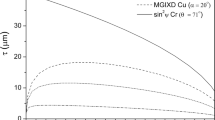
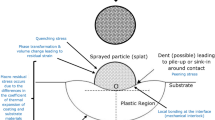
Abstract
Diffraction is a powerful tool for investigation of residual as well as applied stresses in engineering materials and components. Both X-ray and neutron diffraction can be used for this purpose. The interest in neutron stress analysis stems from the high penetrating power of neutrons when compared to laboratory X-ray sources, i.e. several cm instead of a few tens of µm in metallic materials. This contribution gives an overview on current instrumental and methodical developments for non-destructive through surface strain measurements, which bridges the gap between X-rays and neutrons analysis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hofmann, M., Schneider, R., Seidl, G.A., Rebelo Kornmeier, J., Wimpory, R., Garbe, U., Brokmeier, H.G.: The new materials science diffractometer STRESS-SPEC at FRM-II. Physica B 385–386, 1035–1037 (2006)
Brokmeier, H.G., Gan, W.M., Randau, C., Völler, M., Rebelo Kornmeier, J., Hofmann, M.: Texture analysis at neutron diffractometer STRESS-SPEC. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 642, 87–92 (2011)
Zinth, V., von Lüders, C., Hofmann, M., Hattendorff, J., Buchberger, I., Erhard, S., Rebelo Kornmeier, J., Jossen, A., Gilles, R.: Lithium plating in lithium-ion batteries at sub-ambient temperatures investigated by in situ neutron diffraction. J. Power Sources 271, 152–159 (2014)
Cavaliere, P. (ed.): Chapter: 16. In: Cold-Spray Coatings. Recent Trends and Future Perspectives, 1st edn. Springer, Cham (2018)
Vladimir, L., Andrew, V., Valarezo, A., Sanjay, S.: Neutron through-thickness stress measurements in coatings with high spatial resolution. Mater. Sci. Forum 905, 165–173 (2017)
Ramjaun, T.I., Stone, H.J., Karlsson, L., Gargouhri, M.A., Dalaei, K., Moat, R.J., Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H.: Surface residual stresses in multipass welds produced using low transformation temperature filler alloys. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 19(7), 623–630 (2014)
Gibmeier, J., Back, H.C., Mutter, M., Vollert, F., Vaßen, R., Rebelo Kornmeier, J., Mücke, R., Vaßen, R.: Study of stability of microstructure and residual strain after thermal loading of plasma sprayed YSZ by through surface neutron scanning. Physica B 551, 69–78 (2018)
Hutchings, M.T., Withers, P.J., Holden, T.M., Lorentzen, T.: Introduction to the Characterization of Residual Stress by Neutron Diffraction. Taylor and Francis, London (2005)
Webster, P.J., Mills, G., Wang, X.D., Kang, W.P., Holden, T.M.: Impediments to efficient through-surface strain scanning. J. Neutron Res. 3, 223–240 (1995)
Rebelo Kornmeier, J., Gibmeier, J., Hofmann, M.: Minimization of spurious strains by using a Si bent-perfect-crystal monochromator: neutron surface strain scanning of a shot-peened sample. Meas. Sci. Technol. 22, 065705 (2011)
Šaroun, J., Rebelo Kornmeier, J., Hofmann, M., Mikula, P., Vrana, M.: Analytical model for neutron diffraction peak shifts due to the surface effect. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 46, 628–638 (2013)
Köhler, H., Rajput, R., Kahzan, P., Rebelo Kornmeier, J.: On the influence of laser cladding and post-processing strategies on residual stresses in steel specimens. Phys. Procedia 56, 250–261 (2014)
Coppola, R., Crescenzi, F., Gan, W., Hofmann, M., Lie, M., Visca, E., You, J.-H.: Neutron diffraction measurement of residual stresses in an ITER-like tungsten-monoblock type plasma-facing component. Fusion Eng. Des. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fusengdes.2019.01.059
Šaroun, J., Rebelo Kornmeier, J., Gibmeier, J., Hofmann, M.: Treatment of spatial resolution effects in neutron residual strain scanning. Physica B (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2018.01.013
Pirling, T.: Neutron strain scanning at interfaces: an optimised beam optics to reduce the surface effect. Mater. Sci. Forum 347–349, 107–112 (2000)
Šaroun, J., Kulda, J.: Raytrace of neutron optical systems with RESTRAX. In: Modern Developments in X-Ray and Neutron Optics. Springer Series in Optical Sciences, vol. 137, pp. 57–68. Springer, Berlin (2008)
Defendi, I., Egerland, S., Kastenmüller, A., Mühlbauer, M., Panradl, M., Schöffel, T., Zeitelhack, K.: FRM II Annual Report (2005)
Eigenmann, B., Macherauch, E.: Rontgenographische Untersuchung von Spannungszustanden in Werkstoffen. Mater.-wiss. Werkst. 27, 426–437 (1996)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the funding by the German Research Foundation (DFG) within the Project HO 3322/2-1, HO3322/2-2 and Czech Science Foundation Project No. 16-08803J, and by the German Research Foundation (DFG) within the Project HO 3322/4-1 and GI 376/11-1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rebelo Kornmeier, J., Hofmann, M., Gan, W.M. et al. Non-destructive Neutron Surface Residual Stress Analysis. J Nondestruct Eval 38, 79 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-019-0617-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-019-0617-2