Abstract
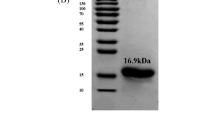
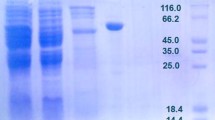
d-Arabinose 5-phosphate isomerases (APIs) catalyze the interconversion of d-ribulose 5-phosphate and d-arabinose 5-phosphate (A5P). A5P is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of 3-deoxy-d-manno-octulosonate (Kdo), an essential component of lipopolysaccharide, the lipopolysaccharide found in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. The genome of the Gram-positive pathogen Listeria monocytogenes contains a gene encoding a putative sugar isomerase domain API, Q723E8, with significant similarity to c3406, the only one of four APIs from Escherichia coli CFT073 that lacks a cystathionine-β-synthase domain. However, L. monocytogenes lacks genes encoding any of the other enzymes of the Kdo biosynthesis pathway. Realizing that the discovery of an API in a Gram-positive bacterium could provide insight into an alternate physiological role of A5P in the cell, we prepared and purified recombinant Q723E8. We found that Q723E8 does not possess API activity, but instead is a novel GPI (d-glucose 6-phosphate isomerase). However, the GPI activity of Q723E8 is weak compared with previously described GPIs. L. monocytogenes contains an ortholog of the well-studied two-domain bacterial GPI, so this maybe redundant. Based on this evidence glucose utilization is likely not the primary physiological role of Q723E8.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A5P:
-
d-Arabinose 5-phosphate
- API:
-
d-Arabinose 5-phosphate isomerase
- Bis–tris propane:
-
2,2′-(Propane-1,3-diyldiimino)bis[2-(hydroxymethyl)propane-1,3-diol]
- BLAST:
-
Basic local alignment search tool
- CBS:
-
Cystathionine-β-synthase
- F6P:
-
d-Fructose 6-phosphate
- G6P:
-
d-Glucose 6-phosphate
- GPI:
-
d-Glucose 6-phosphate isomerase
- HEPES:
-
2-[4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)piperazin-1-yl]ethanesulfonic acid
- IPTG:
-
Isopropyl β-d-1-thiogalactopyranoside
- Kdo:
-
3-Deoxy-d-manno-octulosonate
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- MES:
-
2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid
- MOPS:
-
3-(N-morpholino)propanesulfonic acid
- MW:
-
Molecular weight
- Rf:
-
Relative mobility
- PTS:
-
Phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase
- Ru5P:
-
d-Ribulose 5-phosphate
- SIS:
-
Sugar isomerase
- Tris:
-
2-Amino-2-hydroxymethyl-propane-1,3-diol
References
Murray EGD, Webb RA, Swann MBR (1926) A disease of rabbits characterised by a large mononuclear leucocytosis, caused by a hitherto undescribed bacillus Bacteruim Monocytogenes. J Pathol Microbiol 29:407–439
Gray ML, Killenger AH (1966) Listeria monocytogenes and listeric infections. Bacteriol Rev 30:309–382
Gandhi M, Chikindas ML (2007) Listeria: a foodborne pathogen that knows how to survive. Int J Food Microbiol 113:1–15
Hain T, Ghai R, Billion A, Kuenne CT, Steinweg C, Izar B, Mohamed W, Abu Mraheil M, Domann E, Schaffrath S, Kärst U, Goesmann A, Oehm S, Pühler A, Merkl R, Vorwerk S, Glase P, Garrido P, Rusinol C, Buchrieser C, Goebel W, Chakraborty T (2012) Comparitive genomics and transcriptomics of lineages I, II, and III strains of Listeria monocytogenes. BMC Genomics 13:144
Lingu B, Ricke SC, Johnson MG (2009) Growth, survival, proliferation and pathogenesis of Listeria monocytogenes under low oxygen or anaerobic conditions: a review. Anaerobe 15:7–17
Pine L, Malcolm GB, Brooks JB, Daneshvar MI (1988) Physiological studies on the growth and utilization of sugars by Listeria species. Can J Microbiol 35:245–254
Mosberg JA, Yep A, Meredith TC, Smith S, Wang P-F, Holler TP, Mobley HLT, Woodard RW (2011) A unique arabinose 5-phosphate isomerase found within a genomic island associated with the uropathogenicity of Escherichia coli CFT073. J Bacteriol 193:2981–2988
