Abstract
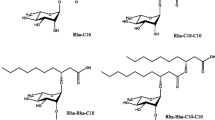
Glycolipids, consisting of a carbohydrate moiety linked to fatty acids, are microbial surface active compounds produced by various microorganisms. Glycolipids are characterized by highly structural diversity and have the ability to decrease the surface and interfacial tension at the surface and interface respectively. It presented initially a detailed classification of glycolipid including rhamnolipids, trehalolipids, mannosylerythritol-lipids, cellobiolipids; along with their producing strain. The review described the main functional properties of glycolipid including emulsification/de-emulsification capacity, foaming and moisturizing, viscosity reduction and hydrocarbon solubilizing and mobilizing capacities. Owing these properties, they can be applied in environmental fields as hydrocarbon emulsifiers, solubilizing and mobilizing agents, for their moisturizing capabilities and ability to reduce viscosity. The review will present a detailed classification of glycolipid biosurfactants, functional properties and the potential related applications in environment and bioremediation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kitamoto D, Isoda H, Nakahara T (2002) Functions and potential applications of glycolipid biosurfactants. J Biosci Bioeng 94:187–201
Benincasa M, Abalos A, Oliveira I, Manresa A (2004) Chemical structure, surface properties and biological activities of the biosurfactant produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa LBI from soapstock. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 85:1–8
Daverey A, Pakshirajan K (2009) Production of sophorolipids by the yeast Candida bombicola using simple and low cost fermentative media. Food Res Int 42:499–504
Daverey A, Pakshirajan K (2009) Production, characterization, and properties of sophorolipids from the yeast Candida bombicola using a low-cost fermentative medium. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 158:663–674
Wadekar SD, Kale SB, Lali AM, Bhowmick DN, Pratap AP (2012) Microbial synthesis of rhamnolipids by Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ATCC10145) on waste frying oil as low cost carbon source. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 142:249–266
Joshi-Navare K, Khanvilkar P, Prabhune A (2013) Jatropha oil derived sophorolipids: production and characterization as laundry detergent additive. Biochem Res Int 2013:169797
Gudiña EJ, Rodrigues AI, Alves E, Domingues MR, Teixeira JA, Rodrigues LR (2015) Bioconversion of agro-industrial by-products in rhamnolipids toward applications in enhanced oil recovery and bioremediation. Bioresour Technol 17:87–93
Vedaraman N, Venkatesh NM (2010) The effect of medium composition on the production of sophorolipids and the tensiometric properties by Starmerella bombicola MTCC 1910. Pol J Chem Technol 12:9–13
Kim H-S, Jeon J-W, Lee H-W, Park Y-I, Seo W-T, Oh H-M, Katsuragi T, Tani Y, Yoon B-D (2002) Extracellular production of a glycolipid biosurfactant, mannosylerythritol lipid, from Candida antarctica. Biotechnol Lett 24:225–229
Kim H-S, Jeon J-W, Kim B-H, Ahn C-Y, Oh H-M, Yoon B-D (2006) Extracellular production of a glycolipid biosurfactant, mannosylerythritol lipid, by Candida sp. SY16 using fed-batch fermentation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 70:391–396
Camilios Neto D, Meira JA, Tiburtius E, Zamora PP, Bugay C, Mitchell DA, Krieger N (2009) Production of rhamnolipids in solid-state cultivation: characterization, downstream processing and application in the cleaning of contaminated soils. Biotechnol J 4:748–755
Abbasi H, Sharafi H, Alidost L, Bodagh A, Zahiri HS, Noghabi KA (2013) Response surface optimization of biosurfactant produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa MA01 isolated from spoiled apples. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 43:398–414
