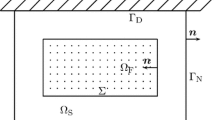
Abstract
In this paper, we present a pressure-based semi-implicit numerical scheme for a first order hyperbolic formulation of compressible two-phase flow with surface tension and viscosity. The numerical method addresses several complexities presented by the PDE system in consideration: (i) The presence of involution constraints of curl type in the governing equations requires explicit enforcement of the zero-curl property of certain vector fields (an interface field and a distortion field); the problem is solved by adopting a set of compatible discrete curl and gradient operators on a staggered grid, allowing to preserve the Schwarz identity of cross-derivatives exactly at the discrete level. (ii) Since the complexity of the studied PDE system does not allow the explicit computation of its exact eigenvalues, reliable and precise analytical estimates are provided. (iii) The evolution equations feature highly nonlinear stiff algebraic source terms which are used for the description of viscous interactions as emergent behaviour of an elasto-plastic solid in the stiff strain relaxation limit; such source terms are reliably integrated with a novel and very efficient semi-analytical technique proposed for the first time in this paper. (iv) In the low-Mach number regime, standard explicit density-based Godunov-type schemes lose efficiency and accuracy; the issue is addressed by means of a simple semi-implicit, pressure-based, split treatment of acoustic and non-acoustic waves, again using staggered grids that recover the implicit solution for a single scalar field (the pressure) through a sequence of symmetric-positive definite linear systems that can be efficiently solved via the conjugate gradient method.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data can be obtained from the authors on reasonable request.
References
Abbate, E., Iollo, A., Puppo, G.: An asymptotic-preserving all-speed scheme for fluid dynamics and nonlinear elasticity. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 41, A2850–A2879 (2019)
Abgrall, R., Busto, S., Dumbser, M.: A simple and general framework for the construction of thermodynamically compatible schemes for computational fluid and solid mechanics. Appl. Math. Comput. (2022)
Abgrall, R., Nordström, R., Öffner, P., Tokareva, S.: Analysis of the SBP-SAT stabilization for finite element methods part II: entropy stability. Commun. Appl. Math. Comput (2021)
Abgrall, R.: How to prevent pressure oscillations in multicomponent flow calculations: a quasi conservative approach. J. Comput. Phys. 125(1), 150–160 (1996)
Abgrall, R.: A general framework to construct schemes satisfying additional conservation relations. Application to entropy conservative and entropy dissipative schemes. J. Comput. Phys. 372, 640–666 (2018)
Abgrall, R., Saurel, R.: Discrete equations for physical and numerical compressible multiphase mixtures. J. Comput. Phys. 186, 361–396 (2003)
Abgrall, R., Nordström, J., Öffner, P., Tokareva, S.: Analysis of the SBP-SAT stabilization for finite element methods. I: Linear problems. J. Sci. Comput. 85(2), 28 (2020)
Al-Dirawi, K.H., Bayly, A.E.: An experimental study of binary collisions of miscible droplets with non-identical viscosities. Exp. Fluids 61 (2020)
Andrianov, N., Warnecke, G.: The Riemann problem for the Baer-Nunziato two-phase flow model. J. Comput. Phys. 212, 434–464 (2004)
Arnold, D., Falk, R., Winther, R.: Finite element exterior calculus, homological techniques, and applications. Acta Numer. 15, 1–155 (2006)
