Abstract
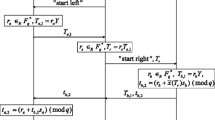
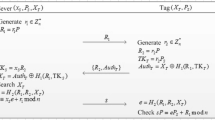
An Institute of Medicine Report stated there are 98,000 people annually who die due to medication related errors in the United States, and hospitals and other medical institutions are thus being pressed to use technologies to reduce such errors. One approach is to provide a suitable protocol that can cooperate with low cost RFID tags in order to identify patients. However, existing low cost RFID tags lack computational power and it is almost impossible to equip them with security functions, such as keyed hash function. To address this issue, a so a real lightweight binding proof protocol is proposed in this paper. The proposed protocol uses only logic gates (e.g. AND, XOR, ADD) to achieve the goal of proving that two tags exist in the field simultaneously, without the need for any complicated security algorithms. In addition, various scenarios are provider to explain the process of adopting this binding proof protocol with regard to guarding patient safety and preventing medication errors.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Institute of Medicine of the National Academies, http://www.iom.edu/Reports.aspx.
Berman, A., Reducing medication errors through naming, labeling, and packaging. J. Med. Syst. 28(1):9–29, 2004.
Crawford, S. Y., Cohen, M. R., and Tafesse, E., Systems factors in the reporting of serious medication errors in hospitals. J. Med. Syst. 27(6):543–551, 2003.
Walton, S. M., The pharmacist shortage and medication errors: Issues and evidence. J. Med. Syst. 28(1):63–59, 2004.
Chung, K., Choi, Y. B., and Moon, S., Toward efficient medication error reduction: Error-reducing information management systems. J. Med. Syst. 27(6), 2003.
Klaus, F., RFID handbook: Fundamentals and applications in contactless smart cards and identification. Wiley, Second Edition, 2003.
Darianian, M., and Michael, M. P., A low power pervasive RFID identification system for medication safety in hospital or home Tele-care. International Symposium Wireless Pervasive Computing 2008, Proceedings on 3rd ISWPC 2008, pp. 143–146, May, 2008.
Lai, C. L., Chien, S. W., Chang, L. H., Chen, S. C., and Fang, K., Enhancing medication safety and healthcare for inpatients using RFID. Portland International Center for Management of Engineering Technology 2007, Proceedings on 7th PICMET 2007, pp. 2783–2790, Aug. 2007.
Chen, P. J., Chen, Y. F., Chai, S. K., and Huang, Y. F., Implementation of an RFID-based management system for operation room. Machine Learning and Cybernetics, pp. 2933–2938, Jul, 2009.
Frisch, P., Miodownik, S., Booth, P., Carragee, P., and Dowling, M., Patient centric identification and association. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society 2009, Proceedings on 31st IEEE EMBS 2009, pp. 1722–1725, Sep. 2009.
Lahtela, A., Hassinen, M., and Jylha, V., RFID and NFC in healthcare: Safety of hospitals medication care. Pervasive Computing Technologies for Healthcare, 2008, Proceedings on 2rd PCTHEALTH 2008, pp. 241–244, Jan. 2008.
Shieh, S. C., Lin, C. C., Yang, T. F., and Tu, G. H., Using RFID technology on clinic’s pharmacy operation management and development of intelligent medicine dispensing cabinet. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society 2008, Proceedings on 30st IEEE EMBS 2008, pp. 2006–2009, 2008.
Sun, P. R., Wang, B. H., and Wu, F., A new method to guard inpatient medication safety by the implementation of RFID. J. Med. Syst. doi:10.1007/s10916-008-9137-9, Published Online, Mar. 2008.
Juels, A., Yoking proof for RFID Tags. Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops, 2004. Proceedings of the Second IEEE Annual Conference on Volume, Issue, pp. 138–143, Mar. 2004.
Saito, J., and Sakurai, K., Grouping proof for RFID tags. Advanced Information Networking and Applications, 2005. AINA 2005, pp. 621–624, Mar. 2005.
Selwyn, P., On existence proofs for multiple RFID Tags. IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Services (ICPS’06), Jun. 2006.
Huang, H. H., and Ku, C. Y., A RFID grouping proof protocol for medication safety of inpatient. J. Med. Syst. doi:10.1007/s10916-008-9207-z, Published Online, Sep. 2008.
Chien, H. Y., Yang, C. C., Wu, T. C., Lee, C. F. Two RFID-based solutions to enhance inpatient medication safety. J. Med. Syst. doi:10.1007/s10916-009-9373-7, Published Online, Aug. 2009.
Peris-Lopez, P., Hernandez-Castro, J. C., Estevez Tapiador, J. M., and Ribagorda, A., LMAP: A real lightweight mutual authentication protocol for low-cost RFID tags. Workshop on RFID and Lightweight Crypto, 2006.
Peris-Lopez, P., Hernandez-Castro, J. C., Estevez Tapiador, J. M., and Ribagorda, A., LAMED—A PRNG for EPC Class-1 Generation-2 RFID specification. Computer Standards and Interfaces, pp. 88–97, Jan. 2009.
Wickboldt A.-K., and Piramuthu, S., Patient safety through RFID: Vulnerabilities in recently proposed grouping protocols. J. Med. Syst. doi:10.1007/s10916-010-9487-y, Published Online, Mar. 2010.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, YC., Hou, TW. & Chiang, TC. Low Cost RFID Real Lightweight Binding Proof Protocol for Medication Errors and Patient Safety. J Med Syst 36, 823–828 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-010-9546-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-010-9546-4