Abstract
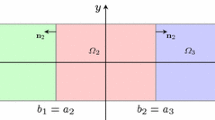
This paper is devoted to the efficient computation of the time dependent Schrödinger equation for quantum particles subject to intense electromagnetic fields including ionization and recombination of electrons with their parent ion. The proposed approach is based on a domain decomposition technique, allowing a fine computation of the wavefunction in the vicinity of the nuclei located in a domain \(\Omega _1\) and a fast computation in a roughly meshed domain \(\Omega _2\) far from the nuclei where the electrons are assumed free. The key ingredients in the method are (i) well designed transmission boundary conditions on \(\partial \Omega _1\) (resp. \(\partial \Omega _2\)) in order to estimate the part of the wavefunction “leaving” Domain \(\Omega _1\) (resp. \(\Omega _2\)), (ii) a Schwarz waveform relaxation algorithm to accurately reconstruct the solution. The developed method makes it possible for electrons to travel from one domain to another without loosing accuracy, when the frontier or the overlapping region between two domains is crossed by the wavefunction.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alinhac, S., Gérard, P.: Pseudo-Differential Operators and the Nash–Moser Theorem, volume 82 of Graduate Studies in Mathematics. American Mathematical Society, Providence, RI (2007). Translated from the 1991 French original by Stephen S. Wilson
Antoine, X., Arnold, A., Besse, C., Ehrhardt, M., Schädle, A.: A review of transparent and artificial boundary conditions techniques for linear and nonlinear Schrödinger equations. Commun. Comput. Phys. 4(4), 729–796 (2008)
Antoine, X., Bao, W., Besse, C.: Computational methods for the dynamics of the nonlinear Schrödinger/Gross–Pitaevskii equations. Comput. Phys. Comm. 184(12), 2621–2633 (2013)
Antoine, X., Barucq, H., Bendali, A.: Bayliss–Turkel-like radiation conditions on surfaces of arbitrary shape. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 229(1), 184–211 (1999)
Antoine, X., Besse C.: Construction, structure and asymptotic approximations of a microdifferential transparent boundary condition for the linear Schrödinger equation. J. Math. Pures Appl. (9), 80(7), 701–738 (2001)
Antoine, X., Besse, C.: Unconditionally stable discretization schemes of non-reflecting boundary conditions for the one-dimensional Schrödinger equation. J. Comput. Phys. 188(1), 157–175 (2003)
Antoine, X., Besse, C., Klein, P.: Absorbing boundary conditions for the one-dimensional Schrödinger equation with an exterior repulsive potential. J. Comput. Phys. 228(2), 312–335 (2009)
Antoine, X., Besse, C., Klein, P.: Absorbing boundary conditions for the two-dimensional Schrödinger equation with an exterior potential. Part I: construction and a priori estimates. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 22(10), 1250026, 38 (2012)
Antoine, X., Besse, C., Klein, P.: Absorbing boundary conditions for the two-dimensional Schrodinger equation with an exterior potential. Part II: discretization and numerical results. Numerische Mathematik 125(2), 191–223 (2013)
Antoine, X., Besse, C., Szeftel, J.: Towards accurate artificial boundary conditions for nonlinear PDEs through examples. Cubo 11(4), 29–48 (2009)
Bandrauk, A.: Molecules in Laser Fields, Chap. 1. M. Dekker, NY (1994)
Bandrauk, A., Chelkowski, S., Yu, H., Constant, E.: Enhanced harmonic generation in extended molecular systems by two-color excitation. Phys. Rev. A 56, 2537–2540 (1997)
Bandrauk, A.D., Fillion-Gourdeau, F., Lorin, E.: Atoms and molecules in intense laser fields: gauge invariance of theory and models. J. Phys. B-Atom. Mol. Opt. Phys. 46(15), 153001 (2013)
Baskakov, V.A., Popov, A.V.: Implementation of transparent boundaries for numerical solution of the Schrödinger equation. Wave Mot. 14(2), 123–128 (1991)