Ascher, U.M., Ruuth, S.J., Spiteri, R.J.: Implicit-explicit Runge-Kutta methods for time-dependent partial differential equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 25(2), 151–167 (1997). (Special Issue on Time Integration)
Baer, M.R., Nunziato, J.W.: A two-phase mixture theory for the deflagration-to-detonation transition (DDT) in reactive granular materials. J. Multiphase Flow 12, 861–889 (1986)
Balsara, D., Käppeli, R., Boscheri, W., Dumbser, M.: Curl constraint-preserving reconstruction and the guidance it gives for mimetic scheme design. Commun. Appl. Math. Comput. Sci. (2021)
Barton, P.: An interface-capturing Godunov method for the simulation of compressible solid-fluid problems. J. Comput. Phys. 390, 25–50 (2019)
Bell, J., Colella, P., Glaz, H.: A second-order projection method for the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. J. Comput. Phys. 85, 257–283 (1989)
Bermúdez, A., Busto, S., Dumbser, M., Ferrín, J., Saavedra, L., Vázquez-Cendón, M.: A staggered semi-implicit hybrid FV/FE projection method for weakly compressible flows. J. Comput. Phys. 421, 109743 (2020)
Berry, R., Saurel, R., Petitpas, F., Daniel, E., Le Métayer, O., Gavrilyuk, S.: Progress in the development of compressible. Multiphase flow modeling capability for nuclear reactor flow applications. Idaho National Laboratory (2008)
Besseling, J.: A thermodynamic approach to rheology. In: H. Parkus, L. Sedov (eds.) Irreversible Aspects of Continuum Mechanics and Transfer of Physical Characteristics in Moving Fluids, IUTAM Symposia, pp. 16–53. Springer Vienna (1968)
Boscarino, S.: Error analysis of IMEX Runge-Kutta methods derived from differential-algebraic systems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 45(4), 1600–1621 (2007)
Boscarino, S.: On an accurate third order implicit-explicit Runge-Kutta method for stiff problems. Appl. Numer. Math. 59(7), 1515–1528 (2009)
Boscarino, S., Russo, G.: On a class of uniformly accurate IMEX Runge-Kutta schemes and applications to hyperbolic systems with relaxation. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 31(3), 1926–1945 (2009)
Boscarino, S., Pareschi, L., Russo, G.: Implicit-explicit Runge-Kutta schemes for hyperbolic systems and kinetic equations in the diffusion limit. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 35(1), A22–A51 (2013)
Boscarino, S., Russo, G., Scandurra, L.: All Mach number second order semi-implicit scheme for the Euler equations of gasdynamics. J. Sci. Comput. 77, 850–884 (2018)
Boscheri, W., Pareschi, L.: High order pressure-based semi-implicit IMEX schemes for the 3D Navier-Stokes equations at all Mach numbers. J. Comput. Phys. 434, 110206 (2021)
Boscheri, W., Dimarco, G., Tavelli, M.: An efficient second order all Mach finite volume solver for the compressible Navier-Stokes equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 374, 113602 (2021)
Boscheri, W., Dumbser, M., Ioriatti, M., Peshkov, I., Romenski, E.: A structure-preserving staggered semi-implicit finite volume scheme for continuum mechanics. J. Comput. Phys. 424, 109866 (2021)
Boscheri, W., Chiocchetti, S., Peshkov, I.: A cell-centered implicit-explicit Lagrangian scheme for a unified model of nonlinear continuum mechanics on unstructured meshes. J. Comput. Phys. 451, 110852 (2022)
Busto, S., Chiocchetti, S., Dumbser, M., Gaburro, E., Peshkov, I.: High order ADER schemes for continuum mechanics. Front. Phys. 8, 32 (2020)
Busto, S., Dumbser, M., Escalante, C., Gavrilyuk, S., Favrie, N.: On high order ADER discontinuous Galerkin schemes for first order hyperbolic reformulations of nonlinear dispersive systems. J. Sci. Comput. 87, 48 (2021)