Manivasagan P, Sivasankar P, Venkatesan J, Sivakumar K, Kim S-K (2014) Optimization, production and characterization of glycolipid biosurfactant from the actinobacterium, Streptomuces sp. MAB36. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 37:783–797
Jadhav M, Kalme S, Tamboli D, Govindwar S (2011) Rhamnolipid from Pseudomonas desmolyticum NCIM-2112 and its role in the degradation of Brown 3REL. J Basic Microbiol 51:385–396
Christova N, Tuleva B, Kril A, Georgieva M, Konstantinov S, Terziyski I, Nikolova B, Stoineva I (2013) Chemical structure and in vitro antitumor activity of rhamnolipids from Pseudomonas aeruginosa BN10. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 170:676–689
Colin VL, Castro MF, Amoroso MJ, Villegas LB (2013) Production of bioemulsifiers by Amycolatopsis tucumanensis DSM 45259 and their potential application in remediation technologies for soils contaminated with hexavalent chromium. J Hazard Mater 261:577–583
Chandran P, Das N (2010) Biosurfactant production and diesel oil degradation by yeast species Trichosporon asahii isolated from petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil. Int J Eng Sci Technol 2:6942–6953
de Souza Sobrinho HB, de Luna JM, Rufino RD, Porto ALF, Sarubbo LA (2013) Application of biosurfactant from Candida sphaerica UCP 0995 in removal of petroleum derivative from soil and sea water. J Life Sci 7:559–569
Joshi-Navare K, Singh PK, Prabhune AA (2014) New yeast isolate Pichia caribbica synthesizes xylolipid biosurfactant with enhanced functionality. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 116:1070–1079
Hewald S, Josephs K, Bolker M (2005) Genetic analysis of biosurfactant production in Ustilago maydis. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:3033–3040
Jing C, Xin S, Hui Z, Yinbo Q (2006) Production, structure elucidation and anticancer properties of sophorolipod from Wickerhaniella domercqiae. Enzym Microbial Technol 39:501–506
Sajna KV, Sukumaran RK, Jayamurthy H, Reddy KK, Kanjilal S, Prasad RBN, Pandey A (2013) Studies on biosurfactants from Pseudozyma sp. NII 08165 and their potential application as laundry detergent additives. Biochem Eng J 78:85–92
Sha R, Jiang L, Meng Q, Zhang G, Song Z (2011) Producing cell-free culture broth of rhamnolipids as a cost-effective fungicide against plant pathogens. J Basic Microbiol 51:1–9
Marquez-Rocha FJ, Hernandez-Rodriguez V, Lamela MT (2011) Biodegradation of engine and diesel oil in soil by a microbial consortium. Water Air Soil Pollut 128:313–320
Shoeb E, Akhlaq F, Badar U, Akhter J, Imtiaz S (2013) Classification and industrial applications of biosurfactants. Part-I: Nat Appl Sci 4:243–252
Abdel-Mawgoud AM, Lépine F, Déziel E (2010) Rhamnolipids: diversity of structures, microbial origins and roles. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:1323–1336
Raza ZA, Khan MS, Khalid ZM (2007) Evaluation of distant carbon sources in biosurfactant production by a gamma ray-induced Pseudomonas putida mutant. Process Biochem 42:686–692
Kulkarni M, Chaudhari R, Chaudhari A (2007) Novel tension-active microbial compounds for biocontrol applications. Gen Concepts Integr Pest Dis Manag 2007:295–304
Whang L-M, Liu P-WG, Ma C-C, Cheng S-S (2009) Application of rhamnolipid and surfactin for enhanced diesel biodegradation—effects of pH and ammonium addition. J Hazard Mater 164:1045–1050
Nayak AS, Vijaykumar MH, Karegoudar TB (2009) Characterization of biosurfactant produced by Pseudoxanthomonas sp. PNK-04 and its application in bioremediation. Int Biodeterior Biodegr 63:73–79
Lotfabad T, Shahcheraghi F, Shooraj F (2012) Assessment of antibacterial capability of rhamnolipids produced by two indigenous Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains. Jundishapur J Microbiol 6:29–35
Franzetti A, Gandolfi I, Bestetti G, Smyth TJP, Banat IM (2010) Production and applications of trehalose lipid biosurfactants. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 112:617–627