Bérenger, J.-P.: A perfectly matched layer for the absorption of electromagnetic waves. J. Comput. Phys. 114(2), 185–200 (1994)
Cohen-Tannoudji, C., Dupont-Roc, J., Grynberg, G.: Atom–Photon Interactions. Wiley, NY (1992)
Corkum, P.-B.: Plasma perspective on strong-field multiphoton ionization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 71, 1994–1997 (1993)
Engquist, B., Majda, A.: Absorbing boundary conditions for the numerical simulation of waves. Math. Comp. 31(139), 629–651 (1977)
Gander, M., Halpern, L.: Optimized schwarz waveform relaxation methods for advection reaction diffusion problems. SIAM J. Num. Anal. 45(2), 666–697 (2007)
Gander, M.J.: Optimized Schwarz methods. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 44(2), 699–731 (2006); (electronic)
Gander, M.J., Halpern, L., Nataf, F.: Optimal Schwarz waveform relaxation for the one dimensional wave equation. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 41(5), 1643–1681 (2003)
Hagstrom, T., Tewarson, R.P., Jazcilevich, A.: Numerical experiments on a domain decomposition algorithm for nonlinear elliptic boundary value problems. Appl. Math. Lett. 1(3), 299–302 (1988)
Halpern, L., Rauch, J.: Error analysis for absorbing boundary conditions. Numer. Math. 51(4), 459–467 (1987)
Halpern, L., Szeftel, J.: Optimized and quasi-optimal Schwarz waveform relaxation for the one-dimensional Schrödinger equation. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 20(12), 2167–2199 (2010)
Hörmander, L.: The Analysis of Linear Partial Differential Operators. III. Classics in Mathematics. Springer, Berlin (2007); Pseudo-Differential Operators
Jiang, S., Greengard, L.: Fast evaluation of nonreflecting boundary conditions for the Schrödinger equation in one dimension. Comput. Math. Appl. 47(6–7), 955–966 (2004)
Kamta, G.L., Bandrauk, A.D.: High-order harmonic generation from two-center molecules: time-profile analysis of nuclear contributions. Phys. Rev. A 70(1), 011404-1–011404-4 (2004)
Lewenstein, M., Balcou, Ph, Ivanov, MYu., L’Huillier, A., Corkum, P.B.: Theory of high-harmonic generation by low-frequency laser fields. Phys. Rev. A 49(3), 2117–2132 (1994)
Lorin, E., Chelkowski, S., Bandrauk, A.: A numerical Maxwell–Schrödinger model for laser-matter interaction and propagation. Comput. Phys. Comm. 177(12), 908–932 (2007)
Lorin, E., Chelkowski, S., Bandrauk, A.: Attosecond pulse generation from aligned molecules—dynamics and propagation in H\(_2^+\). New J. Phys. 10, 025033 (2008)
Lorin, E., Chelkowski, S., Bandrauk, A.D.: Mathematical modeling of boundary conditions for laser-molecule time-dependent Schrödinger equations and some aspects of their numerical computation—one-dimensional case. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 25(1), 110–136 (2009)
Milosevic, D.B., Paulus, G.G., Bauer, D., Becker, W.: Above-threshold ionization by few-cycle pulses. J. Phys. B: Atom. Mol. Opt. Phys. 39(14), R203–R262 (2006)
Strikwerda, J.C.: Finite Difference Schemes and Partial Differential Equations, 2nd ed. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics (SIAM), Philadelphia, PA (2004)
Szeftel, J.: Absorbing boundary conditions for one-dimensional nonlinear Schrödinger equations. Numer. Math. 104(1), 103–127 (2006)
Acknowledgments
The first author thanks the support of the french ANR grants “Bond” (ANR-13-BS01-0009-01) and “BECASIM” (ANR-12-MONU-0007-02). The second and third authors would like to thank NSERC for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antoine, X., Lorin, E. & Bandrauk, A.D. Domain Decomposition Method and High-Order Absorbing Boundary Conditions for the Numerical Simulation of the Time Dependent Schrödinger Equation with Ionization and Recombination by Intense Electric Field. J Sci Comput 64, 620–646 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-014-9902-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-014-9902-5