Busto, S., Dumbser, M., Gavrilyuk, S., Ivanova, K.: On thermodynamically compatible finite volume methods and path-conservative ADER discontinuous Galerkin schemes for turbulent shallow water flows. J. Sci. Comput. 88, 28 (2021)
Busto, S., Rio, L.D., Vázquez-Cendón, M., Dumbser, M.: A semi-implicit hybrid finite volume / finite element scheme for all Mach number flows on staggered unstructured meshes. Appl. Math. Comput. 402, 126117 (2021)
Busto, S., Dumbser, M., Peshkov, I., Romenski, E.: On thermodynamically compatible finite volume schemes for continuum mechanics. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 44(3), A1723–A1751 (2022)
Cardano, G.: Artis magnae sive de regulis algebraicis liber unus. Petreius, Nürnberg (1545)
Castro, M.J., Gallardo, J.M., Parés, C.: High-order finite volume schemes based on reconstruction of states for solving hyperbolic systems with nonconservative products. Applications to shallow-water systems. Math. Comput. 75, 1103–1134 (2006)
Casulli, V.: Semi-implicit finite difference methods for the two-dimensional shallow water equations. J. Comput. Phys. 86, 56–74 (1990)
Casulli, V.: A semi-implicit finite difference method for non-hydrostatic free-surface flows. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 30, 425–440 (1999)
Casulli, V., Greenspan, D.: Pressure method for the numerical solution of transient, compressible fluid flows. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 4(11), 1001–1012 (1984)
Casulli, V., Zanolli, P.: A nested Newton-type algorithm for finite volume methods solving Richards’ equation in mixed form. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 32, 2255–2273 (2009)
Casulli, V., Zanolli, P.: Iterative solutions of mildly nonlinear systems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 236, 3937–3947 (2012)
Chiocchetti, S.: High order numerical methods for a unified theory of fluid and solid mechanics, PhD thesis (2022)
Chiocchetti, S., Müller, C.: A Solver for Stiff Finite-Rate Relaxation in Baer-Nunziato Two-Phase Flow Models. Fluid Mech. Appl. 121, 31–44 (2020)
Chiocchetti, S., Peshkov, I., Gavrilyuk, S., Dumbser, M.: High order ADER schemes and GLM curl cleaning for a first order hyperbolic formulation of compressible flow with surface tension. J. Comput. Phys. 426, 109898 (2021)
Cordier, F., Degond, P., Kumbaro, A.: An Asymptotic-Preserving all-speed scheme for the Euler and Navier-Stokes equations. J. Comput. Phys. 231, 5685–5704 (2012)
de Brauer, A., Iollo, A., Milcent, T.: A cartesian scheme for compressible multimaterial hyperelastic models with plasticity. Commun. Comput. Phys. 22, 1362–1384 (2017)
De Lorenzo, M., Pelanti, M., Lafon, P.: HLLC-type and path-conservative schemes for a single-velocity six-equation two-phase flow model: a comparative study. Appl. Math. Comput. 333, 95–117 (2018)
Dedner, A., Kemm, F., Kröner, D., Munz, C.D., Schnitzer, T., Wesenberg, M.: Hyperbolic divergence cleaning for the MHD equations. J. Comput. Phys. 175, 645–673 (2002)
Dhaouadi, F., Dumbser, M.: A first order hyperbolic reformulation of the Navier–Stokes–Korteweg system based on the GPR model and an augmented Lagrangian approach. J. Comput. Phys. 470, 111544 (2022)
Dhaouadi, F., Favrie, N., Gavrilyuk, S.: Extended Lagrangian approach for the defocusing nonlinear Schrödinger equation. Stud. Appl. Math. 142, 336–358 (2019)
Dumbser, M., Casulli, V.: A conservative, weakly nonlinear semi-implicit finite volume method for the compressible Navier–Stokes equations with general equation of state. Appl. Math. Comput. 272, 479–497 (2016)