Bateman A (1999) The SIS domain: a phosphosugar-binding domain. Trends Biochem Sci 24:94–95
Meredith TC, Woodard RW (2003) Escherichia coli YrbH is a d-arabinose 5-phosphate isomerase. J Biol Chem 278:32771–32777
Meredith TC, Woodard RW (2005) Identification of GutQ from Escherichia coli as a d-arabinose 5-phosphate isomerase. J Bacteriol 187:6936–6942
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 1st edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Tabor S (1985) A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. PNAS 82:1074–1078
Sandoval JM, Arenas FA, Vásquez CC (2011) Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase protects Escherichia coli from tellurite-mediated oxidative stress. PLoS One 6:e25573
Joint Center for Structural Genomics Crystal structure of a putative sugar isomerase (lmof2365_0531) from Listeria monocytogenes str.4b f2365 at 1.60 Å resolution (PDB ID: 3FXA)
Gourlay LJ, Sommaruga S, Nardini M, Sperandeo P, Dehò G, Polissi A, Bolognesi M (2010) Probing the active site of the sugar isomerase domain from E. coli arabinose-5-phosphate isomerase via X-ray crystallography. Protein Sci 19:2430–2439
Meredith TC, Woodard RW (2006) Characterization of Escherichia coli d-arabinose 5-phosphate isomerase encoded by kpsF: implications for group 2 capsule biosynthesis. Biochem J 395:427–432
Yamada M, Yamada Y, Saier MH Jr (1987) Physical and genetic characterization of the glucitol operon in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 169:2990–2994
Nelson KE (2004) Whole genome comparisons of serotype 4b and 1/2a strains of the food-borne pathogen Listeria monocytogenes reveal new insights into the core genome components of this species. Nucleic Acids Res 32:2386–2395
Scheer M, Grote A, Chang A, Schomburg I, Munaretto C, Rother M, Sohngen C, Stelzer M, Thiele J, Schomburg D (2010) BRENDA, the enzyme information system in 2011. Nucleic Acids Res 39:D670–D676
Meredith TC, Aggarwal P, Mamat U, Lindner B, Woodard RW (2006) Redefining the requisite lipopolysaccharide structure in Escherichia coli. ACS Chem Biol 1:33–42
Eidels L, Rick PD, Stimler NP, Osborn MJ (1974) Transport of d-arabinose-5-phosphate and d-sedoheptulose-7-phosphate by the hexose phosphate transport system of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol 119:138–143
Hansen T, Schlichting B, Felgendreher M, Schonheit P (2005) Cupin-type phosphoglucose isomerases (Cupin-PGIs) constitute a novel metal-dependent PGI family representing a convergent line of PGI Evolution. J Bacteriol 187:1621–1631
Katz LA (1996) Transkingdom transfer of the phosphoglucose isomerase gene. J Mol Evol 43:453–459
Romick TL, Fleming HP, McFeeters RF (1996) Aerobic and anaerobic metabolism of Listeria monocytogenes in defined glucose medium. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:304–307
Acknowledgments
This work was supported, in part, by National Institutes of Health Grant AI-061531 (to R.W.W.). The authors thank Jim Windak and Paul Lennon of the University of Michigan Department of Chemistry Mass Spectroscopy facility for performing the LC–MS analysis of recombinant lmof2365_0531, and Ted Houston of the University of Michigan Department of Geology’s W.M. Keck Elemental Geochemistry Laboratory for performing the metals analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cech, D.L., Wang, PF., Holt, M.C. et al. A Novel Glucose 6-Phosphate Isomerase from Listeria monocytogenes . Protein J 33, 447–456 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10930-014-9577-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10930-014-9577-7