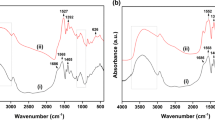
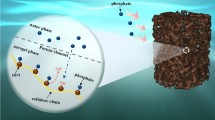
Abstract
Hydrogels with high mechanical properties and excellent adsorption capacity are expected in wastewater treatment. Herein, 3D porous hydrogels were prepared by free radical copolymerization using carboxymethyl cellulose nanofibers (CNFs) grafted with N, S atom doped carbon quantum dots (N, S-CDs) and 1-Allyl-2-thiourea. N, S-CDs introduced in the hydrogel can uniformly disperse and increase the adsorption site of Hg(II) by grafting method. Meanwhile, the good mechanical strength of N, S-CDs is beneficial to improve the hydrogel mechanical properties. The experimental results show that the 3D porous hydrogel has great swelling properties (SR = 875.22 g/g) and mechanical properties (elastic modulus = 86.77 MPa). Moreover, compared with the hydrogel without N, S-CDs, the 3D porous hydrogel has an excellent Hg(II) adsorption capacity (943.77 mg/g). In addition, the 3D porous hydrogel has outstanding regeneration performance. The adsorption capacity accounts for 94.6% of the first adsorption capacity after 5 cycles. Therefore, the 3D porous hydrogels are considered as a promising adsorbent for the hazardous Hg(II) absorption.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time as the data also forms part of an ongoing study.
References
Zhang SZ, Liu CZ, Yuan YK, Fan MH, Zhang DD, Wang DF, Xu Y (2020) Selective, highly efficient extraction of Cr(III), Pb(II) and Fe(III) from complex water environment with a tea residue derived porous gel adsorbent. Bioresour Technol 311:123520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123520
Zhou GY, Luo JM, Liu CB, Chu L, Ma JH, Tang YH, Zeng ZB, Luo SL (2016) A highly efficient polyampholyte hydrogel sorbent based fixed-bed process for heavy metal removal in actual industrial effluent. Water Res 89:151–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.11.053
Dai DH, Yang J, Wang Y, Yang YW (2021) Recent progress in functional materials for selective detection and removal of mercury(II) Ions. Adv Funct Mater 31:2006168. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202006168
Velempini T, Pillay K (2019) Sulphur functionalized materials for Hg(II) adsorption: a review. J Environ Chem Eng 7:103350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103350
Jiang CL, Wang XH, Wang GH, Hao C, Li X, Li TH (2019) Adsorption performance of a polysaccharide composite hydrogel based on crosslinked glucan/chitosan for heavy metal ionsM. Compos Part B 169:45–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.03.082
Luo MK, Lin H, Li B, Dong YB, He YH, Wang L (2018) A novel modification of lignin on corncob-based biochar to enhance removal of cadmium from water. Bioresour Technol 259:312–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.03.075
Ghodbane I, Hamdaoui O (2008) Removal of mercury(II) from aqueous media using eucalyptus bark: kinetic and equilibrium studies. J Hazard Mater 160:301–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.02.116
Blue LY, Jana P, Atwood DA (2010) Aqueous mercury precipitation with the synthetic dithiolate, BDTH2. Fuel 89:1326–1330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2009.10.031
Gao XP, Li MY, Zhao YM, Zhang Y (2019) Mechanistic study of selective adsorption of Hg2+ ion by porous alginate beads. Chem Eng J 378:122096. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122096
Santhana Krishna Kumar A, Jiang S-J (2015) Preparation and characterization of exfoliated graphene oxide-l-cystine as an effective adsorbent of Hg(II) adsorption. RSC Adv 5:6294–6304. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA12564A
Alizadehgiashi M, Khuu N, Khabibullin A, Henry A, Tebbe M, Suzuki T, Kumacheva E (2018) Nanocolloidal hydrogel for heavy metal scavenging. ACS Nano 12:8160–8168. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b03202
Zhang M, Wan Y, Wen YX, Li CG, Kanwal A (2020) A novel Poly(vinyl alcohol)/carboxymethyl cellulose/yeast double degradable hydrogel with yeast foaming and double degradable property. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 187:109765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109765
Zhu XH, Yang RD, Gao WH, Li MW (2017) Sulfur-modified chitosan hydrogel as an adsorbent for removal of Hg(II) from effluents. Fibers Polym 18:1229–1234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-017-7046-6
Ge HC, Du J (2020) Selective adsorption of Pb(II) and Hg(II) on melamine-grafted chitosan. Int J Biol Macromol 162:1880–1887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.070
Yang SP, Fu SY, Liu H, Zhou YM, Li XY (2011) Hydrogel beads based on carboxymethyl cellulose for removal heavy metal ions. J Appl Polym Sci 119:1204–1210. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.32822
Im W, Rajabi Abhari A, Youn HJ, Lee HL (2018) Morphological characteristics of carboxymethylated cellulose nanofibrils: the effect of carboxyl content. Cellulose 25:5781–5789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1993-y
