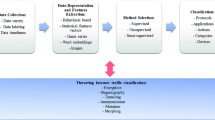
Abstract
The classification of encrypted network traffic represents an important issue for network management and security tasks including quality of service, firewall enforcement, and security. Traffic classification becomes more challenging since the traditional techniques, such as port numbers or Deep Packet Inspection, are ineffective against Peer-to-Peer Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) applications, which used non-standard ports and encryption. Moreover, traffic classification also represents a particularly challenging application domain for machine learning (ML). Solutions should ideally be both simple—therefore efficient to deploy—and accurate. Recent advances in ML provide the opportunity to decompose the original problem into a subset of classifiers with non-overlapping behaviors, in effect providing further insight into the problem domain and increasing the throughput of solutions. In this work, we investigate the robustness of an ML approach to classify encrypted traffic on not only different network traffic but also against evasion attacks. Our ML based approach only employs statistical network traffic flow features without using the Internet Protocol addresses, source/destination ports, and payload information to unveil encrypted VoIP applications in network traffic. What we mean by robust signatures is that the signatures learned by training on one network are still valid when they are applied to traffic coming from totally different locations, networks, time periods, and also against evasion attacks. The results on different network traces, as well as on the evasion of a Skype classifier, demonstrate that the performance of the signatures are very promising, which implies that the statistical information based on the network layer with the use of ML can achieve high classification accuracy and produce robust signatures.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Skype detection task and flow features.
References
IANA, Internet assigned numbers authority, http://www.iana.org/assignments/port-number (last Accessed Oct 2009)
Moore, A.W., Papagiannaki, K.: Toward the accurate identification of network applications. In: Passive and Active Network Measurement: Proceedings of the Passive & Active Measurement Workshop, pp. 41–54 (2005)
Madhukar, A., Williamson, C.: A longitudinal study of p2p traffic classification. In: Modeling, Analysis, and Simulation of Computer and Telecommunication Systems. MASCOTS 2006. 14th IEEE International Symposium on, pp. 179–188 (2006)
Sen, S., Spatscheck, O., Wang, D.: Accurate, scalable in-network identification of p2p traffic using application signatures. In: WWW ’04: Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on World Wide Web, pp. 512–521. ACM, New York, NY, USA (2004)
Erman, J., Arlitt, M., Mahanti, A.: Traffic classification using clustering algorithms. In: MineNet ’06: Proceedings of the 2006 SIGCOMM Workshop on Mining Network Data, pp. 281–286. ACM Press, New York, NY, USA (2006)
Karagiannis, T., Papagiannaki, K., Faloutsos, M.: BLINC: multilevel traffic classification in the dark. In: SIGCOMM ’05: Proceedings of the 2005 Conference on Applications, Technologies, Architectures, and Protocols for Computer Communications, pp. 229–240. ACM Press, New York, NY, USA (2005)
Alshammari, R., Zincir-Heywood, A.N.: Can encrypted traffic be identified without port numbers, IP addresses and payload inspection? Comput. Netw. 55(6), 1326–1350 (2011)
Bernaille, L., Teixeira, R., Akodkenou, I., Soule, A., Salamatian, K.: Traffic classification on the fly. SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. 36(2), 23–26 (2006)
Moore, A.W., Zuev, D.: Internet traffic classification using bayesian analysis techniques. In: SIGMETRICS ’05: Proceedings of the 2005 ACM SIGMETRICS International Conference on Measurement and Modeling of Computer Systems, pp. 50–60. ACM Press, New York, NY, USA (2005)
Alshammari, R., Zincir-Heywood, A.N.: A flow based approach for ssh traffic detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on System, Man and Cybernetics—SMC’2007 (2007)
Alshammari, R., Zincir-Heywood, A.N.: Investigating two different approaches for encrypted traffic classification. In: PST ’08: Proceedings of the 2008 Sixth Annual Conference on Privacy, Security and Trust, pp. 156–166. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, DC, USA (2008)
Alshammari, R., Zincir-Heywood, N.: Generalization of signatures for ssh encrypted traffic identification. In: Computational Intelligence in Cyber Security. CICS ’09. IEEE Symposium on, pp. 167–174 (2009)
Early, J., Brodley, C., Rosenberg, C.: Behavioral authentication of server flows. In: Proceedings of the 19th Annual Computer Security Applications Conference, pp. 46–55 (2003)
Haffner, P., Sen, S., Spatscheck, O., Wang, D.: ACAS: automated construction of application signatures. In: MineNet ’05: Proceeding of the 2005 ACM SIGCOMM Workshop on Mining Network Data, pp. 197–202. ACM Press, New York, NY, USA (2005)
Montigny-Leboeuf, A.D.: Flow Attributes for Use in Traffic Characterization, CRC Technical Note No. CRC-TN-2005-003, Feb 2005.
