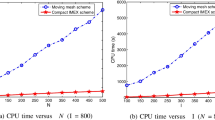
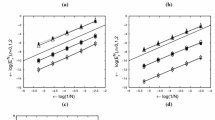
Abstract
In this paper, we study a posteriori error estimates of the IMEX BDF2 scheme for time discretizations of solving parabolic partial integro-differential equations, which describe the jump-diffusion option pricing model in finance. Because of the initial singularities of the solution which is due to the nonsmoothness of the payoff function, a posteriori error control and adaptivity will be crucial in solving numerically this type of equations. To derive optimal order a posteriori error estimates, quadratic reconstructions for the IMEX BDF2 method are introduced. By using these continuous, piecewise time reconstructions, the upper and lower error bounds depending only on the discretization parameters and the data of the problems are derived. Based on these a posteriori error estimates, we further develop a time adaptive algorithm. The numerical implementations are performed with both nonuniform partitions and adaptivity in time. The adaptive algorithm reduce the computational cost substantially and provides efficient error control for the solution.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Code Availability
The code can be made available on reasonable request.
References
Achdou, Y., Pironneau, O.: Computational methods for option pricing. Front. Appl. Math. 30, SIAM, Philadelphia, (2005)
Akrivis, G., Crouzeix, M., Makridadis, C.: Implicit–Explicit Multistep Finite Element Methods for Nonlinear Parabolic Equations. Report 95-22, University of Rennes (1995)
Akrivis, G., Crouzeix, M., Chatzipantelidis, P.: A posteriori error estimates for the two-step backward differentiation formula method for parabolic equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 48, 109–132 (2010)
Ascher, U.M., Ruuth, S.J., Wetton, B.T.R.: Implicit–explicit methods for time-dependent PDE’s. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 32, 797–823 (1995)
Ascher, U.M., Ruuth, S.J., Spiteri, R.J.: Implicit–explicit Runge–Kutta methods for time-dependent partial differential equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 25, 151–167 (1997)
Bänsch, E., Brenner, A.: A posteriori error estimates for pressure-correction schemes. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 54, 2323–2358 (2016)
Becker, J.: A second order backward difference method with variable steps for a parabolic problem. BIT 38, 644–662 (1998)
Boen, L., i’nt Hout, K.J.: Operator splitting schemes for the two-asset Merton jump-diffusion model. J. Comp. Appl. Math. 38, 112309 (2021)
Briani, M., Natalini, R., Russo, G.: Implicit–explicit numerical schemes for jump-diffusion processes. Calcolo 44, 33–57 (2007)
Bänsch, E., Bates, D.S.: Jumps and stochastic volatility: exchange rate processes implicit deutsche mark options. Rev. Financ. Stud. 9, 637–654 (1996)
Chen, F., Shen, J., Xu, H.J.: A new spectral element method for pricing European options under the Black–Scholes and Merton jump diffusion Models. J. Sci. Comput. 52, 499–518 (2012)
Chen, Y.Z., Xiao, A.G., Wang, W.S.: An IMEX-BDF2 compact scheme for pricing options under regime-switching jump-diffusion models. Math. Meth. Appl. Sci. 42, 2646–2663 (2019)
Crouzeix, M.: Une méthode multipas implicite-explicite pour l’approximation des équations d’évolution paraboliques. Numer. Math. 35, 257–276 (1980)
Cont, R., Tankov, P.: Financial Modelling with Jump Processes. Chapman & Hall/CRC, Boca Raton (2004)
Cont, R., Voltchkova, E.: A finite difference scheme for option pricing in jump diffusion and exponential lévy models. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 43, 1596–1624 (2005)
d’Halluin, Y., Forsyth, P.A., Vetzal, K.R.: Robust numerical methods for contingent claims under jump diffusion processes. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 25, 87–112 (2005)
Düring, B., Pitkin, A.: High-order compact finite difference scheme for option pricing in stochastic volatility jump models. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 355, 201–217 (2019)
Feng, F., Linetsky, V.: Pricing options in jump-diffusion models: an extrapolation approach. Oper. Res. 56, 304–325 (2018)
Frank, J., Hundsdorfer, W., Verwer, J.G.: On the stability of implicit–explicit linear multistep methods. Appl. Numer. Math. 25, 193–207 (1997)
Gaviraghi, B., Annunziato, M., Borzía, A.: Analysis of splitting methods for solving a partial integro-differential Fokker–Planck equations. Appl. Math. Comput. 294, 1–17 (2017)
Hairer, E., Nørsett, S., Wanner, G.: Solving Ordinary Differential Equations I. Nonstiff Problems, 2nd edn. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (2000)
in’t Hout, K.J.: Numerical Partial Differential Equations in Finance Explained: An Introduction to Computational Finance. Springer Nature, London (2017)
in’t Hout, K.J., Toivanen, J.: ADI schemes for valuing european options under the bates model. Appl. Numer. Math. 130, 143–156 (2018)
Kadalbajoo, M.K., Tripathi, L.P., Kumar, A.: Second order accurate IMEX methods for option pricing under Merton and Kou jump-diffusion model. J. Sci. Comput. 65, 979–1024 (2015)
Kadalbajoo, M.K., Kumar, A., Tripathi, L.P.: An efficient numerical method for pricing options under jump diffusion model. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Sci. Appl. Math. 7, 114–123 (2015)
Kadalbajoo, M.K., Kumar, A., Tripathi, L.P.: A radial basis function based implicit–explicit method for option pricing under jump-diffusion models. Appl. Numer. Math. 110, 159–173 (2016)
Kadalbajoo, M.K., Tripathi, L.P., Kumar, A.: An error analysis of a finite element method with IMEX-time semidiscretizations for some partial integro-differential inequalities arising in the pricing of American options. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 55, 869–891 (2017)
Kwon, Y., Lee, Y.: A second-order finite difference method for option pricing under jump-diffusion models. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 49, 2598–2617 (2011)
Larsson, E., Åhlander, K., Hall, A.: Multi-dimensional option pricing using radial basis functions and the generalized Fourier transform. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 222(1), 175–192 (2008)
Lee, S.T., Sun, H.W.: Fourth order compact scheme with local mesh refinement for option pricing in jump-diffusion model. Numer. Methods Part. Differ. Equ. 28, 1079–1098 (2012)
Lozinski, A., Picasso, M., Prachittham, V.: An anisotropic error estimator for the Crank–Nicolson method: application to a parabolic problem. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 31, 2757–2783 (2009)
Matache, A.M., Schwab, C., Wihler, T.P.: Fast Numerial Solution of Parabolic Integro-Differential Equations with Applications in Finance. IMA Preprint Series 1954 University of Minnesota, (2004)
Merton, R.C.: Option pricing when underlying stock returns are discontinuous. Financ. Econ. 3, 125–144 (1976)
Nochetto, R.H., Savaré, G., Verdi, C.: A posteriori error estimates for variable time-step discretizations of nonlinear evolution equations. Comm. Pure Appl. Math. 53, 525–589 (2000)
Pindza, E., Patidar, K.C., Ngounda, E.: Robust spectral method for numerical valuation of European options under Merton’s jump-diffusion model. Numer. Methods Part. Differ. Equ. 30, 1169–1188 (2014)
Rad, J.A., Parand, K.: Pricing American options under jump-diffusion models using local weak form meshless techniques. Inter. J. Comput. Math. 94, 1–27 (2016)
Rad, J.A., Parand, K.: Numerical pricing of American options under two stochastic factor models with jumps using a meshless local Petrov-Galerkin method. Appl. Numer. Math. 115, 252–274 (2017)
Ruuth, S.J.: Implicit-explicit methods for reaction–diffusion problems in pattern-formation. J. Math. Biol. 34, 148–176 (1995)
Safdari, A., Heryudono, A., Larsson, E.: A radial basis function partition of unity collocation method for convection–diffusion equations arising in financial applications. J. Sci. Comput. 64, 341–367 (2015)
Salmi, S., Toivanen, J.: IMEX schemes for pricing options under jump-diffusion models. Appl. Numer. Math. 84, 33–45 (2014)
Salmi, S., Toivanen, J., von Sydow, L.: An IMEX-scheme for pricing options under stochastic volatility models with jumps. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 36, B817–B834 (2014)
Shcherbakov, V., Larsson, E.: Radial basis function partition of unity methods for pricing vanilla basket options. Comput. Math. Appl. 71, 185–200 (2016)
von Sydow, L., Toivane, J., Zhang, C.: Adaptive finite differences and IMEX time-stepping to price options under Bates model. Inter. J. Comput. Math. 92, 2515–2529 (2015)
Tavella, D., Randall, C.: Pricing Financial Instruments: The Finite Difference Method. Wiley, Chichester (2000)
Thomée, V.: Galerkin finite element methods for parabolic problems. second ed., In: Springer Series in Computational Mathematics, vol. 25, Springer-Verlag, Berlin (2006)
Varah, J.M.: Stability restrictions on second order, three-level finite-difference schemes for parabolic equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 17, 300–309 (1980)
Verwer, J.G., Blom, J.G., Hundsdorfer, W.: An implicit-explicit approach for atmospheric transport-chemistry problems. Appl. Numer. Math. 20, 191–209 (1996)
Wang, D., Ruuth, S.J.: Variable step-size implicit-explicit linear multistep methods for time-dependent partial differential equations. J. Comput. Math. 26, 838–855 (2008)
Wang, W.S., Chen, Y.Z.: Fast numerical valuation of options with jump under Merton’s models. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 318, 79–92 (2017)
Wang, W.S., Chen, Y.Z., Fang, F.: On the variable two-step IMEX BDF method for parabolic integro-differential equations with nonsmooth initial data arising in finance. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 57, 1289–1317 (2019)
Wang, W.S., Mao, M.L., Huang, Y.: Optimal a posteriori estimators for the variable step-size BDF2 method for linear parabolic equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 413, 114306 (2022)
Wang, W.S., Mao, M.L., Wang, Z.: Stability and error estimates for the variable step-size BDF2 method for linear and semilinear parabolic equation. Adv. Comput. Math. 47, 1–28 (2021)
Wang, W.S., Mao, M.L., Wang, Z.: An efficient variable step-size method for options pricing under jump-diffusion models with nonsmooth payoff function. ESAIM Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 55, 913–938 (2021)
Wilmott, P., Dewynee, J., Howison, S.: Option Pricing: Mathemematical Models and Computation. Oxford Financial Press, Oxford (1993)
Zhang, K., Wang, S.: A computational scheme for options under jump-diffusion processes. Inter. J. Numer. Anal. Model. 6, 110–123 (2009)
Zhang, X.L.: Numerical analysis of American option pricing in a jump-diffusion model. Math. Oper. Res. 22, 668–690 (1997)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the referee for comments and suggestions that led to improvements in the presentation of this paper.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 12271367, 11771060) and Shanghai Science and Technology Planning Projects (Grant No. 20JC1414200), and sponsored by Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (Grant No. 20ZR1441200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This work does not have any conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
We have not submitted this manuscript anywhere, and it will not be submitted anywhere while it is under review.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Mao, M. & Huang, Y. A Posteriori Error Control and Adaptivity for the IMEX BDF2 Method for PIDEs with Application to Options Pricing Models. J Sci Comput 93, 55 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-022-02013-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-022-02013-4
Keywords
- A posteriori error estimates
- Variable step-size IMEX BDF2 method
- BDF2 reconstructions
- Three point reconstructions
- Partial integro-differential equations
- European option pricing
- Jump-diffusion model
- Stochastic volatility model