Abstract
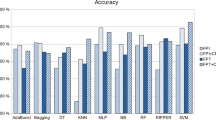
Early and accurate diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease (PD) remains challenging. Neuropathological studies using brain bank specimens have estimated that a large percentages of clinical diagnoses of PD may be incorrect especially in the early stages. In this paper, a comprehensive computer model is presented for the diagnosis of PD based on motor, non-motor, and neuroimaging features using the recently-developed enhanced probabilistic neural network (EPNN). The model is tested for differentiating PD patients from those with scans without evidence of dopaminergic deficit (SWEDDs) using the Parkinson’s Progression Markers Initiative (PPMI) database, an observational, multi-center study designed to identify PD biomarkers for diagnosis and disease progression. The results are compared to four other commonly-used machine learning algorithms: the probabilistic neural network (PNN), support vector machine (SVM), k-nearest neighbors (k-NN) algorithm, and classification tree (CT). The EPNN had the highest classification accuracy at 92.5 % followed by the PNN (91.6 %), k-NN (90.8 %) and CT (90.2 %). The EPNN exhibited an accuracy of 98.6 % when classifying healthy control (HC) versus PD, higher than any previous studies.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya, U. R., Vidya, S., Bhat, S., Adeli, H., and Adeli, A., Computer-aided diagnosis of alcoholism-related EEG signals. Epilepsy Behav. 41:257–263, 2014.
Adeli, H., Ghosh-Dastidar, S., and Dadmehr, N., Alzheimer’s disease and models of computation: Imaging, classification, and neural models. J. Alzheimers Dis. 7(3):187–199, 2005.
Adeli, H., Ghosh-Dastidar, S., and Dadmehr, N., Alzheimer’s disease: Models of computation and analysis of EEGs. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 36(3):131–140, 2005.
Adeli, H., Ghosh-Dastidar, S., and Dadmehr, N., A wavelet-chaos methodology for analysis of EEGs and EEG subbands to detect seizure and epilepsy. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 54(2):205–211, 2007.
Adeli, H., Ghosh-Dastidar, S., and Dadmehr, N., A Spatio-temporal wavelet-chaos methodology for EEG-based diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 444(2):190–194, 2008.
Adeli, H., and Hung, S. L., Machine learning - neural networks, genetic algorithms, and fuzzy sets. Wiley, New York, 1995.
Aerts, M. B., Esselink, R. A., Post, B., van de Warrensburg, P. B., and Bloem, B. R., Improving the diagnostic accuracy in parkinsonism: A three-pronged approach. Pract. Neurol. 12(2):77–87, 2012.
Ahmadlou, A., Adeli, H., and Adeli, A., Fractality and a wavelet-Chao methodology for EEG-based diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 25(1):85–92, 2011.
Ahmadlou, M., and Adeli, H., Enhanced probabilistic neural networks with local decision circles: A robust classifier. Integr. Comput. Aided. Eng. 17:197–210, 2010.
Ahmadlou, M., and Adeli, H., Wavelet-synchronization methodology: A new approach for EEG-based diagnosis of ADHD. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 41(1):1–10, 2010.
Ahmadlou, M., Adeli, H., and Adeli, A., Fractality and a wavelet-chaos-neural network methodology for EEG-based diagnosis of autistic spectrum disorder. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 7(5):328–333, 2010.
Ahmadlou, M., Adeli, H., and Adeli, A., Fractality analysis of frontal brain in major depressive disorder. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 85(2):206–211, 2012.
Ahmadlou, M., Adeli, H., and Adeli, A., Graph theoretical analysis of organization of functional brain networks in ADHD. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 43(1):5–13, 2012.
Ahmadlou, M., Adeli, H., and Adeli, A., Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Relative Convergence (STARC) of EEGs reveals differences between brain dynamics of depressive women and men. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 44:175–181, 2013.
Ahmadlou, M., Adeli, A., Bajo, R., and Adeli, H., Complexity of functional connectivity networks in mild cognitive impairment patients during a working memory task. Clin. Neurophysiol. 125(4):694–702, 2013.
Alexandridis, A., Evolving RBF neural networks for adaptive soft-sensor design. Int. J. Neural Syst. 23(6):1350029, 2013 (14 pages).
Babu, G. S., Suresh, S., and Mahanand, B. S., A novel PBL-McRBFN-RFE approach for identification of critical brain regions responsible for Parkinson’s disease. Expert Syst. Appl. 41(2):478–488, 2014.
Badawy, R. A. B., Vogrin, S. J., Lai, A., and Cook, M. J., On the midway to epilepsy; Are cortical excitability measures in patients with isolated seizures normal? Int. J. Neural Syst. 24(2):1430002, 2014 (7 pages).
Bauer, P. R., Kalitzin, S., Zijlmans, M., Sander, J. W., and Visser, G., Cortical excitability as a clinical marker in epilepsy: A review of the clinical application of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation. Int. J. Neural Syst. 24(2):1430001, 2014 (21 pages).
