Abstract
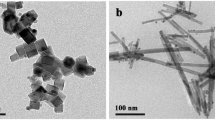
The synthesis of an efficient catalytic system with a safe catalysis approach has always been the concern of researchers to eradicate the problems arising due to the discharge of colored pollutants by industries in water bodies. Herein, we synthesized a magnetically separable nanocatalyst, CSFe3O4@CeO2, by co-precipitation of CeO2 on the surface of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles embedded in a chitosan hydrogel matrix. The synthesized catalyst was characterized by different analyses viz. FTIR, XRD, SEM–EDX and TEM. The CSFe3O4@CeO2 exhibited enhanced catalytic activity due to the unique synergism of adsorption and catalytic reduction for the removal of pollutants, namely methylene blue (MB), congo red (CR), and potassium ferricyanide using NaBH4 as a reducing agent. Further investigations of catalytic efficiency of CSFe3O4@CeO2 were done with MB by varying the catalyst dose, concentrations of MB and NaBH4. The reduction mechanism of MB to LMB (Leucomethylene blue) was studied and explained through adsorption reduction synergism. The reduction rate of MB in all catalytic experiments was determined by pseudo first-order kinetics. The adsorption isotherm data was best fit to Langmuir isotherm model indicated monolayer adsorption of MB on catalyst surface. The reusability of the catalyst with change in catalytic efficiency were also calculated to determine its economic feasibility.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benhadria N, Hachemaoui M, Zaoui F et al (2022) Catalytic reduction of methylene blue dye by copper oxide nanoparticles. J Clust Sci 33:249–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-020-01950-0
Naz M, Rafiq A, Ikram M et al (2021) Elimination of dyes by catalytic reduction in the absence of light: a review. J Mater Sci 56:15572–15608. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-021-06279-1
Malik MA, Alshehri AA, Abomuti MA et al (2021) Bioengineered matricaria recutita extract-assisted palladium nanoparticles for the congo red dye degradation and catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol to 4-aminophenol. Toxics 9:103. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9050103
Farokhi M, Parvareh A, Moraveji MK (2018) Performance of ceria/iron oxide nano-composites based on chitosan as an effective adsorbent for removal of Cr(VI) and Co(II) ions from aqueous systems. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:27059–27073. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2594-x
Fu F, Wang Q (2011) Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: a review. J Environ Manag 92:407–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.11.011
Qasem NAA, Mohammed RH, Lawal DU (2021) Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: a comprehensive and critical review. NPJ Clean Water 4:36. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-021-00127-0
Pantelidou NA, Theologides CP, Olympiou GG et al (2015) Catalytic removal of pharmaceutical compounds in water medium under an H2 stream over various metal-supported catalysts: a promising process. Desalin Water Treat 53:3363–3370. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.933620
Zeng X, Liu J, Zhao J (2018) Highly efficient degradation of pharmaceutical sludge by catalytic wet oxidation using CuO-CeO2/γ-Al2O3 as a catalyst. PLoS ONE 13:e0199520. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0199520
Bakhsh EM, Akhtar K, Fagieh TM et al (2021) Sodium alginate nanocomposite based efficient system for the removal of organic and inorganic pollutants from wastewater. Int J Biol Macromol 191:243–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.09.029
Culica ME, Chibac-Scutaru AL, Melinte V, Coseri S (2020) Cellulose acetate incorporating organically functionalized CeO2 NPs: efficient materials for UV filtering applications. Materials (Basel) 13:2955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13132955
Khan SA, Bakhsh EM, Asiri AM, Khan SB (2021) Chitosan coated NiAl layered double hydroxide microsphere templated zero-valent metal NPs for environmental remediation. J Clean Prod 285:124830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124830
Tan KB, Vakili M, Horri BA et al (2015) Adsorption of dyes by nanomaterials: recent developments and adsorption mechanisms. Sep Purif Technol 150:229–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2015.07.009
Ali H, Khan E, Ilahi I (2019) Environmental chemistry and ecotoxicology of hazardous heavy metals: environmental persistence, toxicity, and bioaccumulation. J Chem 2019:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6730305
