Abstract
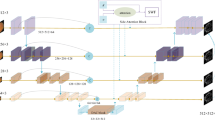
Precise segmentation of retinal vessels is crucial for the prevention and diagnosis of ophthalmic diseases. In recent years, deep learning has shown outstanding performance in retinal vessel segmentation. Many scholars are dedicated to studying retinal vessel segmentation methods based on color fundus images, but the amount of research works on Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscopy (SLO) images is very scarce. In addition, existing SLO image segmentation methods still have difficulty in balancing accuracy and model parameters. This paper proposes a SLO image segmentation model based on lightweight U-Net architecture called MBRNet, which solves the problems in the current research through Multi-scale Bottleneck Residual (MBR) module and attention mechanism. Concretely speaking, the MBR module expands the receptive field of the model at a relatively low computational cost and retains more detailed information. Attention Gate (AG) module alleviates the disturbance of noise so that the network can concentrate on vascular characteristics. Experimental results on two public SLO datasets demonstrate that by comparison to existing methods, the MBRNet has better segmentation performance with relatively few parameters.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used in this paper are public datasets. The IOSTAR and RC-SLO for this study can be found at https://www.retinacheck.org.
References
Mookiah, M. R. K., Acharya, U. R., Chua, C. K., Lim, C. M., Ng, E. Y. K., and Laude, A., Computer-aided diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy: a review. Computers in Biology and Medicine 43(12): 2136-2155, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2013.10.007
Irshad, S., and Akram, M. U., Classification of retinal vessels into arteries and veins for detection of hypertensive retinopathy. In: 2014 Cairo International Biomedical Engineering Conference (CIBEC), pp. 133-136: IEEE, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1109/CIBEC.2014.7020937
Kim, Y. Y., and Yoo, E., Author response: diagnostic ability of retinal arteriolar diameter measurements in glaucoma. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science 57(4): 2167-2167, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.16-19352
Huang, W., Guo, F., and Yan, Y., Retinal vessel segmentation algorithm based on attention mechanism. In: 2022 IEEE Intl Conf on Dependable, Autonomic and Secure Computing, Intl Conf on Pervasive Intelligence and Computing, Intl Conf on Cloud and Big Data Computing, Intl Conf on Cyber Science and Technology Congress (DASC/PiCom/CBDCom/CyberSciTech), pp. 1-5: IEEE, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/DASC/PiCom/CBDCom/Cy55231.2022.9927960
Zhuang, J., LadderNet: multi-path networks based on U-Net for medical image segmentation. arXiv: 1810.07810, 2018. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1810.07810
Liu, Y., Shen, J., Yang, L., Bian, G., and Yu, H., ResDO-UNet: a deep residual network for accurate retinal vessel segmentation from fundus images. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 79: 104087, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2022.104087
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., and Brox, T., U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), pp. 234-241: Springer, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4 28
Qu, Z., Zhuo, L., Cao, J., Li, X., Yin, H., and Wang, Z., TP-Net: two-path network for retinal vessel segmentation. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 27(4): 1979-1990, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2023.3237704
Huang, K. W., Yang, Y. R., Huang, Z. H., Liu, Y. Y., and Lee, S. H., Retinal vascular image segmentation using improved UNet based on residual module. Bioengineering 10(6): 722, 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10060722
Shi, Z., Li, Y., Zou, H., and Zhang, X., TCU-Net: transformer embedded in convolutional u-shaped network for retinal vessel segmentation. Sensors 23(10): 4897, 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104897
Webb, R. H., Hughes, G. W., and Pomerantzeff, O., Flying spot TV ophthalmoscope. Applied Optics 19(17): 2991-2997, 1980. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.19.002991
Abbasi-Sureshjani, S., Smit-Ockeloen, I., Zhang, J., and Ter Haar Romeny, B., Biologically-inspired supervised vasculature segmentation in SLO retinal fundus images. In: Image Analysis and Recognition: 12th International Conference (ICIAR), pp. 325-334: Springer, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-20801-5_35
Zhang, J., Dashtbozorg, B., Bekkers, E., Pluim, J. P., Duits, R., and ter Haar Romeny, B. M., Robust retinal vessel segmentation via locally adaptive derivative frames in orientation scores. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 35(12): 2631-2644, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2016.2587062
Zhao, Y., Zheng, Y., Liu, Y., Zhao, Y., Luo, L., Yang, S., Na, T., Wang, Y., and Liu, J., Automatic 2-D/3-D vessel enhancement in multiple modality images using a weighted symmetry filter. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 37(2): 438-450, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2017.2756073
Srinidhi, C. L., Aparna, P., and Rajan, J., A visual attention guided unsupervised feature learning for robust vessel delineation in retinal images. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 44: 110-126, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2018.04.016
Wang, D., Haytham, A., Pottenburgh, J., Saeedi, O., and Tao, Y., Hard attention net for automatic retinal vessel segmentation. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 24(12): 3384-3396, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2020.3002985