Butcher, J. B., Day, C. R., Austin, J. C., Haycock, P. W., Verstraeten, D., and Schrauwen, B., Defect detection in reinforced concrete using random neural architectures. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 29(3):191–20, 2014.
Castillo, E., Peteiro-Barral, D., Guijarro Berdinas, B., and Fontenla-Romero, O., Distributed one-class support vector machine. Int. J. Neural Syst. 25:7, 2015 (17 pages).
Davie, C. A., A review of Parkinson’s disease. Br. Med. Bull. 86(1):109–127, 2008.
De Dombal, F. T., Leaper, D. J., Staniland, J. R., McCann, A. P., and Horrocks, J. C., Computer-aided diagnosis of acute abdominal pain. Br. Med. J. 2(5804):9–13, 1972.
De Lau, L. M., and Breteler, M. M., Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 5(6):525–535, 2006.
De Rosa, A., Carducci, C., Carducci, C., Peluso, S., Lieto, M., Mazzella, A., Saccà, F., Brescia Morra, V., Pappatà, S., Leuzzi, V., and De Michele, G., Screening for dopa-responsive dystonia in patients with Scans Without Evidence of Dopaminergic Deficiency (SWEDD). J. Neurol. 261(11):2204–2208, 2014.
Doty, R. L., Shaman, P., Kimmelman, C. P., and Dann, M. S., University of Pennsylvania smell identification test: A rapid quantitative olfactory function test for the clinic. Laryngoscope 94:176–178, 1984.
Goetz, C. G., Tilley, B. C., Shaftman, S. R., Stebbins, G. T., Fahn, S., Martinez-Martin, P., Poewe, W., LaPelle, N., and Movement Disorder Society UPDRS Revision Task Force, Movement Disorder Society-sponsored revision of the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS): scale presentation and clinimetric testing results. Mov. Disord. 23(15):2129–2170, 2008.
Illan, I. A., Gorrz, J. M., Ramirez, J., Segovia, F., Jimenez-Hoyuela, J. M., and Ortega Lozano, S. J., Automatic assistance to Parkinson’s disease diagnosis in DaTSCAN SPECT imaging. Med. Phys. 39(10):5971–5980, 2012.
Jankovic, J., Parkinson’s disease: Clinical features and diagnosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 79(4):368–376, 2008.
Kwon, M., Kavuri, S., and Lee, M., Action-perception cycle learning for incremental emotion recognition in a movie clip using 3D fuzzy GIST based on visual and EEG signals. Integr. Comput. Aided Eng. 21(3):295–310, 2014.
Lee, M. J., Kim, S. L., Lyoo, C. H., and Lee, M. S., Kinematic analysis in patients with Parkinson’s disease and SWEDD. J Park. Dis. 4(3):421–430, 2014.
Li, D., Xu, L., Goodman, E., Xu, Y., and Wu, Y., Integrating a statistical background-foreground extraction algorithm and SVM classifier for pedestrian detection and tracking. Integr. Comput. Aided Eng. 20(3):201–216, 2013.
Lin, L. C., Ouyang, C. S., Chiang, C. T., Yang, R. C., Wu, R. C., and Wu, H. C., Early prediction of medication refractoriness in children with idiopathic epilepsy based on scalp EEG analysis. Int. J. Neural Syst. 24(7):1450023, 2014 (16 pages).
Marek, K., Jennings, D., Lasch, S., Siderowf, A., Tanner, C., Simuni, T., Coffey, C., and Taylor, P., The Parkinson Progression Marker Initiative (PPMI). Prog. Neurobiol. 95(4):629–635, 2011.
Liu, C., Wang, J., Chen, Y. Y., Deng, B., Wei, X. L., and Li, H. Y., Closed-loop control of the thalamocortical relay neuron’s Parkinsonian state based on slow variable. Int. J. Neural Syst. 23(4):1350017, 2013 (13 pages).
Luo, C., Zhang, Y., Cao, W., Huang, Y., Yang, F., Wang, J., Tu, S., Wang, X., and Yao, D., Altered Structural and functional feature of striatocortical circuit in benign epilepsy with cectrotemporal spikes. Int. J. Neural Syst. 25(6):1550027, 2015 (13 pages).
Martinez-Murcia, F. J., Gorriz, J. M., Ramirez, J., Illan, I. A., and The Parkinson’s Progression Markers Initiative, Automated Detection of Parkinsonism Using Significance Measures and Component Analysis in DatSCAN imaging. Neurocomputing 126:58–70, 2014.
Mian, O. S., Schneider, S. A., Schwingenschuh, P., Bhatia, K. P., and Day, B. L., Gait in SWEDDs patients: comparison with Parkinson’s disease patients and healthy controls. Mov. Disord. 26(7):1266–1273, 2011.
Parazzini, M., Fiocchi, S., Liorni, I., Priori, A., and Ravazzani, P., Computational modelling of transcranial direct current stimulation in the child brain: Implications for the treatment of refractory childhood focal epilepsy. Int. J. Neural Syst. 24(2):1430006, 2014 (10 pages).
