Abstract
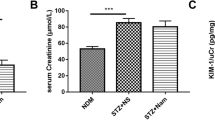
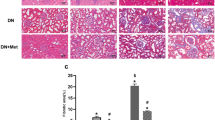
The anti-aging gene klotho is closely related to kidney disease, and an increase in the level of the klotho protein inhibits the progression of various kidney diseases. According to clinical studies, dimethyl-biguanide hydrochloride (DMBG) reduces the urinary protein level in patients with diabetic nephropathy to protect the kidney, but the specific renoprotective mechanism remains unclear. In this study, the application of DMBG partially alleviates the pathological changes in the kidneys of db/db mice, increases the level of the klotho protein in the blood, urine and kidney tissues of the mice, and reduces the levels of the mTOR and p-mTOR proteins. The effects of high glucose and DMBG on klotho and the mTOR pathway in MDCK cells were analyzed at the cellular level. High glucose stimulation activates mTOR pathway and decreases the activity of MDCK cells. DMBG decreases the level of the mTOR protein and reverses the effect of hyperglycaemic stimulation on the activity of MDCK cells. After inhibiting the expression of the klotho protein, DMBG is unable to decrease the level of the mTOR protein. Therefore, klotho plays an important role in the mechanism by which DMBG inhibits the mTOR pathway to protect renal function.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wan, Q., Xu, Y., and Dong, E., Diabetic nephropathy research in China: Data analysis and review from the National Natural Science Foundation of China. Journal of Diabetes 7:307–314, 2015.
Wang, L., Gao, P., Zhang, M. et al., Prevalence and ethnic pattern of diabetes and prediabetes in China in 2013. JAMA 317:2515–2523, 2017.
Alicic, R. Z., Rooney, M. T., and Tuttle, K. R., Diabetic kidney disease: Challenges, progress, and possibilities. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 12:2032–2045, 2017.
Allison, S. J., and disease, C. k., Study warns of burgeoning health burden of CKD in China. Nature Reviews Nephrology 8:251, 2012.
De Boer, I. H., Afkarian, M., and Tuttle, K. R., The surging tide of diabetes: Implications for nephrology. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 67:364–366, 2016.
Kuro-o, M., Matsumura, Y., Aizawa, H. et al., Mutation of the mouse klotho gene leads to a syndrome resembling ageing. Nature 390:45–51, 1997.
Nabeshima, Y. I., Toward a better understanding of klotho. Science of Aging Knowledge Environment 2006:pe11, 2006.
Kurosu, H., Yamamoto, M., Clark, J. D. et al., Suppression of aging in mice by the hormone Klotho. Science 309:1829–1833, 2005.
Xu, Y., Peng, H., and Ke, B., α-klotho and anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease patients: A new perspective. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 14:5691–5695, 2017.
Zou, D., Wu, W., He, Y. et al., The role of klotho in chronic kidney disease. BMC Nephrology 19:285, 2018.
Lin, Y., Kuro-o, M., and Sun, Z., Genetic deficiency of anti-aging gene Klotho exacerbates early nephropathy in STZ-induced diabetes in male mice. Endocrinology 154:3855–3863, 2013.
Ahmad, J., Management of diabetic nephropathy: Recent progress and future perspective. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews 9:343–358, 2015.
Ina, K., Kitamura, H., Nagai, K. et al., Ultrastructural and functional changes of the proximal tubular epithelial cells in the renal cortex from spontaneously diabetic KKAy mice. Microscopy 48:443–448, 1999.
Thomas, M. C., Brownlee, M., Susztak, K. et al., Diabetic kidney disease. Nature Reviews Disease Primers 1:15018, 2015.
Shahbazian, H., and Rezaii, I., Diabetic kidney disease; review of the current knowledge. Journal of Renal Injury Prevention 2:73–80, 2013.
Alicic, R. Z., Johnson, E. J., and Tuttle, K. R., Inflammatory mechanisms as new biomarkers and therapeutic targets for diabetic kidney disease. Advances in Chronic Kidney Disease 25:181–191, 2018.
Bhattacharjee, N., Barma, S., Konwar, N. et al., Mechanistic insight of diabetic nephropathy and its pharmacotherapeutic targets: An update. European Journal of Pharmacology 791:8–24, 2016.
Acknowledgements
This study was partially supported by the Youth Foundation of the Commission of Health and Family Planning of Wuxi under grant Q201654.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this paper to declare.
Human studies
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Patient Facing Systems
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, J., Wang, L., Sun, Z. et al. Basic Research in Diabetic Nephropathy Health Care: A study of the Renoprotective Mechanism of Metformin. J Med Syst 43, 266 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-019-1412-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-019-1412-4