Shao Z (2011) Trehalolipids. In: Soberón-Chávez G (ed) Biosurfactants. Microbiology Monographs, vol 20. Springer, Berlin
White DA, Hird LC, Ali ST (2013) Production and characterization of a trehalolipid biosurfactant produced by the novel marine bacterium Rhodococcus sp., strain PML026. J Appl Microbiol 115:744–755
Daverey A, Pakshirajan K (2010) Sophorolipids from Candida bombicola using mixed hydrophilic substrates: Production, purification and characterization. Colloids Surf B 79:246–253
Tuleva B, Christova N, Cohen R, Stoev G, Stoineva I (2008) Production and structural elucidation of trehalose tetraesters (biosurfactants) from a novel alkanothrophic Rhodococcus wratislaviensis strain. J Appl Microbiol 104:1703–1710
Chang JS, Radosevich M, Jin Y, Cha DK (2004) Enhancement of phenanthrene solubilization and biodegradation by trehalose lipid biosurfactants. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:2816–2822
Tokumoto Y, Nomura N, Uchiyama H, Imura T, Morita T, Fukuoka T, Kitamoto D (2009) Structural characterization and surface-active properties of a succinoyl trehalose lipid produced by Rhodococcus sp. SD-74. J Oleo Sci 58:97–102
Isoda H, Shinmoto H, Matsumura M, Nakahara T (1996) Succinoyl trehalose lipid induced differentiation of human monocytoid leukemic cell line U937 into monocyte-macrophages. Cytotechnol 19:79–88
Sudo T, Zhao X, Wakamatsu Y, Shibahara M, Nomura N, Nakahara T, Suzuki A, Kobayashi Y, Jin C, Murata T, Yokoyama KK (2000) Induction of the differentiation of human HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cell line by succinoyl trehalose lipids. Cytotechnology 33:259–264
Uchida Y, Tsuchiya R, Chino M, Hirano J, Tabuchi T (1989) Extracellular accumulation of mono- and di-succinoyl trehalose lipids by a strain of Rhodococcus erythropolis grown on n-alkanes. Agric Biol Chem 53:757–763
Kurtzman CP, Price NPJ, Ray KJ, Kuo T-M (2010) Production of sophorolipid biosurfactants by multiple species of the Starmerella (Candida) bombicola yeast clade. FEMS Microbiol Lett 311:140–146
Van Bogaert INA, Soetaert W (2011) Sophorolipids. Biosurfactants Microbiol. Monographs 20:179–210
Bölker M, Basse CW, Schirawski J (2008) Ustilago maydis secondary metabolism—from genomics to biochemistry. Fungal Genet Biol 45:S88–S93
Kulakovskaya TV, Golubev WI, Tomashevskaya MA, Kulakovskaya EV, Shashkov AS, Grachev AA, Chizhov AS, Nifantiev NE (2010) Production of antifungal cellobiose lipids by Trichosporon porosum. Mycopathologia 169:117–123
Hua Z, Chen Y, Du C, Chen J (2004) Effects of biosurfactants produced by Candida antarctica on the biodegradation of petroleum compounds. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 20:25–29
Rau U, Nguyen LA, Roeper H, Koch H, Lang S (2005) Downstream processing of mannosylerythritol lipids produced by Pseudozyma aphidis. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 107:373–380
Vollbrecht E, Heckmann R, Wray V, Nimtz M, Lang S (1998) Production and structure elucidation of di- and oligosaccharide lipids (biosurfactants) from Tsukamurella sp. nov. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 50:530–537
Vollbrecht E, Rau U, Lang S (1999) Microbial conversion of vegetable oils into surface active di, tri-, and tetrasaccharide lipids (biosurfactants) by the bacterial strain Tsukamurella spec. Fett/Lipid 101:389–394
Mnif I, Ghribi D (2015) Microbial derived surface active compounds: properties and screening concept. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 31:1001–1020
McBain JW (1913) Mobility of highly-charged micelles. Trans Faraday Soc 9:99–101
Margaritis A, Zajic JE, Gerson DF (1979) Production and surface-active properties of microbial surfactant. Biotechnol Bioeng 21:1151–1162
Nitsche M, Siddhartha GAO, Contiero J (2005) Ramnolipid surfactants: an update on the general aspects of these remarcable biomolecules. Biotechnol Prog 21:1593–1600
Guerra-Santos L, Käppeli O, Fiechter A (1984) Pseudomonas aeruginosa biosurfactant production in continuous culture with glucose as carbon source. Appl Environ Microbiol 48:301–305
