Abstract
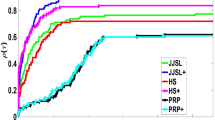
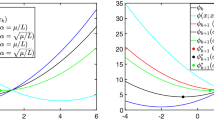
Based on an observation that additive Schwarz methods for general convex optimization can be interpreted as gradient methods, we propose an acceleration scheme for additive Schwarz methods. Adopting acceleration techniques developed for gradient methods such as momentum and adaptive restarting, the convergence rate of additive Schwarz methods is greatly improved. The proposed acceleration scheme does not require any a priori information on the levels of smoothness and sharpness of a target energy functional, so that it can be applied to various convex optimization problems. Numerical results for linear elliptic problems, nonlinear elliptic problems, nonsmooth problems, and nonsharp problems are provided to highlight the superiority and the broad applicability of the proposed scheme.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Badea, L.: Convergence rate of a Schwarz multilevel method for the constrained minimization of nonquadratic functionals. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 44(2), 449–477 (2006)
Badea, L., Krause, R.: One-and two-level Schwarz methods for variational inequalities of the second kind and their application to frictional contact. Numer. Math. 120(4), 573–599 (2012)
Badea, L., Tai, X.C., Wang, J.: Convergence rate analysis of a multiplicative Schwarz method for variational inequalities. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 41(3), 1052–1073 (2003)
Beck, A., Teboulle, M.: A fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 2(1), 183–202 (2009)
Chambolle, A., Dossal, C.: On the convergence of the iterates of the “Fast Iterative Shrinkage/Thresholding Algorithm”. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 166(3), 968–982 (2015)
Chambolle, A., Pock, T.: An introduction to continuous optimization for imaging. Acta Numer. 25, 161–319 (2016)
Chang, H., Tai, X.C., Wang, L.L., Yang, D.: Convergence rate of overlapping domain decomposition methods for the Rudin–Osher–Fatemi model based on a dual formulation. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 8(1), 564–591 (2015)
Ciarlet, P.G.: The Finite Element Method for Elliptic Problems. SIAM, Philadelphia (2002)
Combettes, P.L., Wajs, V.R.: Signal recovery by proximal forward-backward splitting. Multiscale Model. Simul. 4(4), 1168–1200 (2005)
Drori, Y., Teboulle, M.: Performance of first-order methods for smooth convex minimization: a novel approach. Math. Program. 145(1–2), 451–482 (2014)
Herrmann, M., Herzog, R., Schmidt, S., Vidal-Núñez, J., Wachsmuth, G.: Discrete total variation with finite elements and applications to imaging. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 61(4), 411–431 (2019)
Hintermüller, M., Langer, A.: Non-overlapping domain decomposition methods for dual total variation based image denoising. J. Sci. Comput. 62(2), 456–481 (2015)
Kim, D., Fessler, J.A.: Optimized first-order methods for smooth convex minimization. Math. Program. 159(1–2), 81–107 (2016)
Lee, C.O., Park, E.H., Park, J.: A finite element approach for the dual Rudin–Osher–Fatemi model and its nonoverlapping domain decomposition methods. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 41(2), B205–B228 (2019)
Lee, C.O., Park, J.: Fast nonoverlapping block Jacobi method for the dual Rudin–Osher–Fatemi model. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 12(4), 2009–2034 (2019)
Lee, C.O., Park, J.: A finite element nonoverlapping domain decomposition method with Lagrange multipliers for the dual total variation minimizations. J. Sci. Comput. 81(3), 2331–2355 (2019)
Nesterov, Y.: Gradient methods for minimizing composite functions. Math. Program. 140(1), 125–161 (2013)
Nesterov, Y.: Lectures on Convex Optimization. Springer, Cham (2018)
Nesterov, Y.E.: A method for solving the convex programming problem with convergence rate \({O}(1/k^2)\). Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 269, 543–547 (1983)
O’Donoghue, B., Candes, E.: Adaptive restart for accelerated gradient schemes. Found. Comput. Math. 15(3), 715–732 (2015)
Park, J.: Additive Schwarz methods for convex optimization as gradient methods. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 58(3), 1495–1530 (2020)
Park, J.: Pseudo-linear convergence of an additive Schwarz method for dual total variation minimization. Electron. Trans. Numer. Anal. 54, 176–197 (2021)
Roulet, V., d’Aspremont, A.: Sharpness, restart, and acceleration. SIAM J. Optim. 30(1), 262–289 (2020)
Saad, Y.: Iterative Methods for Sparse Linear Systems. SIAM, Philadelphia (2003)
Tai, X.C.: Rate of convergence for some constraint decomposition methods for nonlinear variational inequalities. Numer. Math. 93(4), 755–786 (2003)
Tai, X.C., Heimsund, B., Xu, J.: Rate of convergence for parallel subspace correction methods for nonlinear variational inequalities. In: Domain decomposition methods in science and engineering (Lyon, 2000), Theory Eng. Appl. Comput. Methods, pp. 127–138. Internat. Center Numer. Methods Eng. (CIMNE), Barcelona (2002)
Tai, X.C., Xu, J.: Global and uniform convergence of subspace correction methods for some convex optimization problems. Math. Comput. 71(237), 105–124 (2002)
Teboulle, M.: A simplified view of first order methods for optimization. Math. Program. 170(1), 67–96 (2018)
Toselli, A., Widlund, O.: Domain Decomposition Methods-Algorithms and Theory. Springer, Berlin (2005)
Xu, J.: Iterative methods by space decomposition and subspace correction. SIAM Rev. 34(4), 581–613 (1992)
Funding
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2019R1A6A1A10073887).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that he has no conflicts of interest/competing interests.
Code availability
The source code used to generate all data for the current study is available from the corresponding author upon request.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, J. Accelerated Additive Schwarz Methods for Convex Optimization with Adaptive Restart. J Sci Comput 89, 58 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-021-01648-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-021-01648-z