Li DF, Ye YX, Li DR, Li XY, Mu CD (2016) Biological properties of dialdehyde carboxymethyl cellulose crosslinked gelatin-PEG composite hydrogel fibers for wound dressings. Carbohydr Polym 137:508–514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.11.024
Bahadoran Baghbadorani N, Behzad T, Etesami N, Heidarian P (2019) Removal of Cu2+ ions by cellulose nanofibers-assisted starch-g-poly(acrylic acid) superadsorbent hydrogels. Compos B 176:107084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107084
Garemark J, Yang X, Sheng X, Cheung O, Sun LC, Berglund LA, Li YY (2020) Top-down approach making anisotropic cellulose aerogels as universal substrates for multifunctionalization. ACS Nano 14:7111–7120. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.0c01888
Li L, Liu L, Qing Y, Zhang Z, Yan N, Wu YQ, Tian CH (2018) Stretchable alkaline poly(acrylic acid) electrolyte with high ionic conductivity enhanced by cellulose nanofibrils. Electrochim Acta 270:302–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.03.088
Li XB, Chai CF, Zhang YL, Wang YK, Lv JJ, Bian W, Choi MMF (2020) Microwave synthesis of nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon dots for the selective detection of Hg2+ and glutathione. Opt Mater 99:109559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2019.10955
Ni P, Li QY, Xu CF, Lai HQ, Bai Y, Chen TF (2019) Optical properties of nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon dots and their applicability as fluorescent probes for living cell imaging. Appl Surf Sci 494:377–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.07.196
Demirci S, McNally AB, Ayyala RS, Lawson LB, Sahiner N (2020) Synthesis and characterization of nitrogen-doped carbon dots as fluorescent nanoprobes with antimicrobial properties and skin permeability. J Drug Delivery Sci Technol 59:101889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2020.101889
Sarkar N, Sahoo G, Das R, Prusty G, Swain SK (2017) Carbon quantum dot tailored calcium alginate hydrogel for pH responsive controlled delivery of vancomycin. Eur J Pharm Sci 109:359–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2017.08.015
Wang BB, Jin JC, Xu ZQ, Jiang ZW, Li X, Jiang FL, Liu Y (2019) Single-step synthesis of highly photoluminescent carbon dots for rapid detection of Hg2+ with excellent sensitivity. J Colloid Interface Sci 551:101–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.04.088
Abraham WL, Demirci S, Wypyski MS, Ayyala RS, Bhethanabotla VR, Lawson LB, Sahiner N (2022) Biofilm inhibition and bacterial eradication by C-dots derived from polyethyleneimine-citric acid. Colloids Surf B 217:112704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2022.112704
Sutekin SD, Sahiner M, Suner SS, Demirci S, Güven O, Sahiner N (2021) Poly(vinylamine) derived N-doped C-dots with antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities. C 7(2):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/c7020040
Yu SJ, Chen K, Wang F, Zhu YF, Zhang XH (2017) Polymer composite fluorescent hydrogel film based on nitrogen-doped carbon dots and their application in the detection of Hg2+ ions. Luminescence 32:970–977. https://doi.org/10.1002/bio.3279
Guo ZW, Li Q, Li ZY, Liu C, Liu XR, Liu YY, Dong GL, Lan T, Wei Y (2020) Fabrication of efficient alginate composite beads embedded with N-doped carbon dots and their application for enhanced rare earth elements adsorption from aqueous solutions. J Colloid Interface Sci 562:224–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.12.030
Saber-Samandari S, Gazi M (2015) Pullulan based porous semi-IPN hydrogel: synthesis, characterization and its application in the removal of mercury from aqueous solution. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 51:143–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2015.01.013
Lv QY, Hu XS, Zhang XL, Huang LY, Liu ZP, Sun GX (2019) Highly efficient removal of trace metal ions by using poly(acrylic acid) hydrogel adsorbent. Mater Des 181:107934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2019.107934
Hu ZH, Omer AM, Ouyang XK, Yu D (2018) Fabrication of carboxylated cellulose nanocrystal/sodium alginate hydrogel beads for adsorption of Pb(II) from aqueous solution. Int J Biol Macromol 108:149–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.11.171
Qu D, Zheng M, Du P, Zhou Y, Zhang LG, Li D, Tan HQ, Zhao Z, Xie ZG, Sun ZC (2013) Highly luminescent S N co-doped graphene quantum dots with broad visible absorption bands for visible light photocatalysts. Nanoscale 5:12272–12277. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR04402E
Şahiner N, Malcı S, Çelikbıçak Ö, Kantoğlu Ö, Salih B (2005) Radiation synthesis and characterization of new hydrogels based on acrylamide copolymers cross-linked with 1-allyl-2-thiourea. Radiat Phys Chem 74:76–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2005.02.002
Jiang HB, Yang YR, Lin ZK, Zhao BC, Wang J, Xie J, Zhang AP (2020) Preparation of a novel bio-adsorbent of sodium alginate grafted polyacrylamide/graphene oxide hydrogel for the adsorption of heavy metal ion. Sci Total Environ 744:140653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140653
