Abstract
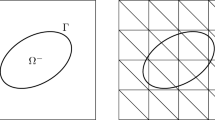
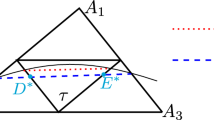
In this paper, we introduce a locally conservative enriched immersed finite element method (EIFEM) to tackle the elliptic problem with interface. The immersed finite element is useful for handling interface with mesh unfit with the interface. However, all the currently available method under IFEM framework may not be designed to consider the conservative flux conservation. We provide an efficient and effective remedy for this issue by introducing a local piecewise constant enrichment, which provides the locally conservative flux. We have also constructed and analyzed an auxiliary space preconditioner for the resulting system based on the application of algebraic multigrid method. The new observation in this work is that by imposing strong Dirichlet boundary condition for the standard IFEM part of EIFEM, we are able to remove the zero eigen-mode of the EIFEM system while still imposing the Dirichlet boundary condition weakly assigned to the piecewise constant enrichment part of EIFEM. A couple of issues relevant to the piecewise constant enrichment given for the mesh unfit to the interface has been discussed and clarified as well. Numerical tests are provided to confirm the theoretical development.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Arnold, D.N.: An interior penalty finite element method with discontinuous elements. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 19, 742–760 (1982)
Arnold, D.N., Brezzi, F., Cockburn, B., Marini, L.D.: Unified analysis of discontinuous Galerkin methods for elliptic problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 39, 1749–1779 (2002)
Bastian, P., Rivière, B.: Superconvergence and \(h(div)\) projection for discontinuous Galerkin methods. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 42, 1043–1057 (2003)
Belytschko, T., Black, T.: Elastic crack growth in finite elements with minimal remeshing. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 45, 601–620 (1999)
Belytschko, T., Parimi, C., Moës, N., Sukumar, N., Usui, S.: Structured extended finite element methods for solids defined by implicit surfaces. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 56, 609–635 (2003)
Bramble, J.H., King, J.T.: A finite element method for interface problems in domains with smooth boundaries and interfaces. Adv. Comput. Math. 6, 109–138 (1996)
Brezzi, F., Fortin, M.: Mixed and Hybrid Finite Element Methods, vol. 15. Springer, New York (1991)
Chen, Z., Zou, J.: Finite element methods and their convergence for elliptic and parabolic interface problems. Numer. Math. 79, 175–202 (1998)
Chippada, S., Dawson, C., Martinez, M., Wheeler, M.: A projection method for constructing a mass conservative velocity field. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 157, 1–10 (1998)
Choi, Y., Jo, G., Kwak, D., Lee, Y.J.: Locally conservative discontinuous bubble scheme for darcy flow and its application to Hele–Shaw equation based on structured grids. Preprint (2021)
Chou, S.H., Kwak, D.Y., Wee, K.T.: Optimal convergence analysis of an immersed interface finite element method. Adv. Comput. Math. 33, 149–168 (2010)
Cockburn, B., Gopalakrishnan, J., Wang, H.: Locally conservative fluxes for the continuous Galerkin method. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 45, 1742–1776 (2007)
Demidov, D.: Amgcl: a c++ library for solution of large sparse linear systems with algebraic multigrid method (2017). https://github.com/ddemidov/amgcl
Demidov, D.: Amgcl: an efficient, flexible, and extensible algebraic multigrid implementation. Lobachevskii J. Math. 40, 535–546 (2019)
Ern, S.N., Alexandre, Vohralík, M.: An accurate \(h(div)\) flux reconstruction for discontinuous Galerkin approximations of elliptic problems. C.R. Math. 345, 709–712 (2007)
Feng, W., He, X., Lin, Y., Zhang, X.: Immersed finite element method for interface problems with algebraic multigrid solver. Commun. Comput. Phys. 15, 1045–1067 (2014)
Guzmán, J., Sánchez, M.A., Sarkis, M.: Higher-order finite element methods for elliptic problems with interfaces. ESAIM Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 50, 1561–1583 (2016)
He, X., Lin, T., Lin, Y.: Approximation capability of a bilinear immersed finite element space. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 24, 1265–1300 (2008)
Hiptmair, R., Xu, J.: Nodal auxiliary space preconditioning in h (curl) and h (div) spaces. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 45, 2483–2509 (2007)
