Abstract
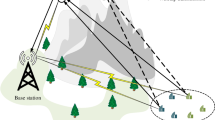
The radio-cast nature of wireless communications is always exposed to the eavesdropping attack. To safeguard 5 G communications where both the CUs and Device to Device (D2D) users can communicate securely becomes a prime objection. To examine this issue we have investigated the eavesdropping attack in a considered 5 G Networks, and analysed the secrecy rate (SR), and data rate of the D2D communication enabled 5 G networks. Different from previous work mentioned in literature we have proposed a joint resource allocation and power allocation scheme with the constraint of unknown channel state information (CSI) of the presented eavesdropper (EDs) in a cell. We have proposed a Stackelberg game-based resource allocation scheme and a state of the art monarch butterflies optimization (MBO) based power allocation (SGR-MOP) scheme to enhance the SR of the CUs along with enhance the data rate of the cell as well. The proposed scheme is further subdivided into two sub-schemes where the resource allocation scheme is designed to form a group of CUs and D2D users to enhance the SR of the CUs. Moreover, the proposed power allocation scheme is designed to enhance the data rate of D2D users. We consider a scenario where the eNodeB (eNB) has all the channel state information (CSI) of the CUs and D2D users however, the presence of the eavesdropper is not known to the eNB. We have compared our proposed scheme with the existing related schemes mentioned in the literature. The simulation results display that our scheme outperforms compared with other related schemes.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clemm, Alexander, Zhani, Mohamed Faten, Boutaba, Raouf: Network management 2030: operations and control of network 2030 services. J. Netw. Syst. Manag. 28(4), 721–750 (2020)
Ahmed, M., Li, Y., Waqas, M., Sheraz, M., Jin, D., Han, Z.: A survey on socially aware device-to-device communications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 20(3), 2169–2197 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2018.2820069
Maenhaut, Pieter-Jan., et al.: Resource management in a containerized cloud: status and challenges. J. Netw. Syst. Manag. 28(2), 197–246 (2020)
Silva, Vinicius F., et al.: Joint content-mobility priority modeling for cached content selection in D2D networks. J. Netw. Syst. Manag. 29(1), 1–37 (2021)
Jameel, F., Hamid, Z., Jabeen, F., Zeadally, S., Javed, M.A.: A survey of device-to-device communications: research issues and challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 20(3), 2133–2168 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2018.2828120
Wen, S., Zhu, X., Lin, Y., Lin, Z., Zhang, X., Yang, D.: Achievable Transmission Capacity of Relay-Assisted Device-to-Device (D2D) Communication Underlay Cellular Networks. In: 2013 IEEE 78th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Fall), Las Vegas, pp. 1–5 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/VTCFall.2013.6692074
Dubey, R., Mishra, P.K., Pandey, S.: Mixed uplink, downlink channel allocation and power allocation schemes for 5G networks. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 112, 2253–2274 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07148-x
Dubey, R., Sharma, R., Mishra, P.K., Pandey, S.: BAT Optimization based Power Allotment Scheme for 5G Networks. In: 2020 IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Computing and Communication Technologies (CONECCT), Bangalore, 2020, pp. 1–5, https://doi.org/10.1109/CONECCT50063.2020.9198676
Melki, L., Najeh, S., Besbes, H.: Interference management scheme for network-assisted multi-hop D2D communications. In: 2016 IEEE 27th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), Valencia, pp. 1–5 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/PIMRC.2016.7794834
Yang, L., Wu, D., Shi, H., Long, Y., Cai, Y.: Social-aware joint mode selection and link allocation for device-to-device communication underlaying cellular networks. China Commun. 15(8), 92–107 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/CC.2018.8438276
Wyner, A.D.: The wire-tap channel. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 54(8), 1355–1387 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1538-7305.1975.tb02040.x
Leung-Yan-Cheong, S., Hellman, M.: The Gaussian wire-tap channel. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 24(4), 451–456 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIT.1978.1055917
Barros, J., Rodrigues, M.R.D.: Secrecy Capacity of Wireless Channels. In: 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory, Seattle, pp. 356–360 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISIT.2006.261613
Vega Sánchez, J.D., Urquiza-Aguiar, L., Paredes Paredes, M.C.: Physical Layer Security for 5G Wireless Networks: A Comprehensive Survey. In: 2019 3rd Cyber Security in Networking Conference (CSNet), Quito, pp. 122–129 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/CSNet47905.2019.9108955
Sánchez, J.D.V., Urquiza-Aguiar, L., Paredes, M.C.P., et al.: Survey on physical layer security for 5G wireless networks. Ann. Telecommun. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12243-020-00799-8
Ashtiani, A.F., Pierre, S.: Secrecy Based Resource Allocation for D2D Communication Using Tabu Search Algorithm. In: 2019 IEEE Canadian Conference of Electrical and Computer Engineering (CCECE), pp. 1–5 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/CCECE43985.2019.9052395
