Abstract
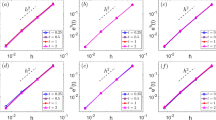
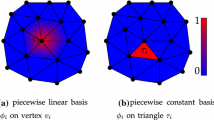
The geodesic curvature flow is an important concept in Riemannian geometry. The flow with level set formulation has many applications in image processing, computer vision, material sciences, etc. The existing discretizations on triangulated surfaces are based on either finite volume method or finite element method with piecewise linear function space, which are suitable for vertex-based two-phase problems. The contour (zero level set) in existing methods passes through triangles of the mesh. However, in some graphic applications, such as mesh segmentation (to divide a whole mesh into several sub-meshes without ambiguous triangular stripes), the cutting contour is needed to be along the edges of the mesh. Moreover, multi-phase segmentation by a single level set function is a difficult problem for a long time. In this paper, we try to tackle these two problems. We propose a new discretization which has simpler formulation and more sparse coefficient matrix. We prove the existence and uniqueness, regularization behavior and maximum–minimum principle of our discrete flow. Therein the maximum–minimum principal has not been presented before. Lots of experiments show that, the limit of the flow would be a piecewise constant solution with ’discontinuity set’ to be the closed geodesics of the surface. We therefore propose a constrained discrete geodesic curvature flow, which is also analyzed theoretically. The linear system of the constrained flow can be equivalently reformulated into a much smaller one (especially in the narrow band algorithm), which dramatically reduces the computation cost. Combined with a narrow band algorithm, the constrained flow with topologically correct initializations (easy to be got by simple existing methods or manual inputs) yields a multi-phase segmentation method by a single level set function. We test our two flows in closed curve evolution and multi-region segmentation applications. The numerical experiments are given to demonstrate the effectiveness.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adalsteinsson, D., Sethian, J.A.: A fast level set method for propagating interfaces. J. Comput. Phys. 118(2), 269–277 (1995)
Adalsteinsson, D., Sethian, J.A.: The fast construction of extension velocities in level set methods. J. Comput. Phys. 148(1), 2–22 (1999)
Brox, T., Weickert, J.: Level set segmentation with multiple regions. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 15(10), 3213–3218 (2006)
Caselles, V., Catté, F., Coll, F., Dibos, F.: A geometric model for active contours in image processing. Numer. Math. 66(1), 1–31 (1993)
Caselles, V., Kimmel, R., Sapiro, G.: Geodesic active contours. In: Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Computer Vision, 1995, pp. 694–699 (1995)
Caselles, V., Kimmel, R., Sapiro, G., Sbert, C.: Minimal surfaces: a geometric three dimensional segmentation approach. Numer. Math. 77(4), 423–451 (1997)
Chan, T., Vese, L.: Active contours without edges. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 10(2), 266–277 (2001)
Cheng, L.T., Burchard, P., Merriman, B., Osher, S.: Motion of curves constrained on surfaces using a level-set approach. J. Comput. Phys. 175(2), 604–644 (2002)
Chopp, D.L.: Computing minimal surfaces via level set curvature flow. J. Comput. Phys. 106(1), 77–91 (1993)
Chopp, D.L., Sethian, J.A.: Flow under curvature: singularity formation, minimal surfaces, and geodesics. Exp. Math. 2(4), 235–255 (1993)
Davis, H.T., Thomson, K.T.: Linear Algebra and Linear Operators in Engineering: With Applications in Mathematica. Academic Press, New York (2000)
Dubrovina, A., Rosman, G., Kimmel, R.: Multi-region active contours with a single level set function. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 37(8), 1585–1601 (2015)
Evans, L.C., Spruck, J.: Motion of level sets by mean curvature: I. J. Differ. Geom. 33(3), 635–681 (1991)
Fu, Z., Jeong, W., Pan, Y., Kirby, R., Whitaker, R.: A fast iterative method for solving the eikonal equation on triangulated surfaces. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 33(5), 2468–2488 (2011)
Gage, M.: Curve shortening makes convex curves circular. Invent. Math. 76(2), 357–364 (1984)
Gage, M.: Curve shortening on surfaces. Ann. Sci. École Norm. Sup. 23(2), 229–256 (1990)
Gage, M., Hamilton, R.S.: The heat equation shrinking convex plane curves. J. Differ. Geom. 23(1), 69–96 (1986)
Goldenberg, R., Kimmel, R., Rivlin, E., Rudzsky, M.: Fast geodesic active contours. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 10(10), 1467–1475 (2001)
Grayson, M.A.: The heat equation shrinks embedded plane curves to round points. J. Differ. Geom. 26(2), 285–314 (1987)
Grayson, M.A.: Shortening embedded curves. Ann. Math. 129(1), 71–111 (1989)