Rahman KSMP, Pasirayi G, Auger V, Ali Z (2010) Production of rhamnolipid biosurfactants by Pseudomonas aeruginosa DS10-129 in a microfluidic bioreactor. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 55:45–52
Ali Raza Z, Saleem Khan M, Khalid ZM, Rehman A (2006) Production kinetics and tensioactive characteristics of biosurfactant from Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutant grown on waste frying oils. Biotechnol Lett 28:1623–1631
Nitschke M, Costa SGVAO, Haddad R, Goncalves LAG, Eberlin MN, Contiero J (2005) Oil wastes as unconventional substrates for rhamnolipid biosurfactant production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa LBI. Biotechnol Prog 21:1562–1566
Konishi M, Morita T, Fukuoka T, Imura T, Kitamoto D (2008) Production of new types of sophorolipids by Candida batistae. J Oleo Sci 57:359–369
Solaiman DKY, Ashby RD, Nuñez A, Foglia TA (2004) Production of sophorolipids by Candida bombicola grown on soy molasses as substrate. Biotechnol Lett 26:1241–1245
Tuleva B, Christova N, Cohen R, Antonova D, Todorov T, Stoineva I (2009) Isolation and characterization of trehalose tetraester biosurfactants from a soil strain Micrococcus luteus BN56. Process Biochem 44:135–141
Singer MEV, Finnerty WR, Tunelid A (1990) Physical and chemical properties of a biosurfactant synthesized by Rhodococcus species H13-A. Can. J Microbiol 36:746–750
Morita T, Ishibashi Y, Hirose N, Wada K, Takahashi M, Fukuoka T, Imura T, Sakai H, Abe M, Kitamoto D (2011) Production and characterization of a glycolipid biosurfactant, mannosylerythriol lipid B, from sugarcane juice by Ustilago scitaminea NBRC 32730. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 75:1371–1376
Morita T, Ogura Y, Takashima M, Hirose N, Fukuoka T, Imura T, Kondo Y, Kitamoto D (2011) Isolation of Pseudozyma churashimaensis sp. nov., a novel ustilaginomycetous yeast species as a producer of glycolipid biosurfactants, mannosylerythritol lipids. J Biosci Bioeng 112:137–144
Morita T, Fukuoka T, Imura T, Kitamoto D (2012) Formation of the two novel glycolipid biosurfactants, mannosylribitol lipid and mannosylarabitol lipid, by Pseudozyma parantarctica JCM 11752 T. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96:931–938
Morita T, Fukuoka T, Konishi M, Imura T, Yamamoto S, Kitagawa M, Sogabe A, Kitamoto D (2009) Production of a novel glycolipid biosurfactant, mannosylmannitol lipid, by Pseudozyma parantarctica and its interfacial properties Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 83:1017–1025
Morita T, Ishibashi Y, Fukuoka T, Imura T, Sakai H, Abe M, Kitamoto D (2011) Production of glycolipid biosurfactants, cellobiose lipids, by Cryptococcus humicola JCM 1461 and their interfacial properties. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 75:1597–1599
Puchkov EO, Zahringer U, Lindner B, Kulakovskaya TV, Seydel U, Wiese A (2002) The mycocidal, membrane-active complex of Cryptococcus humicola is a new type of cellobiose lipid with detergent features. Biochim Biophys Acta 1558:161–170
Satpute SK, Banpurkar AG, Dhakephalkar PK, Banat IM, Chopade BA (2010) Methods for investigating biosurfactants and bioemulsifiers: a review. Crit Rev Biotechnol 30:127–144
Luna JM, Rufino RD, Campos-Takaki GM, Sarubbo LA (2012) Properties of the biosurfactant produced by Candida Sphaerica cultivated in low-cost substrates. Chem Eng Trans 27:67–72
Saimmai A, Rukadee O, Onlamool T, Sobhon V, Maneerat S (2012) Isolation and functional characterization of a biosurfactant produced by a new and promising strain of Oleomonas sagaranensis AT18. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:2973–2986
Abouseoud M, Maachi R, Amrane A (2007) Biosurfactant production from olive oil by Pseudomonas fluorescens. In: Méndez-Vilas A (ed) Communicating Current Research and Educational Topics and Trends in Applied Microbiology, vol 1. pp 340–347
