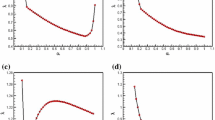
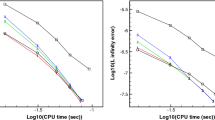
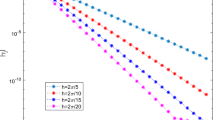
Abstract
A new method is developed to approximate a first-order Hamilton–Jacobi equation. The constant motion of an interface in the normal direction is of interest. The interface is captured with the help of a “Level-Set” function approximated through a finite-volume Godunov-type scheme. Contrarily to most computational approaches that consider smooth Level-Set functions, the present one considers sharp “Level-Set”, the numerical diffusion being controlled with the help of the Overbee limiter (Chiapolino et al. in J Comput Phys 340:389–417, 2017). The method requires gradient computation that is addressed through the least squares approximation. Multidimensional results on fixed unstructured meshes are provided and checked against analytical solutions. Geometrical properties such as interfacial area and volume computation are addressed as well. Results show excellent agreement with the exact solutions.























Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data related to the corresponding computational results are given in the manuscript.
References
Osher, S., Sethian, J.: Fronts propagating with curvature-dependent speed: algorithms based on Hamilton–Jacobi formulations. J. Comput. Phys. 79(1), 12–49 (1988)
Sethian, J.: Curvature and the evolution of fronts. Commun. Math. Phys. 101(4), 487–499 (1985)
Sethian, J.: A fast marching level set method for monotonically advancing fronts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 93(4), 1591–1595 (1996)
Sethian, J.: Numerical algorithms for propagating interfaces: Hamilton–Jacobi equations and conservation laws. J. Differ. Geom. 31(1), 131–161 (1990)
Sethian, J.: Level Set Methods and Fast Marching Methods: Evolving Interfaces in Computational Geometry, Fluid Mechanics, Computer Vision, and Materials Science, vol. 3. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1999)
Morgan, N., Waltz, J.: 3D level set methods for evolving fronts on tetrahedral meshes with adaptive mesh refinement. J. Comput. Phys. 336, 492–512 (2017)
Wei, R., Bao, F., Liu, Y., Hui, W.: Robust three-dimensional level-set method for evolving fronts on complex unstructured meshes. Math. Problems Eng. 2018, 2730829 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2730829
Saurel, R., Le Martelot, S., Tosello, R., Lapébie, E.: Symmetric model of compressible granular mixtures with permeable interfaces. Phys. Fluids 26(12), 123304 (2014)
Saurel, R., Fraysse, F., Furfaro, D., Lapébie, E.: Multiscale multiphase modeling of detonations in condensed energetic materials. Comput. Fluids 159, 95–111 (2017)
Osher, S., Fedkiw, R.: Level Set Methods and Dynamic Implicit Surfaces, vol. 153. Springer, Berlin (2003)
Rouy, E., Tourin, A.: A viscosity solutions approach to shape-from-shading. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 29(3), 867–884 (1992)
Sussman, M., Smereka, P., Osher, S.: A level set approach for computing solutions to incompressible two-phase flow. J. Comput. Phys. 114(1), 146–159 (1994)
Peng, D., Merriman, B., Osher, S., Zhao, H., Kang, M.: A PDE-based fast local level set method. J. Comput. Phys. 155(2), 410–438 (1999)
Sussman, M., Fatemi, E.: An efficient, interface-preserving level set redistancing algorithm and its application to interfacial incompressible fluid flow. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 20(4), 1165–1191 (1999)
Russo, G., Smereka, P.: A remark on computing distance functions. J. Comput. Phys. 163(1), 51–67 (2000)
Olsson, E., Kreiss, G.: A conservative level set method for two phase flow. J. Comput. Phys. 210(1), 225–246 (2005)
Olsson, E., Kreiss, G., Zahedi, S.: A conservative level set method for two phase flow II. J. Comput. Phys. 225(1), 785–807 (2007)
Shukla, R., Pantano, C., Freund, J.: An interface capturing method for the simulation of multi-phase compressible flows. J. Comput. Phys. 229(19), 7411–7439 (2010)
Carmouze, Q., Fraysse, F., Saurel, R., Nkonga, B.: Coupling rigid bodies motion with single phase and two-phase compressible flows and unstructured meshes. J. Comput. Phys. 375, 1314–1338 (2018)
Saurel, R., Pantano, C.: Diffuse interfaces and capturing methods in compressible two-phase flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 50, 105–130 (2018)
Chiapolino, A., Saurel, R., Nkonga, B.: Sharpening diffuse interfaces with compressible fluids on unstructured meshes. J. Comput. Phys. 340, 389–417 (2017)
Dalla, E., Hilpert, M., Miller, C.: Computation of the interfacial area for two-fluid porous medium systems. J. Contam. Hydrol. 56(1–2), 25–48 (2002)
Dauch, F., Ribereau, D.: A software for SRM grain design and internal ballistics evaluation, PIBAL. In: 38th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference & Exhibit, 2002, p. 4299 (2002)
Willcox, M., Brewster, M., Tang, K., Stewart, D.: Solid propellant grain design and burnback simulation using a minimum distance function. J. Propul. Power 23(2), 465–475 (2007)
Cavallini, E.: Modeling and numerical simulation of solid rocket motors internal ballistics. Ph.D. thesis, Sapienza Università di Roma (2010)