Li, X., Jiang, Y., Li, M., and Yin, S., Lightweight attention convolutional neural network for retinal vessel image segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 17(3): 1958-1967, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2020.2993842
Guo, C., Szemenyei, M., Yi, Y., Xue, Y., Zhou, W., and Li, Y., Dense residual network for retinal vessel segmentation. In: ICASSP 2020 - 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 1374-1378: IEEE, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP40776.2020.9054290
Guo, S., CSGNet: cascade semantic guided net for retinal vessel segmentation. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 78: 103930, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2022.103930
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., and Sun, J., Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 770-778: IEEE, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90
Laibacher, T., Weyde, T., and Jalali, S., M2U-Net: effective and efficient retinal vessel segmentation for real-world applications. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), pp. 115-124: IEEE, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW.2019.00020
Aurangzeb, K., Haider, S. I., and Alhussein, M., Retinal vessel segmentation based on the Anam-Net model. Elektronika ir Elektrotechnika 28(3): 54-64, 2022. https://doi.org/10.5755/j02.eie.30594
Haider, S. I., Aurangzeb, K., and Alhussein, M., Modified Anam-Net based lightweight deep learning model for retinal vessel segmentation. Computers, Materials & Continua 73(1):1501-1526. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmc.2022.025479
Hu, J., Shen, L., and Sun, G., Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7132-7141: IEEE, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00745
Wang, J., Li, X., Lv, P., and Shi, C., SERR-U-Net: squeeze-and-excitation residual and recurrent block-based U-Net for automatic vessel segmentation in retinal image. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine 2021: 5976097, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5976097
Xia, H., Wu, L., Lan, Y., Li, H., and Song, S., HRNet: a hierarchical recurrent convolution neural network for retinal vessel segmentation. Multimedia Tools and Applications 81(28): 39829-39851, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-12696-4
Oktay, O., Schlemper, J., Folgoc, L. L., Lee, M., Heinrich, M., Misawa, K., Mori, K., McDonagh, S., Hammerla, N. Y., Kainz, B., and et al., Attention U-Net: learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv: 1804.03999, 2018. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1804.03999
Fu, X., and Zhao, N., AGC-UNet: a global context feature fusion method based on u-net for retinal vessel segmentation. In: 2022 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Information Communication and Software Engineering (ICICSE), pp. 94-99: IEEE, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICICSE55337.2022.9828894
Tang, X., Zhong, B., Peng, J., Hao, B., and Li, J., Multi-scale channel importance sorting and spatial attention mechanism for retinal vessels segmentation. Applied Soft Computing 93: 106353, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106353
Hu, K., Zhang, D., Xia, M., Qian, M., and Chen, B., LCDNet: light-weighted cloud detection network for high-resolution remote sensing images. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 15: 4809-4823, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3181303
Tao, X., Dang, H., Zhou, X., Xu, X., and Xiong, D., A lightweight network for accurate coronary artery segmentation using X-Ray angiograms. Frontiers in Public Health 10: 892418, 2022. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.892418
Ding, X., Guo, Y., Ding, G., and Han, J., ACNet: strengthening the kernel skeletons for powerful CNN via asymmetric convolution blocks. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 1911-1920: IEEE, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00200
Chollet, F., Xception: deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1800-1807: IEEE, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.195
Alom, M. Z., Hasan, M., Yakopcic, C., Taha, T. M., and Asari, V. K., Recurrent residual convolutional neural network based on U-Net (R2U-Net) for medical image segmentation. arXiv: 1802.06955, 2018. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1802.06955
Li, X., Chen, H., Qi, X., Dou, Q., Fu, C. W., and Heng, P. A., H-DenseUNet: hybrid densely connected UNet for liver and tumor segmentation from CT volumes. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 37(12): 2663-2674, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2018.2845918
Wang, Q., Wu, B., Zhu, P., Li, P., Zuo, W., and Hu, Q. ECA-Net: efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 11531-11539: IEEE, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01155
Funding
This research was funded by Project supported by the Education Department of Hainan Province, (Grant No. Hnjg2021ZD-10).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Peipei Li; Methodology: Peipei Li; Formal analysis and investigation: Peipei Li; Writing - original draft preparation: Peipei Li, Zhao Qiu, Yuefu Zhan; Writing - review and editing: Zhao Qiu, Yuefu Zhan, Huajing Chen, Sheng Yuan; Funding acquisition: Zhao Qiu; Resources: Zhao Qiu; Supervision: Zhao Qiu. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., Qiu, Z., Zhan, Y. et al. Multi-scale Bottleneck Residual Network for Retinal Vessel Segmentation. J Med Syst 47, 102 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-023-01992-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-023-01992-7