Abstract
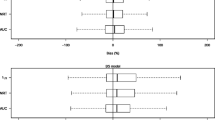
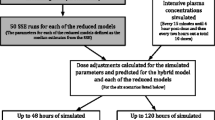
During the course of therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM), doses are adjusted to attain a target concentration range and a correlation between clearance (CL) and dose is introduced. In population pharmacokinetic analyses of such TDM data, CL has frequently been modeled as a function of dose. This paper demonstrates by simulation methodology that the TDM process does indeed introduce a correlation between dose and CL which can be interpreted as a nonlinearity. Using literature values of carbamazepine pharmacokinetics, three steady-state concentrations were simulated following a standard 1000 mg total daily dose (TDD) regimen in 100 in silico subjects. A set of clinical rules was established to adjust the TDD based on these three concentrations, as might be done in the clinical setting. Another set of concentrations using these TDM-derived TDDs for each subject (600–1600 mg) was simulated. A standard population pharmacokinetic analysis of the post-TDM data was conducted using NONMEM. This process was replicated 100 times to estimate the type II error rate. When CL was modeled without TDD, plots of WRES versus PRED demonstrated a clear pattern, as did the delta plots of CL (CL minus TVCL) versus TDD, suggesting the covariate TDD should be incorporated into the model. After TDD was included in the model for CL, the objective function value decreased by an average of 75.7 (p < 0.001). In addition, the inter-individual variability in CL expressed as a coefficient of variation decreased by an average of 9.9% and the diagnostic plots improved. Although CL was simulated to be independent of TDD, it was identified as an important covariate using standard approaches in a simulated TDM setting in 100% of the replicated simulation studies. The TDM process introduces a correlation between CL and TDD that can be misinterpreted as nonlinearity in the system
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Yukawa (1995) ArticleTitlePopulation-Based Investigation of Carbamazepine Relative Clearance Using Routine Clinical Pharmacokinetic Data in Japan Clin Drug Invest 10 29–39 Occurrence Handle10.1056/NEJM196702162760703
E. Yukawa (1995) ArticleTitleA feasibility study of the multiple-peak approach for pharmacokinetic screening: population-based investigation of valproic acid relative clearance using routine clinical pharmacokinetic data J. Pharm. Pharmacol 47 1048–52 Occurrence Handle8932693 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28Xht1Sjt70%3D
E. Yukawa T. Aoyama (1996) ArticleTitleDetection of carbamazepine drug interaction by multiple peak approach screening using routine clinical pharmacokinetic data J. Clin. Pharmacol 36 752–9 Occurrence Handle8877681 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XmtVSrsr4%3D
E. Yukawa H. To S. Ohdo S. Higuchi T. Aoyama (1997) ArticleTitlePopulation-based investigation of valproic acid relative clearance using nonlinear mixed effects modeling: influence of drug-drug interaction and patient characteristics J. Clin. Pharmacol 37 1160–7 Occurrence Handle9506012 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c7ms12isA%3D%3D
E. Yukawa T. Honda S. Ohdo S. Higuchi T. Aoyama (1997) ArticleTitleDetection of carbamazepine-induced changes in valproic acid relative clearance in man by simple pharmacokinetic screening J. Pharm. Pharmacol 49 751–6 Occurrence Handle9379350 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXmt1Wqs7k%3D
E. Yukawa T. Hokazono A. Funakoshi M. Yukawa S. Ohdo S. Higuchi R. Ichimaru T. Makit K. Matsunaga M. Anai Y. Goto (2000) ArticleTitleEpidemiologic investigation of the relative clearance of haloperidol by mixed-effect modeling using routine clinical pharmacokinetic data in Japanese patients J. Clin. Psychopharmacol 20 685–90 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00004714-200012000-00016 Occurrence Handle11106142 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXos1OlsLo%3D
E. Yukawa T. Hokazono M. Yukawa R. Ichimaru T. Maki K. Matsunaga S. Ohdo M. Anai S. Higuchi Y. Goto (2002) ArticleTitlePopulation pharmacokinetics of haloperidol using routine clinical pharmacokinetic data in Japanese patients Clin. Pharmacokinet 41 153–9 Occurrence Handle11888334 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XjtFakt7c%3D
Z. Jiao M.K. Zhong X.J. Shi M. Hu J.H. Zhang (2003) ArticleTitlePopulation pharmacokinetics of carbamazepine in Chinese epilepsy patients Ther. Drug. Monit 25 279–86 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00007691-200306000-00005 Occurrence Handle12766553 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXktlyrsr4%3D
Z. Jiao X.J. Shi Z.G. Zhao M.K. Zhong (2004) ArticleTitlePopulation pharmacokinetic modeling of steady state clearance of carbamazepine and its epoxide metabolite from sparse routine clinical data J. Clin. Pharm. Ther 29 247–56 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1365-2710.2004.00557.x Occurrence Handle15153086 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXmsVOgu70%3D
D.M. Reith W.D. Hooper J. Parke B. Charles (2001) ArticleTitlePopulation pharmacokinetic modeling of steady state carbamazepine clearance in children, adolescents, and adults J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm 28 79–92 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXit1ertro%3D
B. Summers R.S. Summers (1989) ArticleTitleCarbamazepine clearance in paediatric epilepsy patients Influence of body mass, dose, sex and co-medication. Clin. Pharmacokinet 17 208–16 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3c%2FjtFarsQ%3D%3D
Desoky E E.S., Fuseau E., E.L.D.A.S. and Cosson V., Pharmacokinetic modelling of valproic acid from routine clinical data in Egyptian epileptic patients. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 59:783–90 (2004).