Dumbser, M., Enaux, C., Toro, E.F.: Finite volume schemes of very high order of accuracy for stiff hyperbolic balance laws. J. Comput. Phys. 227, 3971–4001 (2008)
Dumbser, M., Peshkov, I., Romenski, E., Zanotti, O.: High order ADER schemes for a unified first order hyperbolic formulation of continuum mechanics: viscous heat-conducting fluids and elastic solids. J. Comput. Phys. 314, 824–862 (2016)
Dumbser, M., Peshkov, I., Romenski, E., Zanotti, O.: High order ADER schemes for a unified first order hyperbolic formulation of Newtonian continuum mechanics coupled with electro-dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 348, 298–342 (2017)
Dumbser, M., Balsara, D., Tavelli, M., Fambri, F.: A divergence-free semi-implicit finite volume scheme for ideal, viscous and resistive magnetohydrodynamics. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 89, 16–42 (2019)
Dumbser, M., Chiocchetti, S., Peshkov, I.: On Numerical Methods for Hyperbolic PDE with Curl Involutions, pp. 125–134. Springer International Publishing, Cham (2020)
Dumbser, M., Fambri, F., Gaburro, E., Reinarz, A.: On GLM curl cleaning for a first order reduction of the CCZ4 formulation of the Einstein field equations. J. Comput. Phys. 404, 109088 (2020)
Einstein, A.: Über die von der molekularkinetischen Theorie der Wärme geforderte Bewegung von in ruhenden Flüssigkeiten suspendierten Teilchen. Ann. Phys. 322(8), 549–560 (1905)
Fambri, F.: A novel structure preserving semi-implicit finite volume method for viscous and resistive magnetohydrodynamics. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 93, 3447–3489 (2021)
Favrie, N., Gavrilyuk, S.: Diffuse interface model for compressible fluid: compressible elastic-plastic solid interaction. J. Comput. Phys. 231, 2695–2723 (2012)
Favrie, N., Gavrilyuk, S., Saurel, R.: Solid-fluid diffuse interface model in cases of extreme deformations. J. Comput. Phys. 228, 6037–6077 (2009)
Feynman, R.P.: The Feynman lectures on physics. Addison-Wesley Pub. Co., Reading (1963)
Finotello, G., Kooiman, R.F., Padding, J.T., Buist, K.A., Jongsma, A., Innings, F., Kuipers, J.A.M.: The dynamics of milk droplet-droplet collisions. Exp. Fluids 59 (2017)
Gabriel, A.A., Li, D., Chiocchetti, S., Tavelli, M., Peshkov, I., Romenski, E., Dumbser, M.: A unified first-order hyperbolic model for nonlinear dynamic rupture processes in diffuse fracture zones. Philos. Trans. Royal Soc. A 379 (2021)
Gaburro, E., Öffner, P., Ricchiuto, M., Torlo, D.: High order entropy preserving ADER-DG schemes. Appl. Math. Comput. (2022)
Gaburro, E., Castro, M.J., Dumbser, M.: A well balanced diffuse interface method for complex nonhydrostatic free surface flows. Comput. Fluids 175, 180–198 (2018)
Gaburro, E., Boscheri, W., Chiocchetti, S., Klingenberg, C., Springel, V., Dumbser, M.: High order direct Arbitrary–Lagrangian–Eulerian schemes on moving Voronoi meshes with topology changes. J. Comput. Phys. 407, 109167 (2020)
Gavrilyuk, S., Favrie, N., Saurel, R.: Modelling wave dynamics of compressible elastic materials. J. Comput. Phys. 227, 2941–2969 (2008)
Godunov, S.K., Romenski, E.I.: Elements of Continuum Mechanics and Conservation Laws. Kluwer Academic/ Plenum Publishers (2003)
Godunov, S.K., Romenski, E.: Elements of Mechanics of Continuous Media. Nauchnaya Kniga (1998)
Godunov, S.K.: Elements of mechanics of continuous media. Nauka (1978)
Godunov, S.: An interesting class of quasilinear systems. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 139(3), 521–523 (1961)
Godunov, S.: Symmetric form of the magnetohydrodynamic equation. Numer. Methods Mech. Contin. Med. 3(1), 26–34 (1972)
