Abstract
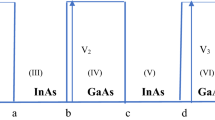
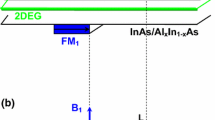
Spin-dependent electron tunneling in InAs/GaAs double-barrier heterostructures was theoretically studied using the matrix method. The effects of Dresselhaus spin–orbit interaction, in-plane wave vector, magnetic field, the magnitude of an electric field, and negative field on its spin-transport were discussed. The Dresselhaus spin–orbit interaction enhances the spin polarization and energy between spin resonances. The in-plane wave vector shifts the resonance of polarization, and the increasing in-plane wave vector shifts the resonance to a higher value on the energy scale. The increasing magnetic field enhances the Zeeman splitting and causes enhanced polarization. The spin splitting was achieved due to the tunable magnitude of the electric field, and the negative electric field highly influences the spin transport properties.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Caliskan, M. Kumru, J. Phys. Condens. Matter 19, 076205 (2007)
J.P. Eisenstein, L.N. Pfeiffer, K.W. West, Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 186801 (2017)
M. Holub, P. Bhattacharya, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 40, R179 (2007)
I. Zutic, J. Fabian, S.D. Sarma, Phys. