Abstract
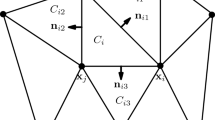
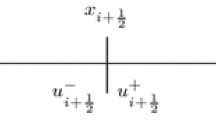
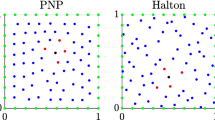
This paper develops a framework for finite volume radial basis function (RBF) approximation of a function u on a stencil of mesh cells in multiple dimensions. The theory of existence of the approximation is given. In one dimension, as the cell diameters tend to zero, numerical evidence is given to show that the RBF approximation converges to u to the same order as a polynomial approximation when the RBF is infinitely differentiable. Specific multiquadric RBFs on stencils of 2 and 3 mesh cells are proven to have this convergence property. A two-level RBF based weighted essentially non-oscillatory (WENO) reconstruction with adaptive order (RBF-WENO-AO) is developed. WENO-AO reconstructions use arbitrary linear weights, and so they can be developed easily for RBF approximations, even on nonuniform meshes in multiple dimensions. Following the classical polynomial based WENO, a smoothness indicator is defined for the reconstruction. For one dimension, the convergence theory is given regarding the cases when u is smooth and when u has a discontinuity. These reconstructions are applied to develop finite volume schemes for hyperbolic conservation laws on nonuniform meshes over multiple space dimensions. The focus is on reconstructions based on multiquadric RBFs that are third order when the solution is smooth and second order otherwise, i.e., RBF-WENO-AO(3,2). Numerical examples show that the scheme maintains proper accuracy and achieves the essentially non-oscillatory property when solving hyperbolic conservation laws.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aboiyar, T., Georgoulis, E.H., Iske, A.: Adaptive ADER methods using kernel-based polyharmonic spline WENO reconstruction. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 32(6), 3251–3277 (2010)
Aràndiga, F., Baeza, A., Belda, A.M., Mulet, P.: Analysis of WENO schemes for full and global accuracy. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 49(2), 893–915 (2011)
Arbogast, T., Huang, C.S., Zhao, X.: Accuracy of WENO and adaptive order WENO reconstructions for solving conservation laws. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 56(3), 1818–1847 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1137/17M1154758
Arbogast, T., Huang, C.S., Zhao, X.: Von Neumann stable, implicit, high order, finite volume WENO schemes. In: SPE Reservoir Simulation Conference 2019, pp. 1–16. Society of Petroleum Engineers, Galveston, Texas (2019). https://doi.org/10.2118/193817-MS
Balsara, D.S., Garain, S., Florinski, V., Boscheri, W.: An efficient class of weno schemes with adaptive order for unstructured meshes. J. Comput. Phys. 404, 109062 (2020)
Balsara, D.S., Garain, S., Shu, C.W.: An efficient class of WENO schemes with adaptive order. J. Comput. Phys. 326, 780–804 (2016)
Bigoni, C., Hesthaven, J.S.: Adaptive WENO methods based on radial basis function reconstruction. J. Sci. Comput. 72(3), 986–1020 (2017)
Cheney, E.W., Light, W.A.: A Course in Approximation Theory. Brooks Cole (1999)
Cravero, I., Puppo, G., Semplice, M., Visconti, G.: CWENO: uniformly accurate reconstructions for balance laws. Math. Comput. 87, 1689–1719 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1090/mcom/3273
Fasshauer, G.E.: Meshfree approximation methods with MATLAB, vol. 6. World Scientific (2007)
Franke, R.: A critical comparison of some methods for interpolation of scattered data. Tech. Rep. TR NPS-53-79-003, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, CA (1979)
Guo, J., Jung, J.H.: A RBF-WENO finite volume method for hyperbolic conservation laws with the monotone polynomial interpolation method. Appl. Numer. Math. (2017)
Guo, K., Hu, S., Sun, X.: Conditionally positive definite functions and Laplace–Stieltjes integrals. J. Approx. Theory 74, 249–265 (1993)