Hughes, T.J., Engel, G., Mazzei, L., Larson, M.G.: The continuous Galerkin method is locally conservative. J. Comput. Phys. 163, 467–488 (2000)
Jo, G., Kwak, D.Y.: A stabilized low order finite element method for three dimensional elasticity problems. Numerical Mathematics: Theory, Methods and Applications
Jo, G., Kwak, D.Y.: An impes scheme for a two-phase flow in heterogeneous porous media using a structured grid. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering (2017)
Jo, G., Kwak, D.Y.: Geometric multigrid algorithms for elliptic interface problems using structured grids. Numerical Algorithms (2018)
Jo, G., Kwak, D.Y.: Recent development of immersed fem for elliptic and elastic interface problems. J. Korea Soc. Ind. Appl. Math. 23, 65–92 (2019)
Krysl, P., Belytschko, T.: An efficient linear-precision partition of unity basis for unstructured meshless methods. Commun. Numer. Methods Eng. 16, 239–255 (2000)
Kwak, D.Y., Jin, S., Kyeong, D.: A stabilized \(p_1\)-nonconforming immersed finite element method for the interface elasticity problems. ESAIM Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 51, 187–207 (2017)
Kwak, D.Y., Wee, K.T., Chang, K.S.: An analysis of a broken \(p_1\)-nonconforming finite element method for interface problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 48, 2117–2134 (2010)
Kwon, I., Kwak, D.Y.: Discontinuous bubble immersed finite element method for Poisson–Boltzmann equation. Commun. Comput. Phys. 25, 928–946 (2019)
Kyeong, D., Kwak, D.Y.: An immersed finite element method for the elasticity problems with displacement jump. Adv. Appl. Math. Mech. 9, 407–428 (2017)
Larson, M.G., Niklasson, A.J.: A conservative flux for the continuous Galerkin method based on discontinuous enrichment. Calcolo 41, 65–76 (2004)
Lee, S., Lee, Y., Wheeler, M.: A locally conservative enriched Galerkin approximation and user-friendly efficient solver for elliptic and parabolic problems. ICES report 15–19 (2015)
Legrain, G., Moes, N., Verron, E.: Stress analysis around crack tips in finite strain problems using the extended finite element method. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 63, 290–314 (2005)
Li, Z., Lin, T., Lin, Y., Rogers, R.C.: An immersed finite element space and its approximation capability. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 20, 338–367 (2004)
Li, Z., Lin, T., Wu, X.: New Cartesian grid methods for interface problems using the finite element formulation. Numer. Math. 96, 61–98 (2003)
Lin, T., Lin, Y., Zhang, X.: Partially penalized immersed finite element methods for elliptic interface problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 53, 1121–1144 (2015)
Moës, N., Dolbow, J., Belytschko, T.: A finite element method for crack growth without remeshing. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 46, 131–150 (1999)
Nepomnyaschikh, S.: Decomposition and Fictitious Domains Methods for Elliptic Boundary Value Problems. Citeseer, Princeton (1991)
Raviart, P.A., Thomas, J.M.: A mixed finite element method for 2-nd order elliptic problems. Mathematical aspects of finite element methods, pp. 292–315 (1977)
Rouitberg, J.A., et al.: A theorem on homeomorphisms for elliptic systems and its applications. Math. USSR Sbornik 7, 439 (1969)
Sun, S., Liu, J.: A locally conservative finite element method based on piecewise constant enrichment of the continuous Galerkin method. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 31, 2528–2548 (2009)
Wheeler, M.F.: An elliptic collocation-finite element method with interior penalties. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 15, 152–161 (1978)
Xu, J.: The auxiliary space method and optimal multigrid preconditioning techniques for unstructured grids. Computing 56, 215–235 (1996)
Acknowledgements
First author is supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No. 2020R1C1C1A01005396). Second author is supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No. 2021R1A2C1003340). Third author is supported by Brain Pool Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea(NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (Grant Number NRF-2020H1D3A2A01041079).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jo, G., Kwak, D.Y. & Lee, YJ. Locally Conservative Immersed Finite Element Method for Elliptic Interface Problems. J Sci Comput 87, 60 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-021-01476-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-021-01476-1