Sullwald, W.: Grain regression analysis. Ph.D. thesis, University of Stellenbosch (2014)
Gueyffier, D., Roux, F., Fabignon, Y., Chaineray, G., Lupoglazoff, N., Vuillot, F., Hijlkema, J., Alauzet, F.: Accurate computation of grain burning coupled with flow simulation in rocket chamber. J. Propul. Power 31(6), 1761–1776 (2015)
Engquist, B., Tornberg, A., Tsai, R.: Discretization of Dirac delta functions in level set methods. J. Comput. Phys. 207(1), 28–51 (2005)
Smereka, P.: The numerical approximation of a delta function with application to level set methods. J. Comput. Phys. 211(1), 77–90 (2006)
Min, C., Gibou, F.: Geometric integration over irregular domains with application to level-set methods. J. Comput. Phys. 226(2), 1432–1443 (2007)
Godunov, S.: A finite difference scheme for numerical computation of the discontinuous wave solutions of equations of fluid dynamics. Math. Sb. 47, 271–306 (1959)
LeVeque, R.: Finite Volume Methods for Hyperbolic Problems, vol. 31. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2002)
Toro, E.: Riemann Solvers and Numerical Methods for Fluid Dynamics: A Practical Introduction. Springer, Berlin (2013)
Harten, A., Lax, P., van Leer, B.: On upstream differencing and Godunov-type schemes for hyperbolic conservation laws. SIAM Rev. 25(1), 35–61 (1983)
Davis, S.: Simplified second-order Godunov-type methods. SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comput. 9(3), 445–473 (1988)
Barth, T., Jespersen, D.: The design and application of upwind schemes on unstructured meshes. In: Proceedings of the AIAA 27th Aerospace Science Meeting. Reno, Nevada (1989)
Sweby, P., Baines, M.: Convergence of Roe’s scheme for the general non-linear scalar wave equation. University of Reading, Department of Mathematics (1981)
Roe, P.: Some contributions to the modelling of discontinuous flows. Large-Scale Comput. Fluid Mech. 1985, 163–193 (1985)
Shyue, K., Xiao, F.: An Eulerian interface sharpening algorithm for compressible two-phase flow: the algebraic THINC approach. J. Comput. Phys. 268, 326–354 (2014)
Ii, S., Xie, B., Xiao, F.: An interface capturing method with a continuous function: the THINC method on unstructured triangular and tetrahedral meshes. J. Comput. Phys. 259, 260–269 (2014)
Harten, A.: High resolution schemes for hyperbolic conservation laws. J. Comput. Phys. 49(3), 357–393 (1983)
Sweby, P.: High resolution schemes using flux limiters for hyperbolic conservation laws. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 21(5), 995–1011 (1984)
Harten, A.: On a class of high resolution total-variation-stable finite-difference schemes. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 21(1), 1–23 (1984)
van Leer, B.: Towards the ultimate conservative difference scheme. II. Monotonicity and conservation combined in a second-order scheme. J. Comput. Phys. 14(4), 361–370 (1974)
Tadmor, E.: Convenient total variation diminishing conditions for nonlinear difference schemes. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 25(5), 1002–1014 (1988)
Furfaro, D., Saurel, R., David, L., Beauchamp, F.: Towards sodium combustion modeling with liquid water. J. Comput. Phys. 403, 109060 (2020)
Drew, D., Passman, S.: Theory of Multicomponent Fluids, vol. 135. Springer, Berlin (2006)
Xiao, Z., He, W., Xu, F.: Emulation and calculation of the burning surface of 3D grains of partially cut multi-perforated stick propellant using the level set method. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 41(1), 148–153 (2016)
Horst, J., Albert, W., Robbins, F.: Programmed-splitting solid propellant grain for improved ballistic performance of guns. US Patent 4,581,998 (1986)
Stals, J.: Form-functions for multi-component propellant charges including inhibited grains and sliver burn. Technical report, Materials Research Labs Ascot Vale (Australia) (1975)
Krier, H., Summerfield, M.: Interior ballistics of guns. In: Progress in Astronautics and Aeronautics, vol. 66 (1979)
White, K.: Effect of propellant grain dimensions on progressivity. Technical report, Army Research Lab Aberdeen Proving Ground MD (1997)
Carlucci, D., Jacobson, S.: Ballistics: Theory and Design of Guns and Ammunition. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2013)
Geuzaine, C., Remacle, J., Dular, P.: Gmsh: a three-dimensional finite element mesh generator. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 79(11), 1309–1331 (2009)
Acknowledgements
The authors are very grateful to Jeaniffer Vides for numerous helpful discussions that definitely helped to improve the quality of this work. This work has been partly funded by Eurenco that is gratefully acknowledged.
Funding
Part of this work has been funded by Eurenco that is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Code availability
No, closed-source software.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiapolino, A., Fraysse, F. & Saurel, R. A Method to Solve Hamilton–Jacobi Type Equation on Unstructured Meshes. J Sci Comput 88, 7 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-021-01517-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-021-01517-9