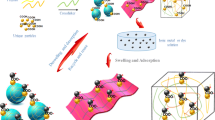
Abstract
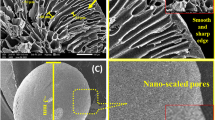
Magnetic particles with active groups on their surfaces can be applied to wastewater purification to remove harmful ions, but the insufficient number of active groups on their surfaces tends to limit their removal rate of ions. Herein, we grafted different generations of dendritic macromolecular polyamidoamine (PAMAM) onto the magnetic chitosan microspheres (MCS) using ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) as core (MCEPs) for the removal of Cu (II). Firstly, 7 μm-sized MCS with good dispersibility was prepared by adjusting conditions such as glacial acetic acid content, emulsifier content and raw material ratio. Secondly, the effect of MCEPs generation, pH and contact time on the adsorption capacity were investigated. The adsorption experiments showed that the MCEPs had a high adsorption capacity, when the adsorbent was the second generation of MCEP (MCEP G2.0), the maximum adsorption capacity can up to 702.9 mg/g and the adsorption process can be completed in 60 min. Moreover, among various isotherms models, MCEP G2.0 was well-fitted by Langmuir adsorption isotherm. Also, adsorption kinetic studies proved that the adsorption mechanism of MCEP G2.0 adsorbent followed the pseudo-second-order kinetic model, demonstrating that the process was chemisorption. The adsorbent has renewability as well, after five adsorption cycles, its adsorption efficiency was still higher than 80%. Therefore, the adsorbent showed a superior adsorption capacity and renewability to remove Cu (II).
Graphical Abstract















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Ab Hamid NH, Bin Mohd Tahir MIH, Chowdhury A et al (2022) The current state-of-art of copper removal from wastewater: a review. Water 14(19):3086. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14193086
Zhu G, Yue K, Ni X et al (2023) The types of microplastics, heavy metals, and adsorption environments control the microplastic adsorption capacity of heavy metals. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(33):80807–80816. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28131-6
Carvalho Barros GKG, Melo RPF, Barros Neto ELD (2018) Removal of copper ions using sodium hexadecanoate by ionic flocculation. Sep Purif Technol 200:294–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.01.062
Liu Y, Wang H, Cui Y et al (2023) Removal of copper ions from wastewater: a review. Int J Environ Res Public Health 20(5):3885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2021.05.013
Awual MR (2015) A novel facial composite adsorbent for enhanced copper(II) detection and removal from wastewater. Chem Eng J 266:368–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.12.094
Hamilton T, Peng Y (2021) The removal of lead from chalcopyrite surfaces in relation to radionuclide removal from copper minerals. Powder Technol 389:63–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2021.05.013
Lenka SP, Shaikh WA, Owens G et al (2021) Removal of copper from water and wastewater using dolochar. Water Air Soil Pollut 232(5):167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05135-x
Ghorbani F, Kamari S, Askari F et al (2021) Production of nZVI–Cl nanocomposite as a novel eco–friendly adsorbent for efficient As(V) ions removal from aqueous media: adsorption modeling by response surface methodology. Sustain Chem Pharm 21:100437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2021.100437
Awual MR (2017) New type mesoporous conjugate material for selective optical copper(II) ions monitoring & removal from polluted waters. Chem Eng J 307:85–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.07.110
Sessarego S, Rodrigues SCG, Xiao Y et al (2019) Phosphonium-enhanced chitosan for Cr(VI) adsorption in wastewater treatment. Carbohydr Polym 211:249–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.02.003
Sheikh MC, Hasan MM, Hasan MN et al (2023) Toxic cadmium(II) monitoring and removal from aqueous solution using ligand-based facial composite adsorbent. J Mol Liq 389:122854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2023.122854
Kubra KT, Salman MS, Hasan MN et al (2021) Utilizing an alternative composite material for effective copper(II) ion capturing from wastewater. J Mol Liq 336:116325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.116325
Jawad AH, Rangabhashiyam S, Abdulhameed AS et al (2022) Process optimization and adsorptive mechanism for reactive blue 19 dye by magnetic crosslinked chitosan/MgO/Fe3O4 biocomposite. J Polym Environ 30(7):2759–2773. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-022-02382-9
Kamari S, Ghorbani F (2017) Synthesis of magMCM-41 with rice husk silica as cadmium sorbent from aqueous solutions: parameters’ optimization by response surface methodology. Environ Technol 38(12):1562–1579. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2016.1237557
