Abstract
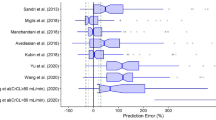
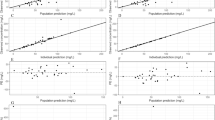
Polymyxin B (PMB) is considered a last-line treatment for multidrug-resistant (MDR) gram-negative bacterial infections. Model-informed precision dosing with population pharmacokinetics (PopPK) models could help to individualize PMB dosing regimens and improve therapy. However, the external prediction ability of the established PopPK models has not been fully elaborated. This study aimed to systemically evaluate eleven PMB PopPK models from ten published literature based on a new independent population, which was divided into four different populations, patients with liver dysfunction, kidney dysfunction, liver and kidney dysfunction, and normal liver and kidney function. The whole data set consisted of 146 patients with 391 PMB concentrations. The prediction- and simulation-based diagnostics and Bayesian forecasting were conducted to evaluate model predictability. In the overall evaluation process, none of the models exhibited satisfactory predictive ability in both prediction- and simulation-based diagnostic simultaneously. However, the evaluation of the models in the subgroup of patients with normal liver and kidney function revealed improved predictive performance compared to those with liver and/or kidney dysfunction. Bayesian forecasting demonstrated enhanced predictability with the incorporation of two to three prior observations. The external evaluation highlighted a lack of consistency between the prediction results of published models and the external validation dataset. Nonetheless, Bayesian forecasting holds promise in improving the predictive performance of the models, and feedback from therapeutic drug monitoring is crucial in optimizing individual dosing regimens.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All datasets analyzed in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material.
References
Yuan Z, Tam VH (2008) Polymyxin B: a new strategy for multidrug-resistant Gram-negative organisms. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 17:661–668. https://doi.org/10.1517/13543784.17.5.661
Cai Y, Lee W, Kwa AL (2015) Polymyxin B versus colistin: an update. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 13:1481–1497. https://doi.org/10.1586/14787210.2015.1093933
Avedissian SN, Liu J, Rhodes NJ, Lee A, Pais GM, Hauser AR, Scheetz MH (2019) A review of the clinical pharmacokinetics of polymyxin B. Antibiot (Basel) 8:E31. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8010031
Nang SC, Azad MAK, Velkov T, Zhou QT, Li J (2021) Rescuing the last-line polymyxins: achievements and challenges. Pharmacol Rev 73:679–728. https://doi.org/10.1124/pharmrev.120.000020
Zavascki AP, Goldani LZ, Li J, Nation RL (2007) Polymyxin B for the treatment of multidrug-resistant pathogens: a critical review. J Antimicrob Chemother 60:1206–1215. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkm357
Orwa JA, Govaerts C, Busson R, Roets E, Van Schepdael A, Hoogmartens J (2001) Isolation and structural characterization of polymyxin B components. J Chromatogr A 912:369–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0021-9673(01)00585-4
Stansly PG, Shepherd RG, White HJ (1947) Polymyxin: a new chemotherapeutic agent. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp 81:43–54
Darwich AS, Ogungbenro K, Vinks AA, Powell JR, Reny J-L, Marsousi N, Daali Y, Fairman D, Cook J, Lesko LJ, McCune JS, Knibbe C, de Wildt SN, Leeder JS, Neely M, Zuppa AF, Vicini P, Aarons L, Johnson TN, Boiani J, Rostami-Hodjegan A (2017) Why has model-informed precision dosing not yet become common clinical reality? Lessons from the past and a roadmap for the future. Clin Pharmacol Ther 101:646–656. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpt.659
Buclin T, Gotta V, Fuchs A, Widmer N, Aronson J (2012) Monitoring drug therapy. Br J Clin Pharmacol 73:917–923. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2125.2012.04237.x
Landersdorfer CB, Wang J, Wirth V, Chen K, Kaye KS, Tsuji BT, Li J, Nation RL (2018) Pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics of systemically administered polymyxin B against Klebsiella pneumoniae in mouse thigh and lung infection models. J Antimicrob Chemother 73:462–468. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkx409
Tsuji BT, Pogue JM, Zavascki AP, Paul M, Daikos GL, Forrest A, Giacobbe DR, Viscoli C, Giamarellou H, Karaiskos I, Kaye D, Mouton JW, Tam VH, Thamlikitkul V, Wunderink RG, Li J, Nation RL, Kaye KS (2019) International consensus guidelines for the optimal use of the polymyxins: endorsed by the American College of Clinical Pharmacy (ACCP), European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious diseases (ESCMID), Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), International Society for anti-infective pharmacology (ISAP), society of critical Care Medicine (SCCM), and Society of Infectious diseases pharmacists (SIDP). Pharmacotherapy 39:10–39. https://doi.org/10.1002/phar.2209