Khan S, Malik A (2014) Environmental and health effects of textile industry wastewater. Environmental deterioration and human health. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 55–71
Ben SH, Chenari Bouket A, Pourhassan Z et al (2021) Diversity of synthetic dyes from textile industries, discharge impacts and treatment methods. Appl Sci 11:6255. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11146255
Levin RL, Degrange MA, Bruno GF et al (2004) Methylene blue reduces mortality and morbidity in vasoplegic patients after cardiac surgery. Ann Thorac Surg 77:496–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-4975(03)01510-8
Jana S, Ray J, Mondal B, Tripathy T (2019) Efficient and selective removal of cationic organic dyes from their aqueous solutions by a nanocomposite hydrogel, katira gum-cl-poly(acrylic acid-co-N, N-dimethylacrylamide)@bentonite. Appl Clay Sci 173:46–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2019.03.009
Lafi R, Montasser I, Hafiane A (2019) Adsorption of congo red dye from aqueous solutions by prepared activated carbon with oxygen-containing functional groups and its regeneration. Adsorpt Sci Technol 37:160–181. https://doi.org/10.1177/0263617418819227
Ozmen EY, Sezgin M, Yilmaz A, Yilmaz M (2008) Synthesis of β-cyclodextrin and starch based polymers for sorption of azo dyes from aqueous solutions. Bioresour Technol 99:526–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.01.023
Omidi S, Kakanejadifard A (2018) Eco-friendly synthesis of graphene–chitosan composite hydrogel as efficient adsorbent for Congo red. RSC Adv 8:12179–12189. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA00510A
Crini G (2006) Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: a review. Bioresour Technol 97:1061–1085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2005.05.001
Ogugbue CJ, Sawidis T (2011) Bioremediation and detoxification of synthetic wastewater containing triarylmethane dyes by aeromonas hydrophila isolated from industrial effluent. Biotechnol Res Int 2011:1–11. https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/967925
Ismail M, Akhtar K, Khan MI et al (2019) Pollution, toxicity and carcinogenicity of organic dyes and their catalytic bio-remediation. Curr Pharm Des 25:3645–3663. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612825666191021142026
Brillas E, Martínez-Huitle CA (2015) Decontamination of wastewaters containing synthetic organic dyes by electrochemical methods. An updated review. Appl Catal B Environ 166–167:603–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.11.016
Tsai H, Shaya J, Tesana S et al (2020) Visible-light driven photocatalytic degradation of pirimicarb by Pt-doped AgInS2 nanoparticles. Catalysts 10:857. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10080857
Vinotha Alex A, Chandrasekaran N, Mukherjee A (2020) Novel enzymatic synthesis of core/shell AgNP/AuNC bimetallic nanostructure and its catalytic applications. J Mol Liq 301:112463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.112463
Xia Q, Fu S, Ren G et al (2016) Fabrication of Fe3O4 @Au hollow spheres with recyclable and efficient catalytic properties. New J Chem 40:818–824. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NJ02436F
Sharma S, Bhattacharya A (2017) Drinking water contamination and treatment techniques. Appl Water Sci 7:1043–1067. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-016-0455-7
Yang Q, Wang Y, Wang J et al (2018) High effective adsorption/removal of illegal food dyes from contaminated aqueous solution by Zr-MOFs (UiO-67). Food Chem 254:241–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.02.011
Gupta VK, Mittal A, Gajbe V, Mittal J (2006) Removal and recovery of the hazardous azo dye acid orange 7 through adsorption over waste materials: bottom ash and de-oiled soya. Ind Eng Chem Res 45:1446–1453. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie051111f
Sood S, Mehta SK, Umar A, Kansal SK (2014) The visible light-driven photocatalytic degradation of Alizarin red S using Bi-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. New J Chem 38:3127–3136. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NJ00179F
Soltani F, Navidjouy N, Rahimnejad M (2022) A review on bio-electro-Fenton systems as environmentally friendly methods for degradation of environmental organic pollutants in wastewater. RSC Adv 12:5184–5213. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1RA08825D
Madrakian T, Afkhami A, Ahmadi M (2013) Simple in situ functionalizing magnetite nanoparticles by reactive blue-19 and their application to the effective removal of Pb2+ ions from water samples. Chemosphere 90:542–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.08.025
