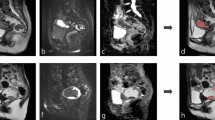
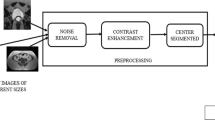
Abstract
With the development of medical technology in China, new difficulties are gradually emerging in traditional medicine. Cervical cancer MRI image segmentation technology based on wireless network is one of the most famous means. But the traditional technology is not strong enough for information processing and analysis. Manual data processing alone may lead to errors in data processing and so on. Therefore, this research was aimed at the MRI image segmentation technology of cervical cancer based on wireless network, using depth learning algorithm to calculate and analyze. Through this kind of wireless network and the computer algorithm form, the data processing ability can be improved and increase the data processing ability be increased.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cai, Y., Yu, F. R., Liang, C. et al., Software-defined device-to-device (D2D) communications in virtual wireless networks with imperfect network state information (NSI)[J]. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 65(9):7349–7360, 2016.
Gong, X., Duan, L., Chen, X. et al., When social network effect meets congestion effect in wireless networks: Data usage equilibrium and optimal pricing[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 35(2):449–462, 2017.
El-Hihi, M., Attar, H., Solyman, A. A. A. et al., Network coding cooperation performance analysis in wireless network over a lossy channel, M users and a destination scenario[J]. Commun. Netw. 08(4):257–280, 2016.
Gong, X., Trogh, J., Braet, Q. et al., Measurement-based wireless network planning, monitoring, and reconfiguration solution for robust radio communications in indoor factories[J]. IET Sci. Meas. Technol. 10(4):375–382, 2016.
Zhu, L., Yu, F. R., Tang, T. et al., Handoff performance improvements in an integrated train-ground communication system based on wireless network virtualization[J]. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. PP(99):1–14, 2017.
Prahs, P., Radeck, V., Mayer, C. et al., OCT-based deep learning algorithm for the evaluation of treatment indication with anti-vascular endothelial growth factor medications[J]. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol.:1–8, 2017.
Brzezicki, M., and Kobetic, M., Using artificial intelligence deep learning algorithm to evaluate and guide the quality improvement work in neurosurgical practice[J]. Int. J. Surg. 47:S61, 2017.
Anitha, J., Reddy, P. V. G. D. P., and Babu, M. S. P., Error tolerant global search incorporated with deep learning algorithm to automatic Hindi text summarization[J]. International Journal of Business Intelligence & Data Mining 1(1):1, 2017.
Gulshan, V., Peng, L., Coram, M. et al., Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm for detection of diabetic retinopathy in retinal fundus photographs[J]. Jama 316(22):2402, 2016.
Ibragimov, B., Pernuš, F., Strojan, P. et al., Development of a novel deep learning algorithm for autosegmentation of clinical tumor volume and organs at risk in head and neck radiation therapy planning[J]. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 96(2S):S226, 2016.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All the authors of this article are aware of the content.
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest in this article.
Human and animal studies
This article does not cover human participants and/or animal studies.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Image & Signal Processing
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, P., Sun, G. & Wei, S. Application of Deep Learning Algorithm in Cervical Cancer MRI Image Segmentation Based on Wireless Sensor. J Med Syst 43, 156 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-019-1284-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-019-1284-7