Jawad AH, Hameed BH, Abdulhameed AS (2023) Synthesis of biohybrid magnetic chitosan-polyvinyl alcohol/MgO nanocomposite blend for remazol brilliant blue R dye adsorption: solo and collective parametric optimization. Polym Bull 80(5):4927–4947. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-022-04294-z
Malek NNA, Jawad AH, Ismail K et al (2021) Fly ash modified magnetic chitosan-polyvinyl alcohol blend for reactive orange 16 dye removal: adsorption parametric optimization. Int J Biol Macromol 189:464–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.08.160
Liu M, Wang H, Sun H et al (2023) Preparation of magnetic metal-organic framework for adsorption of microcystin-RR. Algal Res 70:102984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2023.102984
Gu H, Zhou X, Lyu S et al (2020) Magnetic nanocellulose-magnetite aerogel for easy oil adsorption. J Colloid Interface Sci 560:849–856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.10.084
Kamari S, Ghorbani F, Sanati AM (2019) Adsorptive removal of lead from aqueous solutions by amine–functionalized magMCM-41 as a low–cost nanocomposite prepared from rice husk: modeling and optimization by response surface methodology. Sustain Chem Pharm 13:100153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2019.100153
Malek NNA, Jawad AH, Abdulhameed AS et al (2020) New magnetic Schiff’s base-chitosan-glyoxal/fly ash/Fe3O4 biocomposite for the removal of anionic azo dye: an optimized process. Int J Biol Macromol 146:530–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.01.020
Sanati AM, Kamari S, Ghorbani F (2019) Application of response surface methodology for optimization of cadmium adsorption from aqueous solutions by Fe3O4@SiO2@APTMS core–shell magnetic nanohybrid. Surf Interfaces 17:100374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2019.100374
Pylypchuk IV, Kołodyńska D, Kozioł M et al (2016) Gd-DTPA adsorption on chitosan/magnetite nanocomposites. Nanoscale Res Lett 11(1):168. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-016-1363-3
Velasco-Garduño O, Martínez ME, Gimeno M et al (2020) Copper removal from wastewater by a chitosan-based biodegradable composite. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(23):28527–28535. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07560-2
Kloster GA, Valiente M, Marcovich NE et al (2020) Adsorption of arsenic onto films based on chitosan and chitosan/nano-iron oxide. Int J Biol Macromol 165:1286–1295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.09.244
Lou T, Yan X, Wang X (2019) Chitosan coated polyacrylonitrile nanofibrous mat for dye adsorption. Int J Biol Macromol 135:919–925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.06.008
Saheed IO, Oh WD, Suah FBM (2021) Chitosan modifications for adsorption of pollutants—a review. J Hazard Mater 408:124889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124889
Vakili M, Deng S, Shen L et al (2019) Regeneration of chitosan-based adsorbents for eliminating dyes from aqueous solutions. Sep Purif Rev 48(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/15422119.2017.1406860
Waliullah RM, Rehan AI, Awual ME et al (2023) Optimization of toxic dye removal from contaminated water using chitosan-grafted novel nanocomposite adsorbent. J Mol Liq 388:122763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2023.122763
Wu R, Abdulhameed AS, Jawad AH et al (2023) Development of a chitosan/nanosilica biocomposite with arene functionalization via hydrothermal synthesis for acid red 88 dye removal. Int J Biol Macromol 252:126342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.126342
Molatlhegi O, Alagha L (2017) Adsorption characteristics of chitosan grafted copolymer on kaolin. Appl Clay Sci 150:342–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2017.09.032
Zhang X, Shi X, Ma L et al (2019) Preparation of chitosan stacking membranes for adsorption of copper ions. Polymers 11(9):1463. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11091463
Liu H, Zhang F, Peng Z (2019) Adsorption mechanism of Cr(VI) onto GO/PAMAMs composites. Sci Rep 9(1):3663. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-40344-9
Wong KH, Guo Z, Law M-K et al (2023) Functionalized PAMAM constructed nanosystems for biomacromolecule delivery. Biomater Sci 11(5):1589–1606. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2BM01677J
Qin W, Qian G, Tao H et al (2019) Adsorption of Hg(II) ions by PAMAM dendrimers modified attapulgite composites. React Funct Polym 136:75–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2019.01.005
Sun H, Zhan J, Chen L et al (2023) Preparation of CTS/PAMAM/SA/Ca2+ hydrogel and its adsorption performance for heavy metal ions. Appl Surf Sci 607:155135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.155135
Sun H, Ji Z, He Y et al (2022) Preparation of PAMAM modified PVDF membrane and its adsorption performance for copper ions. Environ Res 204:111943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111943
Cheng R, Kang M, Zhuang S et al (2019) Adsorption of Sr(II) from water by mercerized bacterial cellulose membrane modified with EDTA. J Hazard Mater 364:645–653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.10.083