Amir M, Kurtan U, Baykal A (2015) Rapid color degradation of organic dyes by Fe3O4@His@Ag recyclable magnetic nanocatalyst. J Ind Eng Chem 27:347–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2015.01.013
Albukhari SM, Ismail M, Akhtar K, Danish EY (2019) Catalytic reduction of nitrophenols and dyes using silver nanoparticles @ cellulose polymer paper for the resolution of waste water treatment challenges. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 577:548–561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.05.058
Nagarajan D, Venkatanarasimhan S (2019) Copper(II) oxide nanoparticles coated cellulose sponge: an effective heterogeneous catalyst for the reduction of toxic organic dyes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:22958–22970. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05419-0
Safavi A, Momeni S (2012) Highly efficient degradation of azo dyes by palladium/hydroxyapatite/Fe3O4 nanocatalyst. J Hazard Mater 201–202:125–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.11.048
Zheng L-Q, Yu X-D, Xu J-J, Chen H-Y (2015) Reversible catalysis for the reaction between methyl orange and NaBH4 by silver nanoparticles. Chem Commun 51:1050–1053. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CC07711C
Gupta N, Singh HP, Sharma RK (2011) Metal nanoparticles with high catalytic activity in degradation of methyl orange: an electron relay effect. J Mol Catal A Chem 335:248–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2010.12.001
Ikram M, Umar E, Raza A et al (2020) Dye degradation performance, bactericidal behavior and molecular docking analysis of Cu-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. RSC Adv 10:24215–24233. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA04851H
Rafiq A, Ikram M, Ali S et al (2021) Photocatalytic degradation of dyes using semiconductor photocatalysts to clean industrial water pollution. J Ind Eng Chem 97:111–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2021.02.017
Dontsova TA, Nahirniak SV, Astrelin IM (2019) Metaloxide nanomaterials and nanocomposites of ecological purpose. J Nanomater 2019:1–31. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5942194
Kohantorabi M, Gholami MR (2017) Kinetic analysis of the reduction of 4-nitrophenol catalyzed by CeO2 nanorods-supported CuNi nanoparticles. Ind Eng Chem Res 56:1159–1167. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.6b04208
Rodríguez ARC, McCarthy JE, Alonso A et al (2018) Cerium oxide nanoparticles anchored onto graphene oxide for the removal of heavy metal ions dissolved in water. Desalin Water Treat 124:134–145. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2018.22735
Danish MSS, Bhattacharya A, Stepanova D et al (2020) A systematic review of metal oxide applications for energy and environmental sustainability. Metals (Basel) 10:1604. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10121604
Moskvin M, Marková I, Malínská H et al (2020) Cerium oxide-decorated γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles: design, synthesis and in vivo effects on parameters of oxidative stress. Front Chem. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.00682
Liu S, Yu B, Wang S et al (2020) Preparation, surface functionalization and application of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 281:102165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2020.102165
An Z, Zhang W, Ma J et al (2021) Adsorption of azo dye on magnetically separable Fe3O4/CeO2 nanocomposite: kinetics, isotherm mechanism. Mater Sci. https://doi.org/10.5755/j02.ms.28019
Corma A, Atienzar P, García H, Chane-Ching J-Y (2004) Hierarchically mesostructured doped CeO2 with potential for solar-cell use. Nat Mater 3:394–397. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1129
Cook LM (1990) Chemical processes in glass polishing. J Non Cryst Solids 120:152–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3093(90)90200-6
Reed K, Cormack A, Kulkarni A et al (2014) Exploring the properties and applications of nanoceria: is there still plenty of room at the bottom? Environ Sci Nano 1:390–405. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4EN00079J
Stambouli AB, Traversa E (2002) Solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs): a review of an environmentally clean and efficient source of energy. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 6:433–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1364-0321(02)00014-X