Pirog TP, Shevchuk TA, Voloshina IN, Karpenko EV (2004) Production of surfactants by Rhodococcus erythropolis strain EK-1, grown on hydrophilic and hydrophobic substrates. Appl Biochem Microbiol 40:470–475
Abbasi H, Hamedi MM, Lotfabad TB, Zahiri HS, Sharafi H, Masoomi F, Moosavi-Movahedi AA, Ortiz A, Amanlou M, Noghabi KA (2012) Biosurfactant-producing bacterium, Pseudomonas aeruginosa MA01 isolated from spoiled apples: physicochemical and structural characteristics of isolated biosurfactant. J Biosci Bioeng 113:211–219
Perfumo A, Banat M, Canganella F, Marchant R (2006) Rhamnolipid production by a novel thermophilic hydrocarbon-degrading Pseudomonas aeruginosa AP02-1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:132–138
Dhasayan A, Kiran GS, Selvin J (2014) Biosurfactant by Halomonas sp. MB-30 for potential application in enhanced oil recovery. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 174:2571–2584
Cerón-Camacho R, Martínez-Palou R, Chávez-Gómez B, Cuéllar F, Bernal-Huicochea C, Clavel JC, Aburto J (2013) Synergistic effect of alkyl-O-glucoside and -cellobioside biosurfactants as effective emulsifiers of crude oil in water. A proposal for the transport of heavy crude oil by pipeline. Fuel 110:310–317
Nguyen TT, Sabatini DA (2009) Formulating alcohol-free microemulsions using rhamnolipid biosurfactant and rhamnolipid mixtures. J Surfact Deterg 12:109–115
Nguyen TT, Edelen A Neighbors B, Sabatini DA (2010) Biocompatible lecithin-based microemulsions with rhamnolipid and sophorolipid biosurfactants: formulation and potential applications. J Colloid Interface Sci 348:498–504
Worakitkanchanakul W, Imura T, Morita T, Fukuoka T, Sakai H, Abe M, Rujiravanit R, Chavadej S, Kitamoto D (2008) Formation of W/O microemulsion based on natural glycolipid biosurfactant. J Oleo Sci 57:55–59
Mohebali G, Kaytash A, Etemadi N (2012) Efficient breaking of water/oil emulsions by a newly isolated de-emulsifying bacterium, Ochrobactrum anthropi strain RIPI5-1. Colloids Surf B 98:120–128
Long X, Zhang G, Shen C, Sun G, Wang R, Yin L, Meng Q (2013) Application of rhamnolipid as a novel biodemulsifier for destabilizing waste crude oil. Bioresour Technol 131:1–5
Pacwa-Plociniczak M, Plaza GA, Piotrowska-Seget Z, Cameotra SS (2011) Environmental applications of biosurfactants: recent advances. Int J Mol Sci 12:633–654
Perfumo A, Smyth TJP, Marchant R, Banat IM (2009) Production and roles of biosurfactants and bioemulsifiers in accessing hydrophobic substrates. In: Timmis KN (ed) Microbiology of hydrocarbons, oils, lipids, and derived compounds. Springer, London (in press)
Whang L-M, Liuc P-WG, Ma C-C, Cheng S-S (2008) Application of biosurfactants, rhamnolipid, and surfactin, for enhanced biodegradation of diesel-contaminated water and soil. J Hazard Mater 151:155–163
Abouseoud M, Yataghene A, Amrane A, Maachi R (2010) Production of a biosurfactant by Pseudomonas fluorescens-solubilizing and wetting capacity. J Hazard Mater 183:131–136
Page CA, Bonner JS, Kanga SA, Mills MA, Autenrieth RL (1999) Biosurfactant solubilization of PAHs. Environ Eng Sci 16:465–474
Wong JW, Fang M, Zhao Z, Xing B (2004) Effect of surfactants on solubilization and degradation of phenanthrene under thermophilic conditions. J Environ Qual 33:2015–2025
Abdul Salam J, Das N (2013) Enhanced biodegradation of lindane using oil-in-water bio-microemulsion stabilized by biosurfactant produced by a new yeast strain, Pseudozyma VITJzN01. J Microbiol Biotechnol 23:1598–1609
Peng F, Liu Z, Wang L, Shao Z (2007) An oil-degrading bacterium: Rhodococcus erythropolis strain 3C-9 and its biosurfactants. J Appl Microbiol 102:1603–1611
Schippers C, Geßner K, Muller T, Scheper T (2000) Microbial degradation of phenanthrene by addition of a sophorolipid mixture. J Biotechnol 83:189–198
Song D, Liang S, Yan L, Shang Y, Wang X (2016) Solubilization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by single and binary mixed rhamnolipid-sophorolipid biosurfactants. J Environ Qual 45(4):1405–1412