Gonzalez D, Rao GG, Bailey SC, Brouwer KLR, Cao Y, Crona DJ, Kashuba ADM, Lee CR, Morbitzer K, Patterson JH, Wiltshire T, Easter J, Savage SW, Powell JR (2017) Precision dosing: public health need, proposed framework, and anticipated impact. Clin Transl Sci 10:443–454. https://doi.org/10.1111/cts.12490
Nation RL, Forrest A (2019) Clinical pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and toxicodynamics of polymyxins: implications for therapeutic use. Adv Exp Med Biol 1145:219–249. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-16373-0_15
Thamlikitkul V, Dubrovskaya Y, Manchandani P, Ngamprasertchai T, Boonyasiri A, Babic JT, Tam VH (2017) Dosing and pharmacokinetics of polymyxin B in patients with renal insufficiency. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 61:e01337–e01316. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.01337-16
Wang P, Zhang Q, Zhu Z, Pei H, Feng M, Sun T, Yang J, Zhang X (2021) Comparing the population pharmacokinetics of and acute kidney injury due to polymyxin B in Chinese patients with or without renal insufficiency. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 65:e01900–e01920. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.01900-20
Yu X-B, Jiao Z, Zhang C-H, Dai Y, Zhou Z-Y, Han L, Wen X, Sheng C-C, Lin G-Y, Pan J-Y (2021) Population pharmacokinetic and optimization of polymyxin B dosing in adult patients with various renal functions. Br J Clin Pharmacol 87:1869–1877. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcp.14576
Li Y, Deng Y, Zhu Z-Y, Liu Y-P, Xu P, Li X, Xie Y-L, Yao H-C, Yang L, Zhang B-K, Zhou Y-G (2021) Population pharmacokinetics of polymyxin B and dosage optimization in renal transplant patients. Front Pharmacol 12:727170. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.727170
Ye Q, Wang Q, Chen W, Zhang R, Chen Z, Li P, Zhang X, Zhan Q, Wang C (2022) The population pharmacokinetics and dose optimization of polymyxin B in critically ill patients with or without extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. J Clin Pharm Ther. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpt.13711
Wang P, Zhang Q, Zhu Z, Feng M, Sun T, Yang J, Zhang X (2020) Population pharmacokinetics and limited sampling strategy for therapeutic drug monitoring of polymyxin B in Chinese patients with multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections. Front Pharmacol 11:829. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.00829
Wang P, Zhang Q, Feng M, Sun T, Yang J, Zhang X (2021) Population pharmacokinetics of polymyxin B in obese patients for resistant gram-negative infections. Front Pharmacol 12:754844. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.754844
Wang P, Xing H, Zhang F, Liu S, Lu Y, Zhang X, Yang J, Sun T (2022) Population pharmacokinetics of polymyxin B in critically ill patients receiving continuous venovenous haemofiltration. Int J Antimicrob Agents 60:106599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2022.106599
Wang PL, Liu P, Zhang QW, Yuan WH, Wang D, Zhang XJ, Yang J (2022) Population pharmacokinetics and clinical outcomes of polymyxin B in paediatric patients with multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections. J Antimicrob Chemother Dkac 265. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkac265
Sandri AM, Landersdorfer CB, Jacob J, Boniatti MM, Dalarosa MG, Falci DR, Behle TF, Bordinhão RC, Wang J, Forrest A, Nation RL, Li J, Zavascki AP (2013) Population pharmacokinetics of intravenous polymyxin B in critically ill patients: implications for selection of dosage regimens. Clin Infect Dis 57:524–531. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/cit334
Miglis C, Rhodes NJ, Avedissian SN, Kubin CJ, Yin MT, Nelson BC, Pai MP, Scheetz MH (2018) Population pharmacokinetics of polymyxin B in acutely ill adult patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 62:e01475–e01417. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.01475-17
Manchandani P, Thamlikitkul V, Dubrovskaya Y, Babic JT, Lye DC, Lee LS, Tam VH (2018) Population pharmacokinetics of polymyxin B. Clin Pharmacol Ther 104:534–538. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpt.981
Kubin CJ, Nelson BC, Miglis C, Scheetz MH, Rhodes NJ, Avedissian SN, Cremers S, Yin MT (2018) Population pharmacokinetics of intravenous polymyxin B from clinical samples. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 62:e01493–e01417. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.01493-17
Crass RL, Al Naimi T, Wen B, Souza E, Murray S, Pai MP, Jia S (2021) Pharmacokinetics of polymyxin B in hospitalized adults with cystic fibrosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 65:e0079221. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00792-21