Hoffman, D.D., Richards, W.A.: Parts of recognition. Cognition 18, 65–96 (1984)
Kass, M., Witkin, A., Terzopoulos, D.: Snakes: active contour models. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1(4), 321–331 (1988)
Kimia, B.B., Siddiqi, K.: Geometric heat equation and nonlinear diffusion of shapes and images. In: Proceedings of the 1994 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 1994 (CVPR’94.), pp. 113–120 (1994)
Kimmel, R.: Intrinsic scale space for images on surfaces: the geodesic curvature flow. In: Romeny, B.H., Florack, L., Koenderink, J., Viergever, M. (eds.) Scale-Space Theory in Computer Vision, pp. 212–223. Springer, Berlin (1997)
Lai, R., Shi, Y., Sicotte, N., Toga, A.: Automated corpus callosum extraction via laplace-beltrami nodal parcellation and intrinsic geodesic curvature flows on surfaces. In: Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2034–2040 (2011)
Lai, Y., Hu, S., Martin, R., Rosin, P.: Fast mesh segmentation using random walks. In: Proceedings of the 2008 ACM Symposium on Solid and Physical Modeling, pp. 183–191 (2008)
Lie, J., Lysaker, M., Tai, X.C.: A variant of the level set method and applications to image segmentation. Math. Comput. 75(255), 1155–1174 (2006)
Ma, L., Chen, D.: Curve shortening flow in a riemannian manifold. 2003. arXiv:math/0312463
Malladi, R., Sethian, J.A., Vemuri, B.C.: Shape modeling with front propagation: a level set approach. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 17(2), 158–175 (1995)
Meyer, M., Desbrun, M., Schröder, P., Barr, A.: Discrete differential-geometry operators for triangulated 2-manifolds. In: Hege, H.-C., Polthier, K. (eds.) Visualization and Mathematics III: Mathematics and Visualization, pp. 35–57. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2003)
Mikula, K., Sevcovic, D.: Evolution of curves on a surface driven by the geodesic curvature and external force. Appl. Anal. 85(4), 345–362 (2006)
Osher, S., Sethian, J.A.: Fronts propagating with curvature dependent speed: algorithms based on Hamilton–Jacobi formulations. J. Comput. Phys. 79(1), 12–49 (1988)
Poole, G., Boullion, T.: A survey on M-matrices. SIAM Rev. 16(16), 419–427 (1974)
Qian, J., Zhang, Y., Zhao, H.: Fast sweeping methods for eikonal equations on triangular meshes. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 45(1), 83–107 (2007)
Samson, C., Blanc-Féraud, L., Aubert, G., Zerubia, J.: A level set model for image classification. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 40(3), 187–197 (2000)
Saye, R.I., Sethian, J.A.: The Voronoi implicit interface method for computing multiphase physics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 108(49), 19498–19503 (2011)
Saye, R.I., Sethian, J.A.: Analysis and applications of the Voronoi implicit interface method. J. Comput. Phys. 231(18), 6051–6085 (2012)
Sethian, J.A.: Level Set Methods and Fast Marching Methods: Evolving Interfaces in Geometry, Fluid Mechanics, Computer Vision and Materials Sciences. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1999)
Spira, G., Kimmel, R.: Geometric curve flows on parametric manifolds. J. Comput. Phys. 223(1), 235–249 (2007)
Tsai, A., Yezzi, A., Willsky, A.: Curve evolution implementation of the Mumford–Shah functional for image segmentation, denoising, interpolation, and magnification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 10(8), 1169–1186 (2001)
Vese, L., Chan, T.: A multiphase level set framework for image segmentation using the Mumford and Shah model. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 50(3), 271–293 (2002)
Wu, C., Tai, X.C.: A level set formulation of geodesic curvature flow on simplicial surfaces. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 16(4), 647–662 (2010)
Zhang, H., Wu, C., Zhang, J., Deng, J.: Variational mesh denoising using total variation and piecewise constant function space. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 21(7), 873–886 (2015)
Zhang, J., Wu, C., Cai, J., Zheng, J., Tai, X.C.: Mesh snapping: robust interactive mesh cutting using fast geodesic curvature flow. Comput. Graph. Forum 29(2), 517–526 (2010)
Zhao, H., Chan, T., Merriman, B., Osher, S.: A variational level set approach to multiphase motion. J. Comput. Phys. 127(1), 179–195 (1996)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the NSF of China (No. 11301289), Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities [China University of Geosciences (Wuhan)] and Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities (Nankai University). Chunlin Wu is the corresponding author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Zhang, H. & Wu, C. On Geodesic Curvature Flow with Level Set Formulation Over Triangulated Surfaces. J Sci Comput 70, 631–661 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-016-0260-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-016-0260-3