Abstract
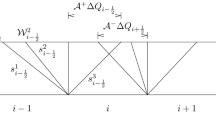
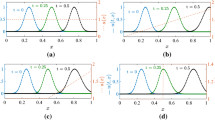
Systems of hyperbolic partial differential equations with source terms (balance laws) arise in many applications where it is important to compute accurate time-dependent solutions modeling small perturbations of equilibrium solutions in which the source terms balance the hyperbolic part. The f-wave version of the wave-propagation algorithm is one approach, but requires the use of a particular averaged value of the source terms at each cell interface in order to be “well balanced” and exactly maintain steady states. A general approach to choosing this average is developed using the theory of path conservative methods. A scalar advection equation with a decay or growth term is introduced as a model problem for numerical experiments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, N., Lindeman, J.: Euler solutions using flux-based wave decomposition. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 54, 47–72 (2006)
Audusse, E., Bouchut, F., Bristeau, M.O., Klein, R., Perthame, B.: A fast and stable well-balanced scheme with hydrostatic reconstruction for shallow water flows. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 25, 2050–2065 (2004)
Bale, D., LeVeque, R.J., Mitran, S., Rossmanith, J.A.: A wave-propagation method for conservation laws and balance laws with spatially varying flux functions. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 24, 955–978 (2002)
Berger, M.J., Calhoun, D.A., Helzel, C., LeVeque, R.J.: Logically rectangular finite volume methods with adaptive refinement on the sphere. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 367, 4483–4496 (2009)
Bermúdez, A., Vázquez Cendón, M.E.: Upwind methods for hyperbolic conservations laws with source term. Comput. Fluids 23, 1049–1071 (1994)
Botta, N., Klein, R., Langenberg, S., Lützenkirchen, S.: Well balanced finite volume methods for nearly hydrostatic flows. J. Comput. Phys. 196, 539–565 (2004)
Bouchut, F.: Nonlinear Stability of Finite Volume Methods for Hyperbolic Conservation Laws and Well-Balanced Schemes for Sources. Birkhäuser, Boston (2004)
Castro, M., Gallardo, J.M., López, J.A., Parés, C.: Well-balanced high order extensions of Godunov’s method for semilinear balance laws. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 46, 1012–1039 (2008)
Castro, M.J., LeFloch, P.G., Munoz, M.L., Parés, C.: Why many theories of shock waves are necessary: convergence error in formally path-consistent schemes. J. Comput. Phys. 227, 8107–8129 (2008)
Castro Díaz, M.J., Chacón Rebollo, T., Fernández-Nieto, E.D., Parés, C.: On well-balanced finite volume methods for nonconservative nonhomogeneous hyperbolic systems. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 29(3), 1093–1126 (2007)
Colombeau, J.-F., LeRoux, A.Y., Noussair, A., Perrot, B.: Microscopic profiles of shock waves and ambiguities in multiplications of distributions. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 26, 871–883 (1989)
Dal Maso, G., LeFloch, P.G., Murat, F.: Definition and weak stability of nonconservative products. J. Math. Pure Appl. 74, 483–548 (1995)
George, D.L.: Finite volume methods and adaptive refinement for tsunami propagation and inundation. PhD thesis, University of Washington (2006)
George, D.L.: Augmented Riemann solvers for the shallow water equations over variable topography with steady states and inundation. J. Comput. Phys. 227, 3089–3113 (2008)
George, D.L., LeVeque, R.J.: Finite volume methods and adaptive refinement for global tsunami propagation and local inundation. Sci. Tsunami Hazards 24, 319–328 (2006)
Gosse, L.: A well-balanced flux-vector splitting scheme designed for hyperbolic systems of conservation laws with source terms. Comput. Math. Appl. 39, 135–159 (2000)
Gosse, L.: A well-balanced scheme using non-conservative products designed for hyperbolic systems of conservation laws with source terms. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 11, 339–365 (2001)
Greenberg, J.M., LeRoux, A.Y.: A well-balanced scheme for the numerical processing of source terms in hyperbolic equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 33, 1–16 (1996)
Gundlach, C., LeVeque, R.J.: Universality in the run-up of shock waves to the surface of a star. J. Fluid Mech., submitted. arXiv:1008.2834v1 [astro-ph.SR]
Khouider, B., Majda, A.J.: A non-oscillatory balanced scheme for an idealized tropical climate model. Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 19, 331–354 (2005)
Kurganov, A., Levy, D.: Central-upwind schemes for the Saint-Venant system. Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 36, 397–425 (2002)
LeVeque, R.J.: Balancing source terms and flux gradients in high-resolution Godunov methods: The quasi-steady wave-propagation algorithm. J. Comput. Phys. 146, 346–365 (1998)
LeVeque, R.J.: Finite Volume Methods for Hyperbolic Problems. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2002)
LeVeque, R.J., et al.: clawpack software. www.clawpack.org
LeVeque, R.J., Pelanti, M.: A class of approximate Riemann solvers and their relation to relaxation schemes. J. Comput. Phys. 172, 572–591 (2001)
Marche, F., Bonneton, P., Fabrie, P., Seguin, N.: Evaluation of well-balanced bore-capturing schemes for 2d wetting and drying processes. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 53, 867–894 (2007)
Noelle, S., Pankrantz, N., Puppo, G., Natvig, J.R.: Well-balanced finite volume schemes of arbitrary order of accuracy for shallow water flows. J. Comput. Phys. 213, 474–499 (2006)
Noelle, S., Xing, Y., Shu, C.-W.: High-order well-balanced finite volume WENO schemes for shallow water equation with moving water. J. Comput. Phys. 226, 29–58 (2007)
Pelanti, M., Bouchut, F., Mangeney, A.: A Roe-type scheme for two-phase shallow granular flows over variable topography. Model. Math. Anal. Numer. 42, 851–885 (2008)
Pelanti, M., Bouchut, F., Mangeney, A., Vilotte, J.-P.: Numerical modeling of two-phase gravitational granular flows with bottom topography. In: Hyperbolic Problems: Theory, Numerics, Applications, Proc. 11th Intl. Conf. on Hyperbolic Problems, 2006, pp. 825–832. Springer, Berlin (2008)
Toumi, I.: A weak formulation of Roe’s approximate Riemann solver. J. Comput. Phys. 102, 360–373 (1992)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
LeVeque, R.J. A Well-Balanced Path-Integral f-Wave Method for Hyperbolic Problems with Source Terms. J Sci Comput 48, 209–226 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-010-9411-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-010-9411-0