Wright, C., Monrose, F., Masson, G.M.: HMM profiles for network traffic classification. In: VizSEC/DMSEC ’04: Proceedings of the 2004 ACM Workshop on Visualization and Data Mining for Computer Security, pp. 9–15. ACM Press, New York, NY, USA (2004)
Williams, N., Zander, S., Armitage, G.: A preliminary performance comparison of five machine learning algorithms for practical IP traffic flow classification. SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. 36(5), 5–16 (2006)
Pise, N., Kulkarni, P.: A survey of semi-supervised learning methods. In: Computational Intelligence and Security. CIS ’08. International Conference on, vol. 2, pp. 30–34 (2008)
Alshammari, R.: Automatically classifying encrypted network traffic: a case study of ssh. Mater thesis, Dalhousie University, NS, Canada, 133 pp. (2008)
Quinlan, J.: See5-comparison, http://www.rulequest.com/see5-comparison.html (last Accessed Feb 2011)
Callado, A., Kelner, J., Sadok, D.: Alberto Kamienski C, Fernandes S.: Better network traffic identification through the independent combination of techniques. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 33(4), 433–446 (2010)
Nguyen, T., Armitage, G.: A survey of techniques for internet traffic classification using machine learning. Commun. Surv. Tutor. IEEE 10(4), 56–76 (2008)
Callado, A., Kamienski, C., Szabo, G., Gero, B., Kelner, J., Fernandes, S., Sadok, D.: A survey on internet traffic identification. Commun. Surv. Tutor. IEEE 11(3), 37–52 (2009)
Bonfiglio, D., Mellia, M., Meo, M., Rossi, D., Tofanelli, P.: Revealing skype traffic: when randomness plays with you. SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. 37(4), 37–48 (2007)
Freire, E., Ziviani, A., Salles, R.: Detecting skype flows in web traffic. In: Network Operations and Management Symposium. NOMS 2008, pp. 89–96. IEEE (2008)
Este, A., Gringoli, F., Salgarelli, L.: Support vector machines for TCP traffic classification. Comput. Netw. 53(14), 2476–2490 (2009)
Erman, J., Mahanti, A., Arlitt, M., Cohen, I., Williamson, C.: Offline/realtime traffic classification using semi-supervised learning. Perform. Eval. 64, 1194–1213 (2007)
Bacquet, C., Gumus, K., Tizer, D., Zincir-Heywood, A., Heywood, M.I.: A comparison of unsupervised learning techniques for encrypted traffic identification. J. Inf. Assur. Secur. 5, 464–472 (2010)
Iliofotou, M., Kim, H.C., Faloutsos, M., Mitzenmacher, M., Pappu, P., Varghese, G.: Graption: a graph-based p2p traffic classification framework for the internet backbone. Comput. Netw. 55(8), 1909–1920 (2011)
Park, J., Tyan, H.-R., Kuo, C.-C.: Ga-based internet traffic classification technique for QoS provisioning. In: Intelligent Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing. IIH-MSP ’06. International Conference on, pp. 251–254 (2006)
Hu, Y., Chiu, D.-M., Lui, J.C.S.: Profiling and identification of p2p traffic. Comput. Netw. 53(6), 849–863 (2009)
Wright, C.V., Coull, S.E., Monrose, F.: Traffic morphing: an efficient defense against statistical traffic analysis. In: Proceedings of the Network and Distributed Security Symposium—NDSS ’09 (2009)
Wright, C.V., Ballard, L., Monrose, F., Masson, G.M.: Language identification of encrypted VoIP traffic: Alejandra y roberto or alice and bob? In: Proceedings of 16th USENIX Security Symposium on USENIX Security Symposium, pp. 4:1–4:12. USENIX Association, Berkeley, CA, USA (2007)
Liberatore, M., Levine, B.N.: Inferring the source of encrypted http connections. In: Proceedings of the 13th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security, CCS ’06, pp. 255–263. ACM, New York, NY, USA (2006)
Baset, S.A., Schulzrinne, H.G.: An analysis of the skype peer-to-peer internet telephony protocol. In: INFOCOM 2006. 25th IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications. Proceedings, pp. 1–11 (2006)
Bonfiglio, D., Mellia, M., Meo, M., Ritacca, N., Rossi, D.: Tracking down skype traffic. In: INFOCOM 2008. The 27th Conference on Computer Communications, pp. 261–265. IEEE (2008)
De Cicco, L., Mascolo, S., Palmisano, V.: Skype video responsiveness to bandwidth variations. In: Proceedings of the 18th International Workshop on Network and Operating Systems Support for Digital Audio and Video (NOSSDAV ’08), pp. 81–86. ACM, New York, NY, USA (2008)