Godunov, S.K., Peshkov, I.: Thermodynamically consistent nonlinear model of elastoplastic maxwell medium. Comput. Math. Math. Phys. 50(8), 1409–1426 (2010)
Godunov, S.K., Romenski, E.I.: Nonstationary equations of the nonlinear theory of elasticity in Euler coordinates. J. Appl. Mech. Tech. Phys. 13, 868–885 (1972)
Godunov, S.K., Romenski, E.: Elements of Continuum Mechanics and Conservation Laws. Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York (2003)
Godunov, S.K., Mikhaîlova, T.Y., Romenskiî, E.I.: Systems of thermodynamically coordinated laws of conservation invariant under rotations. Sib. Math. J. 37(4), 690–705 (1996)
Hank, S., Gavrilyuk, S., Favrie, N., Massoni, J.: Impact simulation by an Eulerian model for interaction of multiple elastic-plastic solids and fluids. Int. J. Impact Eng 109, 104–111 (2017)
Harlow, F., Welch, J.: Numerical calculation of time-dependent viscous incompressible flow of fluid with a free surface. Phys. Fluids 8, 2182–2189 (1965)
Hennemann, S., Rueda-Ramírez, A., Hindenlang, F., Gassner, G.: A provably entropy stable subcell shock capturing approach for high order split form DG for the compressible Euler equations. J. Comput. Phys. 426 (2021)
Hinterbichler, H., Planchette, C., Brenn, G.: Ternary drop collisions. Exp. Fluids 56, 190/1-190/12 (2015)
Hyman, J., Shashkov, M.: Natural discretizations for the divergence, gradient, and curl on logically rectangular grids. Comput. Math. Appl. 33, 81–104 (1997)
Jackson, H., Nikiforakis, N.: A numerical scheme for non-Newtonian fluids and plastic solids under the GPR model. J. Comput. Phys. 387, 410–429 (2019)
Jackson, H., Nikiforakis, N.: A unified Eulerian framework for multimaterial continuum mechanics. J. Comput. Phys. 401, 109022 (2019)
Kapila, A.K., Menikoff, R., Bdzil, J.B., Son, S.F., Stewart, D.S.: Two-phase modelling of deflagration-to-detonation in granular materials: reduced equations. Phys. Fluids 13, 3002–3024 (2001)
Kemm, F., Gaburro, E., Thein, F., Dumbser, M.: A simple diffuse interface approach for compressible flows around moving solids of arbitrary shape based on a reduced Baer-Nunziato model. Comput. Fluids 204, 104536 (2020)
Kennedy, C.A., Carpenter, M.H.: Additive Runge-Kutta schemes for convection-diffusion-reaction equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 44(1), 139–181 (2003)
Klainermann, S., Majda, A.: Singular Limits of Quasilinear Hyperbolic Systems with Large Parameters and the Incompressible Limit of Compressible Fluid. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 34, 481–524 (1981)
Klainermann, S., Majda, A.: Compressible and incompressible fluids. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 35, 629–651 (1982)
Klein, R., Botta, N., Schneider, T., Munz, C., Roller, S., Meister, A., Hoffmann, L., Sonar, T.: Asymptotic adaptive methods for multi-scale problems in fluid mechanics. J. Eng. Math. 39, 261–343 (2001)
Lipnikov, K., Manzini, G., Shashkov, M.: Mimetic finite difference method. J. Comput. Phys. 257, 1163–1227 (2014)
Loubère, R., Maire, P.H., Shashkov, M., Breil, J., Galera, S.: ReALE: a reconnection-based arbitrary-Lagrangian–Eulerian method. J. Comput. Phys. 229, 4724–4761 (2010)
Lukácová-Medvidóvá, M., Puppo, G., Thomann, A.: An all Mach number finite volume method for isentropic two-phase flow. J. Numer. Math. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1515/jnma-2022-0015
Margolin, G., Shashkov, M., Smolarkiewicz, P.: A discrete operator calculus for finite difference approximations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 187, 365–383 (2000)
Munz, C., Klein, R., Roller, S., Geratz, K.: The extension of incompressible flow solvers to the weakly compressible regime. Comput. Fluids (2003)
