Abstract
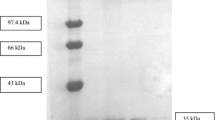
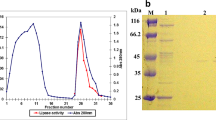
The objective of the present study was the isolation, molecular cloning and biochemical characterization of a thermophilic organic solvent-resistant lipase from Bacillus sp. DR90. The lipase gene was expressed in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) using pET-28a(+) vector. The purification of recombinant lipase was conducted by nickel affinity chromatography and its biochemical properties were determined. The lipase sequence with an ORF of 639 bp contains the conserved pentapeptide Ala-His-Ser-Met-Gly. His-tagged recombinant lipase had a specific activity of 1,126 U/mg with a molecular mass of 26.8 kDa. The cloned lipase was optimally active at pH 8.0 and 75 °C representing high stability in broad ranges of temperature and pH. High performance liquid chromatography was used to determine the major compounds released during the lipase-catalyzed reaction of p-nitrophenyl derivatives as well as the substrate specificity. The purified lipase showed high compatibility towards various organic solvents, surfactants and commercial solid/liquid detergents; therefore the recombinant DR90 lipase could be considered as a probable candidate for future applications, predominantly in detergent processing industries.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HPLC:
-
High performance liquid chromatography
- ILs:
-
Ionic liquids
- LB:
-
Luria–Bertani
- PMSF:
-
Phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride
- IPTG:
-
Isopropyl-b-d-thiogalactopyranoside
- IMAC:
-
Immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography
- pNPB:
-
p-Nitrophenyl butyrate
- pNPA:
-
p-Nitrophenyl acetate
- pNPP:
-
p-Nitrophenyl palmitate
- pNP:
-
p-Nitrophenol
- PPL:
-
Porcine pancreatic lipase
- ORF:
-
Open reading frame
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulphate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- EDTA:
-
Ethylene diaminetetraacetic acid
- DTNB:
-
55′-Dithiobis-2-nitrobenzoic acid
- DTT:
-
Dithiothreitol
- CTAB:
-
Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide
- [EMIm][Br]:
-
1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide
- [BMIm][Br]:
-
1-n-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide
- [HMIm][Br]:
-
1-Hexyl-3-methylimidazoliumbromide
- [BMIm][Cl]:
-
1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride
References
Guncheva M, Zhiryakova D (2011) Catalytic properties and potential applications of Bacillus lipases. J Mol Catal B Enzym 68:1–21
Gupta R, Gupta N, Rathi P (2004) Bacterial lipases: an overview of production, purification and biochemical properties. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64:763–781
Joseph B, Ramteke PW, Thomas G (2008) Cold active microbial lipases: some hot issues and recent developments. Biotechnol Adv 26:457–470
Ghosh PK, Saxena RK, Gupta R, Yadav RP, Davidson S (1996) Microbial lipases: production and applications. Sci Prog 79:119–157
Hasan F, Ali Shah A, Hameed A (2006) Industrial applications of microbial lipases. Enzyme Microb Technol 39:235–251
Kapoor M, Gupta MN (2012) Lipase promiscuity and its biochemical applications. Process Biochem 47:555–569
Doukyua N, Ogino H (2010) Organic solvent-tolerant enzymes. Biochem Eng J 48:270–282
Moniruzzaman M, Nakashima K, Kamiya N, Masahiro G (2010) Recent advances of enzymatic reactions in ionic liquids. Biochem Eng J 48:295–314
Reetz MT (2002) Lipases as practical biocatalysts. Curr Opin Chem Biol 6:145–150
Hasan F, Ali Shah A, Javed S, Hameed A (2010) Enzymes used in detergents: lipases. Afr J Biotechnol 9:4836–4844
Asoodeh A, Alemi A, Heydari A, Akbari J (2013) Purification and biochemical characterization of an acidophilic amylase from a newly isolated Bacillus sp. DR90. Extremophiles 17:339–348