Avedissian SN, Miglis C, Kubin CJ, Rhodes NJ, Yin MT, Cremers S, Prickett M, Scheetz MH (2018) Polymyxin B pharmacokinetics in adult cystic fibrosis patients. Pharmacotherapy 38:730–738. https://doi.org/10.1002/phar.2129
Zhao C-Y, Jiao Z, Mao J-J, Qiu X-Y (2016) External evaluation of published population pharmacokinetic models of tacrolimus in adult renal transplant recipients: external evaluation of popPK models of tacrolimus. Br J Clin Pharmacol 81:891–907. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcp.12830
Konecki C, Feliu C, Cazaubon Y, Giusti D, Tonye-Libyh M, Brixi H, Cadiot G, Biron A, Djerada Z (2021) External evaluation of Population Pharmacokinetic models and bayes-based dosing of Infliximab. Pharmaceutics 13:1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13081191
Hwang MF, Beechinor RJ, Wade KC, Benjamin DK, Smith PB, Hornik CP, Capparelli EV, Duara S, Kennedy KA, Cohen-Wolkowiez M, Gonzalez D (2017) External evaluation of two fluconazole infant population pharmacokinetic models. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 61:e01352–e01317. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.01352-17
Schräpel C, Kovar L, Selzer D, Hofmann U, Tran F, Reinisch W, Schwab M, Lehr T (2021) External model performance evaluation of twelve infliximab population pharmacokinetic models in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Pharmaceutics 13:1368. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13091368
Hanafin PO, Nation RL, Scheetz MH, Zavascki AP, Sandri AM, Kwa AL, Cherng BPZ, Kubin CJ, Yin MT, Wang J, Li J, Kaye KS, Rao GG (2021) Assessing the predictive performance of population pharmacokinetic models for intravenous polymyxin B in critically ill patients. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol 10:1525–1537. https://doi.org/10.1002/psp4.12720
Li Y-Q, Chen K-F, Ding J-J, Tan H-Y, Yang N, Lin Y-Q, Wu C-F, Xie Y-L, Yang G-P, Liu J-J, Pei Q (2021) External evaluation of published population pharmacokinetic models of polymyxin B. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 77:1909–1917. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-021-03193-y
Tam V, Lee L, Ng T-M, Lim T-P, Cherng B, Adewusi H, Hee K, Ding Y, Chung S, Ling L-M, Chlebicki P, Kwa A, Lye D (2020) Performance of population pharmacokinetic models in predicting polymyxin B exposures. Microorganisms 8:1814. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8111814
Zhang B, Li X, Chen Y, Chen B, Cheng Y, Lin H, Que W, Liu M, Zhou L, Zhang H, Qiu H, Wu C (2023) Determination of polymyxin B in human plasma and epithelial lining fluid using LC-MS/MS and its clinical application in therapeutic drug monitoring. J Pharm Biomed Anal 227:115291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2023.115291
Macpherson IR, He Y, Palmieri C (2021) Eribulin, child-pugh score, and liver-function tests: lessons from pivotal breast cancer studies 301 and 305. Breast Cancer Res 23:33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-021-01407-w
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER), Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER) (2003) Guidance for Industry: Pharmacokinetics in Patients with Impaired Hepatic Function: Study Design, Data Analysis, and Impact on Dosing and Labeling. In: U.S. Food and Drug Administration. https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/pharmacokinetics-patients-impaired-hepatic-function-study-design-data-analysis-and-impact-dosing-and. Accessed 31 Oct 2022
European Medicines Agency, Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) (2005) Guideline evaluation pharmacokinetics medicinal products patients impaired hepatic function. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/guideline-evaluation-pharmacokinetics-medicinal-products-patients-impaired-hepatic-function_en.pdf. Accessed 31 Oct 2022
Nguyen THT, Mouksassi M, Holford N, Al-Huniti N, Freedman I, Hooker AC, John J, Karlsson MO, Mould DR, Pérez Ruixo JJ, Plan EL, Savic R, van Hasselt JGC, Weber B, Zhou C, Comets E, Mentré F, for the Model Evaluation Group (2017) Model evaluation of continuous data pharmacometric models: metrics and graphics. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol 6:87–109. https://doi.org/10.1002/psp4.12161. of the International Society of Pharmacometrics (ISoP) Best Practice Committee
Sheiner LB, Beal SL (1981) Some suggestions for measuring predictive performance. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 9:503–512. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01060893
Broeker A, Nardecchia M, Klinker KP, Derendorf H, Day RO, Marriott DJ, Carland JE, Stocker SL, Wicha SG (2019) Towards precision dosing of vancomycin: a systematic evaluation of pharmacometric models for Bayesian forecasting. Clin Microbiol Infect 25:1286.e1–1286.e7
