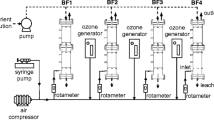
Abstract
In this study, the effects of temperature and inlet concentration on acetone biofiltration in a composite bead biofilter were investigated. Both microbial growth rate and biochemical reaction rate would be inhibited with increasing average inlet concentration. The inhibitive effect was more pronounced at higher operation temperature for microbial growth rate, and it was more pronounced at lower operation temperature for biochemical reaction rate. Both microbial growth rate and biochemical reaction rate would be enhanced with increasing operation temperature. Both microbial growth and biochemical reaction processes were more temperature dependent at higher average inlet concentration. The microbial growth process was more temperature dependent than the biochemical reaction process. The values of maximum reaction rate Vm and half-saturation constant Ks ranged from 0.04 to 0.05 g-C/h-kg packing material and from 37.19 to 42.77 ppm, respectively. The zero-order kinetic with the diffusion rate limitation could be regarded as the most adequate biochemical reaction model. The maximum elimination capacity of biofilter increased with increasing operation temperature. The values of critical and maximum elimination capacity ranged from 0.07 to 0.15 and from 0.13 to 0.16 g-C/h-kg packing material, respectively.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deviney JS, Deshusses MA, Webster T (1999) Biofiltration for air pollution control. Lewis publishers, New York
Williams TO, Miller FC (1992) Biocycle 33:75
Hodge DS, Tahatabai F and Winer AM (1991) Environ Technol 12:655
Bhno HL (1993) In: Proceedings of the 86th Annual Meeting & Exhibition of the Air & Waste Management Association, Denver, Coloado
Ottengraf SPP, Konings JHG (1986) Bioprocess Eng 1:61
Peters DA, Hickman GT, Stefanoff JG, Garcia Jr MB (1993) In: Proceedings of the 86th Annual Meeting & Exhibition of the Air & Waste Management Association, Denver, Coloado
Ergas SJ (1994) In: Proceedings of the 87th Annual Meeting & Exhibition of the Air & Waste Management Association, Cincinnati, Ohio
Ottengraf SPP, van den Oever AHC (1983) Biotechnol Bioeng 25:3089
Carlson DA, Leiser CP (1966) J Water Pollut Control Fed 38:829
Chan WC, Lin ZY (2004) Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 26:223
Reynold TD (1982) Unit operation and process in environmental engineering. Wadsworth Inc, California
Valsaraj KT (1995) Elements of environmental engineering: thermodynamics and kinetics. Lewis publishers, New York
Leson G, Winer AM (1991) J Air Waste Manage Assoc 41:1045
Yani M, Mirai M, Shoda M (1998) J Ferment Eng 85:502
Yang Y, Allen ER (1994) J Air Waste Manage Assoc 44:1315
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chan, WC., Chang, LY. Effects of Temperature and Inlet Concentration on Acetone Biofiltration in a Composite Bead Biofilter. J Polym Environ (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-006-0046-z
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-006-0046-z