Munz, C., Omnes, P., Schneider, R., Sonnendrücker, E., Voss, U.: Divergence correction techniques for Maxwell solvers based on a hyperbolic model. J. Comput. Phys. 161, 484–511 (2000)
Munz, C., Roller, S., Klein, R., Geratz, K.: The extension of incompressible flow solvers to the weakly compressible regime. Comput. Fluids 32, 173–196 (2003)
Munz, C., Dumbser, M., Roller, S.: Linearized acoustic perturbation equations for low Mach number flow with variable density and temperature. J. Comput. Phys. 224, 352–364 (2007)
Ndanou, S., Favrie, N., Gavrilyuk, S.: Criterion of hyperbolicity in hyperelasticity in the case of the stored energy in separable form. J. Elast. 115, 1–25 (2014)
Ndanou, S., Favrie, N., Gavrilyuk, S.: Multi-solid and multi-fluid diffuse interface model: applications to dynamic fracture and fragmentation. J. Comput. Phys. 295, 523–555 (2015)
Niederhaus, C.E., Jacobs, J.W.: Experimental study of the Richtmyer–Meshkov instability of incompressible fluids. J. Fluid Mech. 485, 243–277 (2003)
Parés, C.: Numerical methods for nonconservative hyperbolic systems: a theoretical framework. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 44, 300–321 (2006)
Pareschi, L., Russo, G.: Implicit-explicit Runge-Kutta schemes and applications to hyperbolic systems with relaxation. J. Sci. Comput. 25(1), 129–155 (2005)
Park, J., Munz, C.: Multiple pressure variables methods for fluid flow at all mach numbers. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 49, 905–931 (2005)
Peshkov, I., Romenski, E.: A hyperbolic model for viscous Newtonian flows. Continuum Mech. Thermodyn. 28, 85–104 (2016)
Peshkov, I., Pavelka, M., Romenski, E., Grmela, M.: Continuum mechanics and thermodynamics in the Hamilton and the Godunov-type formulations. Continuum Mech. Thermodyn. 30(6), 1343–1378 (2018)
Peshkov, I., Dumbser, M., Boscheri, W., Romenski, E., Chiocchetti, S., Ioriatti, M.: Simulation of non-Newtonian viscoplastic flows with a unified first order hyperbolic model and a structure-preserving semi-implicit scheme. Comput. Fluids 224, 104963 (2021)
Planchette, C., Hinterbichler, H., Liu, M., Bothe, D., Brenn, G.: Colliding drops as coalescing and fragmenting liquid springs. J. Fluid Mech. 814, 277–300 (2017)
Powell, K.: An Approximate Riemann Solver for Magnetohydrodynamics. In: v.L.B. M.Y., V.R. J. (eds.) Upwind and High-Resolution Schemes, pp. 570–583. Springer, Berlin (1997)
Powell, K., Roe, P., Linde, T., Gombosi, T., Zeeuw, D.D.: A solution-adaptive upwind scheme for ideal magnetohydrodynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 154(2), 284–309 (1999)
Re, B., Abgrall, R.: A pressure-based method for weakly compressible two-phase flows under a Baer-Nunziato type model with generic equations of state and pressure and velocity disequilibrium. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 94, 1183–1232 (2022)
Romenski, E.: Hyperbolic systems of thermodynamically compatible conservation laws in continuum mechanics. Math. Comput. Model. 28(10), 115–130 (1998)
Romenski, E., Resnyansky, A., Toro, E.: Conservative hyperbolic formulation for compressible two-phase flow with different phase pressures and temperatures. Q. Appl. Math. 65, 259–279 (2007)
Romenski, E., Drikakis, D., Toro, E.: Conservative models and numerical methods for compressible two-phase flow. J. Sci. Comput. 42, 68–95 (2010)
Romensky, E.I.: Thermodynamics and hyperbolic systems of balance laws in continuum mechanics. In: Toro, E. (ed.) Godunov Methods: Theory and Applications, pp. 745–761. Springer, New York (2001)