Hardy, R.L.: Multiquadric equations of topograpy and other irregular surfaces. J. Geophy. Res. 76, 1905–1915 (1971)
Harten, A., Osher, S.: Uniformly high-order accurate nonoscillatory schemes I. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 24(2), 279–309 (1987)
Henrick, A.K., Aslam, T.D., Powers, J.M.: Mapped weighted essentially non-oscillatory schemes: achieving optimal order near critical points. J. Comput. Phys. 207, 542–567 (2005)
Hesthaven, J.S., Mönkeberg, F.: Entropy stable essentially nonoscillatory methods based on RBF reconstruction. ESAIM: M2AN 53(3), 925–958 (2019)
Hesthaven, J.S., Mönkeberg, F.: Two-dimensional RBF-ENO method on unstructured grids. J. Sci. Comput. 82(76) (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-020-01176-2
Hu, C., Shu, C.W.: Weighted essentially non-oscillatory schemes on triangular meshes. J. Comput. Phys. 150, 97–127 (1999)
Jiang, G.S., Shu, C.W.: Efficient implementation of weighted ENO schemes. J. Comput. Phys. 126, 202–228 (1996)
Jiang, G.S., Tadmor, E.: Nonoscillatory central schemes for multidimensional hyperbolic conservation laws. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 19, 1892–1917 (1998)
Kolb, O.: On the full and global accuracy of a compact third order WENO scheme. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 52, 2335–2355 (2014)
Levy, D., Puppo, G., Russo, G.: Compact central WENO schemes for multidimensional conservation laws. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 22(2), 656–672 (2000)
Liu, H., Jian, X.: WLS-ENO: weighted-least-squares based essentially non-oscillatory schemes for finite volume methods on unstructured meshes. J. Comput. Phys. 314, 749–773 (2016)
Liu, X.D., Osher, S., Chan, T.: Weighted essentially non-oscillatory schemes. J. Comput. Phys. 115, 200–212 (1994)
Micchelli, C.A.: Interpolation of scattered data: distance matrices and conditionally positive definite functions. Constr. Approx. 2, 11–22 (1986)
Schulz-Rinne, C.W., Collins, J.P., Glaz, H.M.: Numerical solution of the Riemann problem for two-dimensional gas dynamics. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 14(6), 1394–1414 (1993)
Shu, C.W., Osher, S.: Efficient implementation of essentially non-oscillatory shock capturing schemes. J. Comput. Phys. 77, 439–471 (1988)
Sun, X.: Conditionally positive definite functions and their application to multivariate interpolations. J. Approx. Theory 74, 159–180 (1993)
Wang, Y., Zhu, J.: A new type of increasingly high-order multi-resolution trigonometric WENO schemes for hyperbolic conservation laws and highly oscillatory problems. Comput. Fluids 200, 104448 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compfluid.2020.104448
Widder, D.: The Laplace Transform. Princeton University Press (1941)
Woodward, P., Colella, P.: The numerical simulation of two-dimensional fluid flow with strong shocks. J. Comput. Phys. 54, 115–173 (1984)
Zhu, J., Qiu, J.: Trigonometric WENO shemes for hyperbolic conservation laws and highly oscillatory problems. Commun. Comput. Phys. 8, 1242–1263 (2010)
Zhu, J., Qiu, J.: A new fifth order finite difference WENO scheme for solving hyperbolic conservation laws. J. Comput. Phys. 318, 110–121 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no financial or proprietary interests in any material discussed in this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Todd Arbogast was funded in part by the U.S. National Science Foundation Grant DMS-1912735. Chieh-Sen Haung and Ming-Hsien Kuo were funded by the Taiwan Ministry of Science and Technology Grant MOST 109-2115-M-110-003-MY3 and the National Center for Theoretical Sciences, Taiwan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arbogast, T., Huang, CS. & Kuo, MH. RBF WENO Reconstructions with Adaptive Order and Applications to Conservation Laws. J Sci Comput 91, 51 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-022-01827-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-022-01827-6