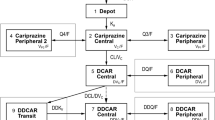
A population model was developed with the aim to simultaneously describe risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone pharmacokinetics; to obtain estimates for pharmacokinetic parameters and associated inter- and intra-individual variability of risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone; and to evaluate the influence of patient demographic characteristics and other factors on risperidone, 9-hydroxyrisperidone, and active moiety pharmacokinetics. Data were obtained from 407 patients enrolled in four Phase 1 (serial blood sampling) and three Phase 3 trials (sparse sampling), representing dosage regimens ranging from 4 mg single dose to flexible 1–6 mg once daily. A pharmacokinetic model with two-compartment submodels for risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone disposition and a sequential zero- and first-order absorption pathway was selected based on prior knowledge. A mixture model was incorporated due to CYP2D6 polymorphism of risperidone conversion to 9-hydroxyrisperidone. Patient characteristics tested as potential covariates were: age, sex, race, body weight, lean body mass, body mass index, creatinine clearance, liver function laboratory parameters, study, and carbamazepine comedication. The quasi-clearance of active moiety (the sum of risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone) was simulated and linear regression performed to identify significant covariates. The selected pharmacokinetic model described the plasma concentration-time profiles for risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone quite well and was able to determine each patient’s phenotype. Covariates significantly affecting the pharmacokinetics were carbamazepine comedication, and study because the proportion of patients assigned to the intermediate metabolizer status decreased from single to multiple dosing while the proportion assigned to extensive metabolizer status increased. Covariates with limited and clinically irrelevant effects on active moiety concentrations were patient phenotype, race, and total protein. Carbamazepine also decreased active moiety concentrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leysen J.E., Janssen P.M., Gommeren W., Wynants J., Pauwels P.J., Janssen P.A. (1992) In vitro and in vivo receptor binding and effects on monoamine turnover in rat brain regions of the novel antipsychotics risperidone and ocaperidone. Mol. Pharmacol. 41:494–508
Hirschfeld R.M., Keck P.E., Jr., Kramer M., Karcher K., Canuso C., Eerdekens M., Grossman F. (2004) Rapid antimanic effect of risperidone monotherapy: a 3-week multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Am. J. Psychiatry 161:1057–1065
Smulevich A.B., Khanna S., Eerdekens M., Karcher K., Kramer M., Grossman F. (2005) Acute and continuation risperidone monotherapy in bipolar mania: a 3-week placebo-controlled trial followed by a 9-week double-blind trial of risperidone and haloperidol. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 15:75–84
Sachs G.S., Grossman F., Ghaemi S.N., Okamoto A., Bowden C.L. (2002) Combination of a mood stabilizer with risperidone or haloperidol for treatment of acute mania: a double-blind, placebo-controlled comparison of efficacy and safety. Am. J. Psychiatry 159:1146–1154
Yatham L.N., Grossman F., Augustyns I., Vieta E., Ravindran A. (2003) Mood stabilisers plus risperidone or placebo in the treatment of acute mania. International, double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Br. J. Psychiatry 182:141–147
Bowden C.L., Myers J.E., Grossman F., Xie Y. (2004) Risperidone in combination with mood stabilizers: a 10-week continuation phase study in bipolar I disorder. J. Clin. Psychiatry 65:707–714
Vieta E., Goikolea J.M., Corbella B., Benabarre A., Reinares M., Martinez G., Fernandez A., Colom F., Martinez-Aran A., Torrent C. (2001) Risperidone safety and efficacy in the treatment of bipolar and schizoaffective disorders: results from a 6-month, multicenter, open study. J. Clin. Psychiatry 62:818–825
Yatham L.N., Binder C., Riccardelli R., Leblanc J., Connolly M., Kusumakar V. (2003) Risperidone in acute and continuation treatment of mania. Int. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 18:227–235
Heykants J., Huang M.L., Mannens G., Meuldermans W., Snoeck E., Van Beijsterveldt L., Van Peer A., Woestenborghs R. (1994) The pharmacokinetics of risperidone in humans: a summary. J. Clin. Psychiatry 55(Suppl May):13–17
Byerly M.J., DeVane C.L. (1996) Pharmacokinetics of clozapine and risperidone: a review of recent literature. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 16:177–187
Huang M.L., Van Peer A., Woestenborghs R., De Coster R., Heykants J., Jansen A.A., Zylicz Z., Visscher H.W., Jonkman J.H. (1993) Pharmacokinetics of the novel antipsychotic agent risperidone and the prolactin response in healthy subjects. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 54:257–268
Ereshefsky L. (1996) Pharmacokinetics and drug interactions: update for new antipsychotics. J. Clin. Psychiatry 57(Suppl 11):12–25
Spina E., Avenoso A., Facciola G., Salemi M., Scordo M.G., Giacobello T., Madia A.G., Perucca E. (2000) Plasma concentrations of risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone: effect of comedication with carbamazepine or valproate. Ther. Drug Monit. 22:481–485
Yasui-Furukori N., Hidestrand M., Spina E., Facciola G., Scordo M.G., Tybring G. (2001) Different enantioselective 9-hydroxylation of risperidone by the two human CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 enzymes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 29:1263–1268
A. Boeckman, L. Sheiner, and S. Beal. NONMEM Users Guides. University of at San Francisco, San Francisco, 1992–1999.
Mannens G., Huang M.L., Meuldermans W., Hendrickx J., Woestenborghs R., Heykants J. (1993) Absorption, metabolism, and excretion of risperidone in humans. Drug Metab. Dispos. 21:1134–1141
Kirchheiner J., Nickchen K., Bauer M., Wong M.L., Licinio J., Roots I., Brockmoller J. (2004) Pharmacogenetics of antidepressants and antipsychotics: the contribution of allelic variations to the phenotype of drug response. Mol. Psychiatry 9:442–473
Sheiner L.B., Beal S.L. (1981) Some suggestions for measuring predictive performance. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm. 9:503–512
Jung S.M., Kim K.-A., Cho H.-K., Jung I.G., Park P.-W., Byun W.T., Park J.-Y. (2005) Cytochrome P450 3A inhibitor itraconazole affects plasma concentrations of risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone in schizophrenic patients. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 78:520–528
Lippert H., Lehman H.P. (1978) SI Units in Medicine. Urban & Schwarzenberg, Baltimore-Munich
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vermeulen, A., Piotrovsky, V. & Ludwig, E.A. Population Pharmacokinetics of Risperidone and 9-Hydroxyrisperidone in Patients with Acute Episodes Associated with Bipolar I Disorder. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 34, 183–206 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10928-006-9040-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10928-006-9040-2