E. Yukawa (1996) ArticleTitleOptimisation of antiepileptic drug therapy The importance of serum drug concentration monitoring. Clin. Pharmacokinet 31 120–30 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XltlantLw%3D
Winter M.E.,, Koda -Kimble M.A.,, and Young L.Y.,. Basic clinical pharmacokinetics Applied Therapeutics, Vancouver, Wa., 1994.
N.M. Graves R.C. Brundage Y. Wen G. Cascino E. So P. Ahman J. Rarick S. Krause I.E. Leppik (1998) ArticleTitlePopulation pharmacokinetics of carbamazepine in adults with epilepsy Pharmacotherapy 18 273–81 Occurrence Handle9545146 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXkt1Kjtb0%3D
L.B. Sheiner B. Rosenberg. V.V. Marathe (1977) ArticleTitleEstimation of population characteristics of pharmacokinetic parameters from routine clinical data J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm 5 445–79 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01061728 Occurrence Handle925881 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE1cXksVOiuw%3D%3D
H.M. Park S.S. Kang Y.B. Lee D.J. Shin O.N. Kim S.B. Lee D.S. Yim (2002) ArticleTitlePopulation pharmacokinetics of intravenous valproic acid in Korean patients J. Clin. Pharm. Ther 27 419–25 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2710.2002.00440.x Occurrence Handle12472981 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXksV2qsA%3D%3D
Martin E.S. 3rd, Crismon M.L.,, and Godley P.J.,. Postinduction carbamazepine clearance in an adult psychiatric population. Pharmacotherapy 11:296–302 (1991).
A.H. Kumps (1981) ArticleTitleDose-dependency of the ratio between carbamazepine serum level and dosage in patients with epilepsy Ther. Drug. Monit 3 271–4 Occurrence Handle7324091 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL38XksV2gsro%3D
Y. Suzuki S. Cox J. Hayes P.D. Walson (1991) ArticleTitleCarbamazepine age-dose ratio relationship in children Ther. Drug. Monit 13 201–8 Occurrence Handle1926272 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK38%2FitlCnuw%3D%3D
M.F. Delgado Iribarnegaray D. Santo Bueldga M.J. Garcia Sanchez M.J. Otero A.C. Falcao A. Dominguez-Gil (1997) ArticleTitleCarbamazepine population pharmacokinetics in children: mixed-effect models Ther. Drug. Monit 19 132–9 Occurrence Handle9108639 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2s3mt1amtA%3D%3D
B. Blanco-Serrano M.J. Otero D. Santos-Buelga M.J. Garcia -Sanchez J. Serrano A. Dominguez-Gil (1999) ArticleTitlePopulation estimation of valproic acid clearance in adult patients using routine clinical pharmacokinetic data Biopharm. Drug Dispos 20 233–40 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1099-081X(199907)20:5<233::AID-BDD179>3.0.CO;2-5 Occurrence Handle10594867 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXks1Wruw%3D%3D
B.B. Serrano M.J. Garcia Sanchez M.J. Otero D.S. Buelga J. Serrano A. Dominguez-Gil (1999) ArticleTitleValproate population pharmacokinetics in children J. Clin. Pharm. Ther 24 73–80 Occurrence Handle10319910 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXislKrsbg%3D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahn, J.E., Birnbaum, A.K. & Brundage, R.C. Inherent Correlation Between Dose and Clearance in Therapeutic Drug Monitoring Settings: Possible Misinterpretation in Population Pharmacokinetic Analyses. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 32, 703–718 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10928-005-0083-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10928-005-0083-6