Muliwa AM, Oyewo OA, Maity A (2023) Recent progress on the removal of aqueous mercury by carbon-based adsorbents: a review. Inorg Chem Commun 156:111207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2023.111207
Yue Y, Gu J, Han J, Wu Q, Jiang J (2021) Effects of cellulose/salicylaldehyde thiosemicarbazone complexes on PVA based hydrogels: portable, reusable, and high-precision luminescence sensing of Cu2+. J Hazard Mater 401:123796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123798
Sun Y, Yang C, Fu Y, Guo T, Yan G, Hu J (2023) Sulfur-containing adsorbent made by inverse vulcanization of sulfur/oleylamine/potato starch for efficient removal of Hg(II) ions. J Environ Chem Eng 11(3):109806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2023.109806
Xu X, Yang C, Guo Q, Sun Y, Chen Q, Hu J (2023) Efficient mercury(II) removal by corn bract/dopamine@ZnS composites. Environ Sci Pollut R 30(42):96554–96561. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29253-7
Ma M, Chen R, Feng L (2023) Efficient and selective removal of mercury ions from aqueous solution by 2,5-dimercaptothiadiazole covalently grafted chitosan derivative. Int J Biol Macromol 251:126272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.126272
Zhao W, Zhang Z, Xin Y, Xiao R, Gao F, Wu H, Wang W, Guan Q, Lu K (2024) Na2S-modified biochar for Hg(II) removal from wastewater: a techno-economic assessment. Fuel 356:129641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2023.129641
Ryu M, Lee MY, Song MG, Baeck S-H, Shim SE, Qian Y (2020) Highly selective removal of Hg(II) ions from aqueous solution using thiol-modified porous polyaminal-networked polymer. Sep Purif Technol 250:117120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117120
Lin G, Zeng B, Liu X, Li J, Zhang B, Zhang L (2022) Enhanced performance of functionalized MOF adsorbents for efficient removal of anthropogenic Hg(II) from water. J Clean Prod 381:134766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134766
Gao X, Liu B, Zhao X (2023) Thiol-decorated defective metal-organic framework for effective removal of mercury(II) ion. Chemosphere 317:137891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.137891
Lu JR, Wu XN, Li Y, Liang YH, Cui WQ (2019) Facile fabrication of 3D graphene-silica hydrogel composite for enhanced removal of mercury ions. Nanomaterials 9:314. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9030314
Zhao BC, Jiang HB, Lin ZK, Xu SF, Xie J, Zhang AP (2019) Preparation of acrylamide/acrylic acid cellulose hydrogels for the adsorption of heavy metal ions. Carbohydr Polym 224:115022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115022
Das R, Giri S, Muliwa AM, Maity A (2017) High-performance Hg(II) removal using thiol-functionalized polypyrrole (PPy/MAA) composite and effective catalytic activity of Hg(II)-adsorbed waste material. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:7524–7536. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b00477
Tran L, Wu PX, Zhu YJ, Liu S, Zhu NW (2015) Comparative study of Hg(II) adsorption by thiol- and hydroxyl-containing bifunctional montmorillonite and vermiculite. Appl Surf Sci 356:91–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.08.038
Suner SS, Demirci S, Sutekin DS, Yilmaz S, Sahiner N (2022) Thiourea-isocyanate-based covalent organic frameworks with tunable surface charge and surface area for methylene blue and methyl orange removal from aqueous media. Micromachines 13(6):983. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13060938
Hanif Z, Lee S, Hussain Qasim G, Ardiningsih I, Kim J-A, Seon J, Han S, Hong S, Yoon M-H (2016) Polypyrrole multilayer-laminated cellulose for large-scale repeatable mercury ion removal. J Mater Chem A 4:12425–12433. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TA01219A
Wang W, Chen M, Chen X, Wang J (2014) Thiol-rich polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane as a novel adsorbent for mercury adsorption and speciation. Chem Eng J 242:62–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.12.063
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22068033).
Funding
This work was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 22068033), Provincial Key Research and Development Project (Grant No. 2021DB004) and Tianshan Talent Training Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XY: conceptualization, investigation, methodology, writing—original draft. XM: data curation, investigation, visualization, software. ZP: data curation, investigation, visualization. XM: data curation, investigation, software. XJ: investigation, visualization, software. YL: investigation, methodology, supervision, project administration, writing—review & editing. ZW: conceptualization, supervision, resources, writing—review & editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, X., Ma, X., Pan, Z. et al. Preparation of 3D Cellulose-Carbon Quantum Dots Hydrogels for Adsorption of Mercury from Aqueous Solution. J Polym Environ (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-023-03172-7
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-023-03172-7