Urum K, Pekdemir T (2004) Evaluation of biosurfactants for crude oil contaminated soil washing. Chemosphere 57:1139–1150
Urum K, Grigson S, Pekdemir T, McMenamy S (2006) A comparison of the efficiency of different surfactants for removal of crude oil from contaminated soils. Chemosphere 62:1403–1410
Lai C-C, Huang Y-C, Wei Y-H, Chang J-S (2009) Biosurfactant-enhanced removal of total petroleum hydrocarbons from contaminated soil. J Hazard Mater 167:609–614
Kang SW, Kim YB, Shin JD, Kim EK (2010) Enhanced biodegradation of hydrocarbons in soil by microbial biosurfactant, sophorolipid. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 160:780–790
Zhang Y, Miller RM (1994) Effect of a Pseudomonas rhamnolipid biosurfactant on cell hydrophobicity and biodegradation of octadecane. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:2101–2106
Kaczorek E, Olszanowski A (2011) Uptake of hydrocarbon by Pseudomonas fluorescens (P1) and Pseudomonas putida (K1) strains in the presence of surfactants: a cell surface modification. Water Air Soil Pollut 214:451–459
Saeki H, Sasaki M, Komatsu K, Miura A, Matsuda H (2009) Oil spill remediation by using the remediation agent JE1058BS that contains a biosurfactant produced by Gordonia sp. strain JE-1058. Bioresour Technol 100:572–577
Zhang Y, Miller RM (1992) Enhanced octadecane dispersion and biodegradation by a Pseudomonas rhamnolipid surfactant (biosurfactant). Appl Environ Microbiol 58:3276–3282
Providenti MA, Flemming CA, Lee H, Trevors JT (1995) Effect of addition of rhamnolipid biosurfactants or rhamnolipid-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa on phenanthrene mineralization in soil slurries. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 17:15–26
Zhang Y, Miller RM (1995) Effect of rhamnolipid (biosurfactant) structure on solubilization and biodegradation of n–alkanes. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:2247–2251
Rahman KSM, Rahman TJ, Kourkoutas Y, Petsas I, Marchant R, Banat IM (2003) Enhanced bioremediation of n-alkane in petroleum sludge using bacterial consortium amended with rhamnolipid and micronutrients. Bioresour Technol 90:159–168
Abalos A, Vinas M, Sabaté J, Manresa MA, Solanas AM (2004) Enhanced biodegradation of Casablanca crude oil by a microbial consortium in presence of a rhamnolipid produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa AT10. Biodegradation 15:249–260
Inakollu S, Hung H-C, Shreve GS (2004) Biosurfactant enhancement of microbial degradation of various structural classes of hydrocarbon in mixed waste systems. Environ Eng Sci 21:463–469
Nguyen TT, Youssef NH, McInerney MJ, Sabatini DA (2008) Rhamnolipid biosurfactant mixtures for environmental remediation. Water Res 42:1735–1743
Owsianiak M, Chrzanowski L, Szulc A, Staniewski J, Olszanowski A, Olejnik-Schmidt AK, Heipieper HJ (2009) Biodegradation of diesel/biodiesel blends by a consortium of hydrocarbon degraders: effect of the type of blend and the addition of biosurfactants. Bioresour Technol 100:1497–1500
Chen Q, Bao M, Fan X, Liang S, Sun P (2013) Rhamnolipids enhance marine oil spill bioremediation in laboratory system. Mar Pollut Bull 71:269–275
Lennarz WJ, Talamo B (1966) The chemical characterization and enzymatic synthesis of mannolipids in Micrococcus lysodeikticus. J Biol Chem 241:2707–2719
Nie M, Yin X, Ren C, Wang Y, Xu F, Shen Q (2010) Novel rhamnolipid biosurfactants produced by a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain NY32. Biotechnol Adv 28:635–643
Dean SM, Jin Y, Cha DK, Wilson SW, Radosevich M (2001) Phenanthrene degradation in soils co-inoculated with phenanthrene-degrading and biosurfactant-producing bacteria. J Environ Qual 30:1126–1133
Kumar M, Leon V, Materano AS, Ilzins OA (2006) Enhancement of oil degradation by co-culture of hydrocarbon degrading and biosufactant producing bacteria. Pol J Microbiol 55:139–146