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Nielsen H, Engelbrecht J, Brunak S, von Heijne G (1997) Identification of prokaryotic and eukaryotic signal peptides and predication of their cleavage sites. Protein Eng 10:1–6
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Simpson R (2004) Purifying proteins for proteomics: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Cho AR, Yoo SK, Kim EJ (2000) Cloning, sequencing and characterization of thermostable lipase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 186:235–238
Ebrahimpour A, Rahman RNZRA, Basri M, Salleh AB (2011) High level expression and characterization of a novel thermostable, organic solvent tolerant, 1,3-regioselective lipase from Geobacillus sp. strain ARM. Bioresour Technol 102:6972–6981
Cherif S, Mnif S, Hadrich F, Abdelkafi S, Sayadi S (2011) A newly high alkaline lipase: an ideal choice for application in detergent formulations. Lipids Health Dis 10:221–228
Tjalsma H, Bolhuis A, Jongbloed JDH, Bron S, Van Dijl JM (2000) Signal peptide-dependent protein transport in Bacillus subtilis: a genome-based survey of the secretome. Microbiol Mol Biol 63:515–547
Arpigny JL, Jaeger KE (1999) Bacterial lipolytic enzymes: classification and properties. Biochem J 343:177–183
Wang CS, Hartsuck JA (1993) A bile salt-activated lipase. A multiple function lipolytic enzyme. Biochem Biophys Acta 1166:1–19
Dartois V, Baulard A, Schanck K, Colson C (1992) Cloning, nucleotide sequence and expression in Escherichia coli of a lipase gene from Bacillus subtilis 168. Biochim Biophys Acta 1131:253–260
Laane C, Boeren S, Vos K, Veeger C (1987) Rules of optimization of biocatalysis inorganic solvent. Biotechnol Bioeng 3:81–87
Kragl U, Eckstein M, Kaftzik N (2002) Enzyme catalysis in ionic liquids. Curr Opin Biotech 13:565–571
Ruiz C, Blanco A, Javier Pastor FI, Diaz P (2002) Analysis of Bacillus megaterium lipolytic system and cloning of LipA, a novel subfamily I.4 bacterial lipase. FEMS Microbiol Lett 217:263–267
Shi B, Wu W, Wen J, Shi Q, Wu S (2010) Cloning and expression of a lipase gene from Bacillus Subtilis FS1403 in Escherichia coli. Ann Microbiol 60:399–404
Sabri S, Rahman RNZRA, Chor Leow T, Basri M, Salleh AB (2009) Secretory expression and characterization of a highly Ca2+-activated thermostable L2 lipase. Protein Expr Puri 68:161–166
Zhang H, Zhang F, Li Z (2009) Gene analysis, optimized production and property of marine lipase from Bacillus pumilus B106 associated with South China Sea sponge Halichondria rugosa. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:1267–1274
Riaz M, Ali Shah A, Hameed A, Hasan F (2010) Characterization of lipase produced by Bacillus sp. FH5in immobilized and free state. Ann Microbiol 60:169–175
Shariff FM, Rahman RNZRA, Basri M, Salleh AB (2011) A newly isolated thermostable lipase from Bacillus sp. Int J Mol Sci 12:2917–2934
Ventura SPM, Santos LDF, Saraiva JA, Coutinho JAP (2012) Concentration effect of hydrophilic ionic liquids on the enzymatic activity of Candida antarctica lipase B. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:2303–2310
Mukherjeea AK, Borahb M, Rai SK (2009) To study the influence of different components of fermentable substrates on induction of extracellular α-amylase synthesis by Bacillus subtilis DM-03 in solid-state fermentation and exploration of feasibility for inclusion of α-amylase in laundry detergent formulations. Biochem Eng J 43:149–156
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by Grant number 91058286 from Iran National Science Foundation (INSF) and is gratefully acknowledged by the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asoodeh, A., Emtenani, S. & Emtenani, S. Expression and Biochemical Characterization of a Thermophilic Organic Solvent-Tolerant Lipase from Bacillus sp. DR90. Protein J 33, 410–421 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10930-014-9574-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10930-014-9574-x