Barbosa, R., Callado, A., Kamienski, C., Fernandes, S., Mariz, D., Sadok, D.: Performance evaluation of P2P VoIP application. In: Proceedings of the 17th International Workshop on Network and Operating Systems Support for Digital Audio and Video (NOSSDAV ’07), IL, USA (2007)
IETF, http://www3.ietf.org/proceedings/97apr/97apr-final/xrtftr70.htm
Arndt, D.: How to calculating flow statistics using netmate, http://dan.arndt.ca/nims/calculating-flow-statistics-using-netmate/ (last Accessed Sept 2011)
Quinlan, J.: see5-info, http://www.rulequest.com/see5-info.html (last Accessed July 2010)
Alpaydin, E.: Introduction to Machine Learning. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA (2004)
Lichodzijewski, P., Heywood, M.I.: Managing team-based problem solving with symbiotic bid-based genetic programming. In: Proceedings of the Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference, pp. 363–370 (2008)
de Jong, E.: A monotonic archive for pareto-coevolution. Evol. Comput. 15(1), 61–93 (2007)
T. U. of Waikato, WEKA software, http://www.cs.waikato.ac.nz/ml/weka/
SBB-GP, Symbiotic bid-based (sbb) paradigm, http://www.cs.dal.ca/mheywood/Code/SBB/SCM.9.r20081212.tar.gz (last Accessed March 2008)
PacketShaper, http://www.packeteer.com/products/p-acketshaper/ (last Accessed March 2008). CalladoBetter2010
Traces, S.: Telecommunication networks group—politecnico ditorino, http://tstat.tlc.polito.it/traces-skype.shtml (last Accessed August 2009)
Alshamamri, R.: Downloading the NIMS data sets, http://web.cs.dal.ca/riyad/Site/Download.html (last Accessed Sept 2011)
Wireshark, http://www.wireshark.org/ (last Accessed Sept 2008)
Peeker, N.: Netpeeker, http://www.net-peekerCalladoBetter2010.com (last Accessed Oct 2009)
Signalogic, Speech codec wav samples, http://www.signalogic.com/index.pl?page=codec_samples (last Accessed Oct 2009)
Zimmermann, P.: The Zfone project, http://zfoneproject.com/ (last Accessed Oct 2009)
Zimmermann, E.P., Johnston, A., Callas, J.: Zrtp: media path key agreement for secure rtp, http://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-zimmermann-avt-zrtp-17 (2010)
P. T. C. Inc, Primus softphone client, http://www.primus.ca/en/residential/talkbroadband/talkBroadband-softphone.htm (last Accessed Oct 2009)
ETSI, Digital cellular telecommunications system (phase 2+), general packet radio service (gprs), overall description of the gprs radio interface, stage 2 (gsm 03.64, version 7.0.0, release 1999)
BirdsSoft, Vpn-x, http://birdssoft.com/ (last Accessed March 2011)
Kent, S., Atkinson, R.: Security architecture for the internet protocol, http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2401.txt (1998)
MAWI, Mawi working group traffic archive, http://tracer.csl.sony.co.jp/mawi/
Fink, R., Hinden, R.: 6bone (IPv6 testing address allocation), http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3701 (2004)
Ehlert, S., Petgang, S., Magedanz, T., Sisalem, D.: Analysis and signature of Skype VoIP session traffic. In: CIIT 2006: 4th IASTED International Conference on Communications, Internet, and Information Technology, pp. 83–89 (2006)
Skype, Skype garage, http://blogs.skype.com/garage/windows/ (last Accessed Sept 2011)
Valin, J.-M., Montgomery, C.: Improved noise weighting in CELP coding of speech—applying the Vorbis psychoacoustic model to speex, http://www.speex.org (2006)
N. software, Switch audio converter for mac, http://www.nch.com.au/switch/index.html (last Accessed May 2011)
OpenDPI, the open source version of ipoque’s dpi engine, http://www.opendpi.org/ (last Accessed April 2011)
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by a Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) grant. This work is conducted as part of the Dalhousie NIMS Lab at http://projects.cs.dal.ca/projectx/.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alshammari, R., Zincir-Heywood, A.N. How Robust Can a Machine Learning Approach Be for Classifying Encrypted VoIP?. J Netw Syst Manage 23, 830–869 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10922-014-9324-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10922-014-9324-6