Liang M, Guo H, Xiu W (2020) Arsenite oxidation and arsenic adsorption on birnessite in the absence and the presence of citrate or EDTA. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(35):43769–43785. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10292-3
Luan L, Tang B, Liu Y et al (2022) Direct synthesis of sulfur-decorating PAMAM dendrimer/mesoporous silica for enhanced Hg(II) and Cd(II) adsorption. Langmuir 38(2):698–710. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.1c02547
Pistone A, Iannazzo D, Celesti C et al (2020) Chitosan/PAMAM/hydroxyapatite engineered drug release hydrogels with tunable rheological properties. Polymers 12(4):754. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040754
Beltrame KK, Cazetta AL, De Souza PSC et al (2018) Adsorption of caffeine on mesoporous activated carbon fibers prepared from pineapple plant leaves. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 147:64–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.08.034
Li X, Wu G, Chen J et al (2017) Low-crystallinity molybdenum sulfide nanosheets assembled on carbon nanotubes for long-life lithium storage: unusual electrochemical behaviors and ascending capacities. Appl Surf Sci 392:297–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.09.055
Ghoochian M, Panahi HA, Sobhanardakani S et al (2019) Synthesis and application of Fe3O4/SiO2/thermosensitive/PAMAM-CS nanoparticles as a novel adsorbent for removal of tamoxifen from water samples. Microchem J 145:1231–1240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2018.12.004
Hu X, Li G, Lin Y (2018) A novel high-capacity immunoadsorbent with PAMAM dendritic spacer arms by click chemistry. New J Chem 42(19):15726–15732. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NJ02142B
Islam MA, Ali I, Karim SMA et al (2019) Removal of dye from polluted water using novel nano manganese oxide-based materials. J Water Process Eng 32:100911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.100911
Crini G, Peindy HN, Gimbert F et al (2007) Removal of C.I. Basic Green 4 (Malachite Green) from aqueous solutions by adsorption using cyclodextrin-based adsorbent: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Sep Purif Technol 53(1):97–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2006.06.018
He J, Lin R, Long H et al (2015) Adsorption characteristics of amino acids on to calcium oxalate. J Colloid Interface Sci 454:144–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.02.014
Ren B, Wang K, Zhang B et al (2019) Adsorption behavior of PAMAM dendrimers functionalized silica for Cd(II) from aqueous solution: experimental and theoretical calculation. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 101:80–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2019.04.037
Li H, Niu Y, Xue Z et al (2019) Adsorption property and mechanism of PAMAM dendrimer/silica gel hybrids for Fe(III) and Ag(I) from N, N-dimethylformamide. J Mol Liq 273:305–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.10.039
Deng H, Mao Z, Xu H et al (2019) Synthesis of fibrous LaFeO3 perovskite oxide for adsorption of Rhodamine B. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 168:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.09.056
Wang Y, Lu Q (2020) Dendrimer functionalized nanocrystalline cellulose for Cu(II) removal. Cellulose 27(4):2173–2187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02919-7
Ilaiyaraja P, Singha Deb AK, Sivasubramanian K et al (2013) Adsorption of uranium from aqueous solution by PAMAM dendron functionalized styrene divinylbenzene. J Hazard Mater 250–251:155–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.01.040
Ma J, Xia M, Zhu S et al (2020) A new alendronate doped HAP nanomaterial for Pb2+, Cu2+ and Cd2+ effect absorption. J Hazard Mater 400:123143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123143
Sun H, Zhang X, He Y et al (2019) Preparation of PVDF-g-PAA-PAMAM membrane for efficient removal of copper ions. Chem Eng Sci 209:115186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2019.115186
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by Jilin Scientific and Technological Development Program (No. 20220201108GX and No. 20210201067GX).
Funding
Funding was provided by Jilin Scientific and Technological Development Program (Grant no. 20220201108GX).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RW: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing— original draft. XS: Methodology, Investigation. LL: Supervision, Validation, Funding acquisition. CZ: Supervision, Project administration. GW: Writing—review & editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Resources.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships could have appeared to influence the work reported in paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, R., Song, X., Liu, L. et al. PAMAM Grafted Magnetic Chitosan Particles by EDTA Core for Efficient Removal of Cu (II). J Polym Environ (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-023-03164-7
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-023-03164-7