Liu S, Yang Z, Chang Y et al (2018) An enzyme-free electrochemical biosensor combining target recycling with Fe3O4/CeO2@Au nanocatalysts for microRNA-21 detection. Biosens Bioelectron 119:170–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.08.006
Walkey C, Das S, Seal S et al (2015) Catalytic properties and biomedical applications of cerium oxide nanoparticles. Environ Sci Nano 2:33–53. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4EN00138A
Wang H, Zhong Y, Yu H et al (2019) High-efficiency adsorption for acid dyes over CeO2·xH2O synthesized by a facile method. J Alloys Compds 776:96–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.10.228
Xu C, Qu X (2014) Cerium oxide nanoparticle: a remarkably versatile rare earth nanomaterial for biological applications. NPG Asia Mater 6:e90–e90. https://doi.org/10.1038/am.2013.88
Das M, Patil S, Bhargava N et al (2007) Auto-catalytic ceria nanoparticles offer neuroprotection to adult rat spinal cord neurons. Biomaterials 28:1918–1925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.11.036
Zhang T (2020) Heterogeneous catalytic process for wastewater treatment. In: Bustillo-Lecompte C (ed) Advanced Oxidation Processes - Applications, Trends, and Prospects. IntechOpen, London
Azhar MR, Arafat Y, Zhong Y et al (2021) An adsorption-catalysis pathway toward sustainable application of mesoporous carbon nanospheres for efficient environmental remediation. ACS ES&T Water 1:145–156. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsestwater.0c00026
Li N, Bai R (2005) A novel amine-shielded surface cross-linking of chitosan hydrogel beads for enhanced metal adsorption performance. Ind Eng Chem Res 44:6692–6700. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie050145k
Singh N, Riyajuddin S, Ghosh K et al (2019) Chitosan-graphene oxide hydrogels with embedded magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for dye removal. ACS Appl Nano Mater 2:7379–7392. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.9b01909
Kang S, Zhao Y, Wang W et al (2018) Removal of methylene blue from water with montmorillonite nanosheets/chitosan hydrogels as adsorbent. Appl Surf Sci 448:203–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.04.037
Vidal RRL, Moraes JS (2019) Removal of organic pollutants from wastewater using chitosan: a literature review. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:1741–1754. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2061-8
Gopinathan R, Bhowal A, Garlapati C (2019) Adsorption studies of some anionic dyes adsorbed by chitosan and new four-parameter adsorption isotherm model. J Chem Eng Data 64:2320–2328. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.8b01102
Konwar A, Chowdhury D, Dan A (2019) Chitosan based in situ and ex situ magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for rapid endotoxin removal from protein solutions. Mater Chem Front 3:716–725. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8QM00668G
Garg U, Azim Y, Kar A, Pradeep CP (2020) Cocrystals/salt of 1-naphthaleneacetic acid and utilizing Hirshfeld surface calculations for acid–aminopyrimidine synthons. CrystEngComm 22:2978–2989. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CE00106F
Danish M, Muneer M (2021) Excellent visible-light-driven Ni-ZnS/g-C3N4 photocatalyst for enhanced pollutants degradation performance: Insight into the photocatalytic mechanism and adsorption isotherm. Appl Surf Sci 563:150262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.150262
Khan FU, Asimullah KSB et al (2017) Novel combination of zero-valent Cu and Ag nanoparticles @ cellulose acetate nanocomposite for the reduction of 4-nitro phenol. Int J Biol Macromol 102:868–877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.04.062
Janoš P, Henych J, Pelant O et al (2016) Cerium oxide for the destruction of chemical warfare agents: a comparison of synthetic routes. J Hazard Mater 304:259–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.10.069
Ai L, Zeng C, Wang Q (2011) One-step solvothermal synthesis of Ag-Fe3O4 composite as a magnetically recyclable catalyst for reduction of Rhodamine B. Catal Commun 14:68–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2011.07.014
Loh K-S, Lee Y, Musa A et al (2008) Use of Fe3O4 nanoparticles for enhancement of biosensor response to the herbicide 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Sensors 8:5775–5791. https://doi.org/10.3390/s8095775
Sayyed SA, Beedri NI, Kadam VS, Pathan HM (2016) Rose bengal-sensitized nanocrystalline ceria photoanode for dye-sensitized solar cell application. Bull Mater Sci 39:1381–1387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-016-1279-7