Prashanth, R., Roy, S. D., Mandal, P. K., and Ghosh, S., Automatic classification and prediction models for early Parkinson’s disease diagnosis from SPECT imaging. Expert Syst. Appl. 41:3333–3342, 2014.
Salvatore, C., Cerasa, A., Augimeri, A., Quattrone, A., Castiglioni, I., Gallivanone, F., Gilardi, M. C., and Morelli, M., Machine learning on brain MRI data for differential diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease and progressive supranuclear palsy. J. Neurosci. Methods 222:230–237, 2014.
Sankari, Z., and Adeli, H., Probabilistic neural networks for diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease using conventional and wavelet coherence. J. Neurosci. Methods 197(1):165–170, 2011.
Sankari, Z., Adeli, H., and Adeli, A., Intrahemispheric, interhemispheric and distal EEG coherence in Alzheimer’s disease. Clin. Neurophysiol. 122(5):897–906, 2011.
Sankari, Z., Adeli, H., and Adeli, A., Wavelet coherence model for diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Clin. EEG Neurosc. 43(3):268–278, 2012.
Schneider, S. A., Edwards, M. J., Mir, P., Cordivari, C., Hooker, J., Dickson, J., Quinn, N., and Bhatia, K. P., Patients with adult-onset dystonic tremor resembling parkinsonian tremor have scans without evidence of dopaminergic deficit (SWEDDs). Mov. Disord. 22(15):2210–2215, 2007.
Schwingenschuh, P., Ruge, D., Edwards, M. J., Terranova, C., Katschnig, P., Carrillo, F., Silveira-Moriyama, L., and Bhatia, K. P., Distinguishing SWEDDs patients with asymmetric resting tremor from Parkinson’s disease: a clinical and electrophysiological study. Mov. Disord. 25(5):560–569, 2010.
Siddique, N., and Adeli, H., Computational intelligence - synergies of fuzzy logic, neural networks and evolutionary computing. Wiley, West Sussex, 2013.
Silveira-Moriyama, L., Schwingenschuh, P., O’Donnell, A., Schneider, S. A., Mir, P., Carrillo, F., Terranova, C., Petrie, A., Grosset, D. G., Quinn, N. P., Bhatia, K. P., and Lees, A. J., Olfaction in patients with suspected Parkinsonism and scans without evidence of dopaminergic deficit (SWEDDs). J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 80(7):744–748, 2009.
Specht, D. F., Probabilistic neural networks. Neural Netw. 3:109–118, 1990.
Su, F., Wang, J., Deng, B., Wei, X. L., Chen, Y. Y., and Li, H. Y., Adaptive control of Parkinson’s state based on a nonlinear computational model with unknown parameters. Int. J. Neural Syst. 25(1):1450030, 2015 (13 pages).
Story, B. A., and Fry, G. T., A structural impairment detection system using competitive arrays of artificial neural networks. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 29(3):180–190, 2014.
Su, F., Wang, J., Deng, B., Wei, X. L., Chen, Y. Y., and Li, H. Y., Adaptive control of Parkinson’s state based on a nonlinear computational model with unknown parameters. Int. J. Neural Syst. 25(1):1450030, 2015 (13 pages).
Tolosa, E., Wenning, G., and Poewe, W., The diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 5(1):75–86, 2006.
Visser, M., Marinus, J., Stiggelbout, A. M., and Van Hilten, J. J., Assessment of autonomic dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease: The SCOPA-AUT. Mov. Disord. 19(11):1306–1312, 2004.
Yang, H. J., Kim, Y. E., Yun, J. Y., Ehm, G., Kim, H. J., and Jeon, B. S., Comparison of sleep and other non-motor symptoms between SWEDDs patients and de novo Parkinson’s disease patients. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 20(12):1419–1422, 2014.
Yuan, Q., Zhou, W., Yuan, S., Li, X., Wang, J., and Jia, G., Epileptic EEG classification based on kernel sparse representation. Int. J. Neural Syst. 24(4):1450015, 2014 (13 pages).
Zhang, C., Wang, H., Wang, H., and Wu, M., EEG-based expert system using complexity measures and probability density function control in alpha sub-band. Integr. Comput. Aided Eng. 20(4):391–405, 2013.
Zhang, Y., and Zhou, W., Multifractal analysis and relevance vector machine-based automatic seizure detection in intracranial. Int. J. Neural Syst. 25(6):1550020, 2015 (14 pages).
Zhou, L. R., Ou, J. P., and Yan, G. R., Response surface method based on radial basis functions for modeling large-scale structures in model updating. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 28(3):210–226, 2013.
Acknowledgments
PPMI – a public-private partnership – is funded by the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research and funding partners, including AbbVie, Avid, Biogen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Covance, GE Healthcare, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Eli Lilly and Company, Lundbeck, Merck, Meso Scale Discovery, Pfizer, Piramal Imaging, Roche, Servier, and UCB.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Patient Facing Systems
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hirschauer, T.J., Adeli, H. & Buford, J.A. Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Parkinson’s Disease Using Enhanced Probabilistic Neural Network. J Med Syst 39, 179 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-015-0353-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-015-0353-9