Guo T, van Hest RM, Roggeveen LF, Fleuren LM, Thoral PJ, Bosman RJ, van der Voort PHJ, Girbes ARJ, Mathot RAA, Elbers PWG (2019) External evaluation of population pharmacokinetic models of vancomycin in large cohorts of intensive care unit patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 63:e02543–e02518. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.02543-18
Bergstrand M, Hooker AC, Wallin JE, Karlsson MO (2011) Prediction-corrected visual predictive checks for diagnosing nonlinear mixed-effects models. AAPS J 13:143–151. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-011-9255-z
Comets E, Brendel K, Mentré F (2008) Computing normalised prediction distribution errors to evaluate nonlinear mixed-effect models: the npde add-on package for R. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 90:154–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2007.12.002
Zavascki AP, Goldani LZ, Cao G, Superti SV, Lutz L, Barth AL, Ramos F, Boniatti MM, Nation RL, Li J (2008) Pharmacokinetics of intravenous polymyxin B in critically ill patients. Clin Infect Dis 47:1298–1304. https://doi.org/10.1086/592577
Manchandani P, Zhou J, Ledesma KR, Truong LD, Chow DS-L, Eriksen JL, Tam VH (2016) Characterization of polymyxin B biodistribution and disposition in an animal model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 60:1029–1034. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.02445-15
Abdelraouf K, He J, Ledesma KR, Hu M, Tam VH (2012) Pharmacokinetics and renal disposition of polymyxin B in an animal model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56:5724–5727. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.01333-12
Droździk M, Oswald S, Droździk A (2020) Extrahepatic drug transporters in liver failure: focus on kidney and gastrointestinal tract. Int J Mol Sci 21:5737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21165737
Lu X, Chan T, Xu C, Zhu L, Zhou QT, Roberts KD, Chan H-K, Li J, Zhou F (2016) Human oligopeptide transporter 2 (PEPT2) mediates cellular uptake of polymyxins. J Antimicrob Chemother 71:403–412. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkv340
Avedissian SN, Scheetz MH (2021) Does renal function matter for polymyxin B? Br J Clin Pharmacol 87:2629–2632. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcp.14675
Aarons L, Balant LP, Mentre F, Morselli PL, Rowland M, Steimer JL, Vozeh S (1996) Practical experience and issues in designing and performing population pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic studies. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 49:251–254. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00226323
Aarons L, Ogungbenro K (2010) Optimal design of pharmacokinetic studies. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 106:250–255. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-7843.2009.00533.x
Ogungbenro K, Aarons L (2008) How many subjects are necessary for population pharmacokinetic experiments? Confidence interval approach. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 64:705–713. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-008-0493-7
Tam VH, Hou J, Kwa AL, Prince RA (2009) Comment on: Development and validation of a reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography assay for polymyxin B in human plasma. J Antimicrob Chemother 63:627–628 ; author reply 628–629. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkn483
He J, Ledesma KR, Lam W-Y, Figueroa DA, Lim T-P, Chow DS-L, Tam VH (2010) Variability of polymyxin B major components in commercial formulations. Int J Antimicrob Agents 35:308–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2009.11.005
Funding
This study was supported by the Joint Funds for the Innovation of Science and Technology, Fujian Province (Grant No. 2019Y9051), Guiding Project of Science and Technology, Fujian Province (Grant No. 2021Y0019), and Fujian Natural Science Foundation Project (Grant No. 2021J01761).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, H. Q., H. Z., and Q. W.; methodology, X. L., Y. C., and B. Z.; software, X. L.; validation, B. Z. and Y. C.; formal analysis, B. C. and L. Z.; investigation, Y. C. and H. L.; resources, Y. C. and Y. H.; data curation, X. L.; writing—original draft preparation, X. L.; writing—review and editing, H. Q.; visualization, X. L.; supervision, H. Z., M. L. and H. Q.; project administration, W. Q.; funding acquisition, Y. C. and H. Q. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics statement
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the Fujian Medical University Union Hospital Research and Ethics Committee on 31-Mar-2021 (No. 2021KJT052). Patients or their relatives provided written informed consent to participate in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Cheng, Y., Zhang, B. et al. A systematic evaluation of population pharmacokinetic models for polymyxin B in patients with liver and/or kidney dysfunction. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10928-024-09916-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10928-024-09916-9