Phung Hai TA, Sugimoto R (2018) Fluorescence control of chitin and chitosan fabricated via surface functionalization using direct oxidative polymerization. RSC Adv 8:7005–7013. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA00287H
Begum R, Najeeb J, Sattar A et al (2020) Chemical reduction of methylene blue in the presence of nanocatalysts: a critical review. Rev Chem Eng 36:749–770. https://doi.org/10.1515/revce-2018-0047
Jia Z, Sun H, Du Z, Lei Z (2014) Catalytic bubble-free hydrogenation reduction of azo dye by porous membranes loaded with palladium nanoparticles. J Environ Sci 26:478–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(13)60416-7
Allen SJ, Mckay G, Porter JF (2004) Adsorption isotherm models for basic dye adsorption by peat in single and binary component systems. J Colloid Interface Sci 280:322–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.08.078
Foo KY, Hameed BH (2010) Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem Eng J 156:2–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.09.013
Maruthapandi M, Kumar VB, Luong JHT, Gedanken A (2018) Kinetics, isotherm, and thermodynamic studies of methylene blue adsorption on polyaniline and polypyrrole macro-nanoparticles synthesized by C-dot-initiated polymerization. ACS Omega 3:7196–7203. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b00478
Langmuir DA (2012) Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin and Dubinin-Radushkevich isotherms studies of equilibrium sorption of Zn 2+ unto phosphoric acid modified rice husk. IOSR J Appl Chem 3:38–45. https://doi.org/10.9790/5736-0313845
Ayawei N, Ebelegi AN, Wankasi D (2017) Modelling and interpretation of adsorption isotherms. J Chem 2017:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3039817
Pulido Melián E, Henríquez-Cárdenes E, González Díaz O, Doña Rodríguez JM (2016) Study of adsorption and degradation of dimethylphthalate on TiO2-based photocatalysts. Chem Phys 475:112–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemphys.2016.04.021
Olivera S, Nataraj D, Archana S et al (2018) Alpha-cellulose derived from teakwood sawdust for cationic dyes removal. Mater Focus 7:132–139. https://doi.org/10.1166/mat.2018.1490
Kiani Ghaleh sardi F, Behpour M, Ramezani Z, Masoum S (2021) Simultaneous removal of Basic Blue41 and Basic Red46 dyes in binary aqueous systems via activated carbon from palm bio-waste: Optimization by central composite design, equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies. Environ Technol Innov 24:102039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.102039
Laoufi I, Saint-Lager M-C, Lazzari R et al (2011) Size and catalytic activity of supported gold nanoparticles: an in operando study during CO oxidation. J Phys Chem C 115:4673–4679. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp1110554
Rauf MA, Meetani MA, Khaleel A, Ahmed A (2010) Photocatalytic degradation of Methylene Blue using a mixed catalyst and product analysis by LC/MS. Chem Eng J 157:373–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.11.017
DAS PSATM and PP (2017) Highly efficient catalytic reductive degradation of various organic dyes by Au/CeO2-TiO2 nano-hybrid. J Chem Sci 1:81–93
Ucar A, Findik M, Gubbuk IH et al (2017) Catalytic degradation of organic dye using reduced graphene oxide–polyoxometalate nanocomposite. Mater Chem Phys 196:21–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2017.04.047
Ali F, Khan SB, Kamal T et al (2017) Chitosan coated cotton cloth supported zero-valent nanoparticles: simple but economically viable, efficient and easily retrievable catalysts. Sci Rep 7:16957. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-16815-2
Banerjee S, Chattopadhyaya MC (2017) Adsorption characteristics for the removal of a toxic dye, tartrazine from aqueous solutions by a low cost agricultural by-product. Arab J Chem 10:S1629–S1638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.06.005
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Department of Applied Chemistry, Aligarh Muslim University for providing research facilities. AA and KUK thanks UGC for Non-Net fellowship. UG is thankful to the CSIR-SRF (Grant No: 09/112(0633)/2019-EMR-I) for providing financial assistance.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, A., Garg, U., Khan, K.U. et al. Removal of Organic and Inorganic Pollutants Using CSFe3O4@CeO2 Nanocatalyst via Adsorption–Reduction Catalysis: A Focused Analysis on Methylene Blue. J Polym Environ 30, 4435–4451 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-022-02522-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-022-02522-1