Saurel, R., Abgrall, R.: A multiphase Godunov method for compressible multifluid and multiphase flows. J. Comput. Phys. 150, 425–467 (1999)
Schlichting, H., Gersten, K.: Grenzschichttheorie. Springer, New York (2005)
Schmidmayer, K., Petitpas, F., Daniel, E., Favrie, N., Gavrilyuk, S.: A model and numerical method for compressible flows with capillary effects. J. Comput. Phys. 334, 468–496 (2017)
Sommerfeld, M., Pasternak, L.: Advances in modelling of binary droplet collision outcomes in sprays: a review of available knowledge. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 117, 182–205 (2019)
Tavelli, M., Dumbser, M.: A staggered space-time discontinuous Galerkin method for the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations on two-dimensional triangular meshes. Comput. Fluids 119, 235–249 (2015)
Tavelli, M., Dumbser, M.: A pressure-based semi-implicit space-time discontinuous Galerkin method on staggered unstructured meshes for the solution of the compressible Navier–Stokes equations at all Mach numbers. J. Comput. Phys. 341, 341–376 (2017)
Tavelli, M., Chiocchetti, S., Romenski, E., Gabriel, A.A., Dumbser, M.: Space-time adaptive ADER discontinuous Galerkin schemes for nonlinear hyperelasticity with material failure. J. Comput. Phys. 422, 109758 (2020)
Thein, F., Romenski, E., Dumbser, M.: Exact and numerical solutions of the Riemann problem for a conservative model of compressible two-phase flows. J. Sci. Comput. 93, 83 (2022)
Thomann, A., Puppo, G., Klingenberg, C.: An all speed second order well-balanced IMEX relaxation scheme for the Euler equations with gravity. J. Comput. Phys. 420, 109723 (2020)
Toro, E.F.: Riemann Solvers and Numerical Methods for Fluid Dynamics. A Practical Introduction, 3rd edn. Springer, Berlin (2009)
Toro, E., Vázquez-Cendón, M.: Flux splitting schemes for the Euler equations. Comput. Fluids 70, 1–12 (2012)
van Leer, B.: Towards the ultimate conservative difference scheme. II. Monotonicity and conservation combined in a second-order scheme. J. Comput. Phys. 14, 361–370 (1974)
van Leer, B.: Towards the ultimate conservative difference scheme. V. A second-order sequel to Godunov’s method. J. Comput. Phys. 32, 101–136 (1979)
Wood, A.: A Textbook of Sound. B. Bell and Sons LTD, London (1930)
Acknowledgements
The research presented in this paper has been funded by the Italian Ministry of Education, University and Research (MIUR) in the frame of the Departments of Excellence Initiative 2018–2022 attributed to DICAM of the University of Trento (grant L. 232/2016) and in the frame of the PRIN 2017 project Innovative numerical methods for evolutionary partial differential equations and applications. The research was also funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) via the project DROPIT, grant no. GRK 2160/2. Furthermore, S. C. has also received funding within Project HPC-EUROPA3 (INFRAIA-2016-1-730897), with the support of the EC Research Innovation Action under the H2020 Programme. In particular, S. C. gratefully acknowledges the support of Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Claus-Dieter Munz at IAG and the computer resources and technical support provided by HLRS in Stuttgart. M. D. and S. C. are both members of the INdAM GNCS group.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chiocchetti, S., Dumbser, M. An Exactly Curl-Free Staggered Semi-Implicit Finite Volume Scheme for a First Order Hyperbolic Model of Viscous Two-Phase Flows with Surface Tension. J Sci Comput 94, 24 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-022-02077-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-022-02077-2