Cameotra SS, Singh P (2009) Synthesis of rhamnolipid biosurfactant and mode of hexadecane uptake by Pseudomonas species. Microb Cell Fact 8:1–7
Millioli VS, Servulol ELC, Sobrald LGS, de Carvalho DD (2009) Bioremediation of crude oil-bearing soil: evaluating the effect of rhamnolipid addition to soil toxicity and to crude oil biodegradation efficiency. Glob Nest J 11:181–188
Yin X, Nie M, Shen Q (2011) Rhamnolipid biosurfactant from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain NY3 and methods of use (United States Patent 2011, 0306569 A1). Oregon State University; the State of Oregon Acting by and through the State Board of Higher Education on behalf of
Cristina Souza E, Vessoni-Penna TC, de Souza Oliveira RP (2014) Review biosurfactant-enhanced hydrocarbon bioremediation: an overview. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 89:88–94
Mu-tai Bao, Dong-yang Cui, Sheng-kang Liang, Qiu-fang Cao, Ke-ji Sun (2009) Application of Rhamnolipid Biosurfactant in Heavy Oil Viscosity Reduction. Modern Chem Ind; Master Thesis; 2011-02-21
Md Noh NA, Salleh SM, Mohamad Ibrahim MN, Mohd Yahya AR (2011) Pseudomonas aeruginosa USM-AR2 culture containing biosurfactant facilitates crude oil distillation process. In: Proceedings of 2011 International Conference on Biotechnology and Environment Management, vol 18. Press, Singapoore
Planckaert M (2005) Oil reservoirs and oil production. In: Ollivier B, Magot M (eds) Petroleum microbiology. ASM Press, Washington, DC
Wang Q, Fang X, Bai B, Liang X, Shuler PJ, Goddard WA, Tang Y (2007) Engineering bacteria for production of rhamnolipid as an agent for enhanced oil recovery. Biotechnol Bioeng 98:842–853
Pornsunthorntawee O, Arttaweeporn N, Paisonjit T, Smboonthanate P, Abe M, Rajiravanit R, Chavades S (2008) Isolation and comparison of biosurfactants produced by B. subtilis PT2 of P. aeruginosa SP4 for microbial surfactant enhanced oil recovery. Biochem Eng J 42:172–179
Amani H, Müller MM, Syldatk C, Hausmann R (2013) Production of microbial rhamnolipid by Pseudomonas aeruginosa MM1011 for ex situ enhanced oil recovery. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 170:1080–1093
Singh P, Cameotra SS (2004) Enhancement of metal bioremediation by use of microbial surfactants. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 319:291–297
El Zeftawy MAM, Mulligan CN (2011) Use of rhamnolipid to remove heavy metals from wastewater by micellar-enhanced ultrafiltration (MEUF). Sep Purif Technol 77:120–127
Mulligan CN, Wang S (2006) Remediation of heavy metal-contaminated soil by a rhamnolipid foam. Eng Geol 85:75–81
Juwarkar AA, Dubey KV, Nair A, Singh SK (2008) Bioremediation of multi-metal contaminated soil using biosurfactant—a novel approach. Ind J Microbiol 48:142–146
Aşçi Y, Nurbas M, Açikel YS (2008) A comparative study for the sorption of Cd (II) by K-feldspar and sepiolite as soil components and the recovery of Cd(II) using rhamnolipid biosurfactant. J Env Manag 88:383–392
Wang S, Mulligan CN (2009) Rhamnolipid biosurfactant-enhanced soil flushing for the removal of arsenic and heavy metals from mine tailings. Process Biochem 44:296–301
Basak G, Das N (2014) Characterization of sophorolipid biosurfactant produced by Cryptococcus sp. VITGBN2 and its application on Zn(II) removal from electroplating wastewater. J Env Biol 35:1087–1094
Mulligan CN, Yong RN, Gibbs BF (2001) Heavy metal removal from sediments by biosurfactants. J Hazard Mater 85:111–125
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by grants from ‘‘Tunisian Ministry of Higher Education, Scientific Research and Technology”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mnif, I., Ellouz-Chaabouni, S. & Ghribi, D. Glycolipid Biosurfactants, Main Classes, Functional Properties and Related Potential Applications in Environmental Biotechnology. J Polym Environ 26, 2192–2206 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-017-1076-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-017-1076-4