Zhang, R., Cheng, X., Yang, L.: Cooperation via spectrum sharing for Physical layer security in device-to-device communications cnderlaying cellular networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 15(8), 5651–5663 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TWC.2016.2565579
Xu, H., Pan, C., Xu, W., Shi, J., Chen, M., Heng, W.: Improving Wireless Physical Layer Security via D2D Communication. In: 2018 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Abu Dhabi, pp. 1–7 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/GLOCOM.2018.8647915
Jia, L., Yao, F., Sun, Y., Niu, Y., Zhu, Y.: Bayesian Stackelberg game for antijamming transmission with incomplete information. IEEE Commun. Lett. 20(10), 1991–1994 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/LCOMM.2016.2598808
Xu, Y., et al.: A one-leader multi-follower Bayesian-Stackelberg game for anti-jamming transmission in UAV communication networks. IEEE Access 6, 21697–21709 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2828033
Shah, H.A., Koo, I.: A novel physical layer security scheme in OFDM-based cognitive radio networks. IEEE Access 6, 29486–29498 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2842826
Zou, Y.: Physical-layer security for spectrum sharing systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 16(2), 1319–1329 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TWC.2016.2645200
Lee, K., Hong, J.: Power control for energy efficient D2D communication in heterogeneous networks with eavesdropper. IEEE Commun. Lett. 21(11), 2536–2539 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/LCOMM.2017.2718521
Wang, W., Teh, K.C., Li, K.H.: Enhanced physical layer security in D2D spectrum sharing networks. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 6(1), 106–109 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/LWC.2016.2634559
Liu, C., Lv, T., Gao, H., Lu, Y.: Enhanced Physical Layer Security for Ultra-Dense D2D Communications Underlaying Cellular Networks with Full-Duplex Users. In: 2017 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), Singapore, pp. 1–6 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/GLOCOMW.2017.8269199
Mei, W., Chen, Z., Fang, J., Fu, B.: Secure D2D-enabled cellular communication against selective eavesdropping. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Paris, pp. 1–7 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICC.2017.7996937
Zhao, N., Yu, F.R., Li, M., Yan, Q., Leung, V.C.M.: Physical layer security issues in interference- alignment-based wireless networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 54(8), 162–168 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/MCOM.2016.7537191
Zou, Y., Zhu, J., Li, X., Hanzo, L.: Relay selection for wireless communications against eavesdropping: a security-reliability trade-off perspective. IEEE Netw. 30(5), 74–79 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/MNET.2016.7579030
Le, T.N., Chin, W., Lin, Y.: Non-cooperative and cooperative PUEA detection using physical layer in mobile OFDM-based cognitive radio networks. In: 2016 International Conference on Computing, Networking and Communications (ICNC), Kauai, pp. 1–5 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCNC.2016.7440583
Zhang, W., He, W., Chen, X., Cai, Y., Guan, X., Qu, J.: Power allocation for improving physical layer security in D2D communication via stackelberg game. In: 2016 8th International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Processing (WCSP), Yangzhou, pp. 1–5 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/WCSP.2016.7752663
Qu, J., Cai, Y., Zheng, J., et al.: Power allocation for device-to-device communication underlaying cellular networks under a probabilistic eavesdropping scenario. Ann. Telecommun. 71, 389–398 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12243-016-0515-x
Myung, Hyung G.: Technical overview of 3GPP LTE. Polytechnic University of New York, New York (2008)
Guidelines for evaluation of radio interface technologies for IMT-advanced, Int. Telecommun. Union (ITU), Tech. Rep. ITU-R M.2135 (2008)
Propagation data and prediction methods for the planning of short-range outdoor radio communication systems and radio local area networks in the frequency range 300 MHz to 100 GHz. Int. Telecommun. Union (ITU), Tech. Rep. ITU-R (P.1411-4) (2007)
Monderer, Dov, Shapley, Lloyd: Potential games. Games Econ. Behav. 14(1), 124–143 (1996)
Lucchetti, R., Mignanego, F., Pieri, G.: Existence theorems of equilibrium points in Stackelberg. Optimization 18(6), 857–866 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1080/02331938708843300
Wang, G., Deb, S., Cui, Z.: Monarch butterfly optimization. Neural. Comput. Applic. 31, 1995–2014 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-015-1923-y
Breed, Greg A., Severns, Paul M., Edwards, Andrew M.: Apparent power-law distributions in animal movements can arise from intraspecific interactions. J. R Soc Interface 12(103), 20140927 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript. The authors have no financial or proprietary interests in any material discussed in this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dubey, R., Mishra, P.K. & Pandey, S. SGR-MOP Based Secrecy-Enabled Resource Allocation Scheme for 5G Networks. J Netw Syst Manage 31, 60 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10922-023-09750-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10922-023-09750-3