aqualate Mere (central England): assessing the potential for lake restoration. J Paleolimnol 33, 205–228 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-004-3991-3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-004-3991-3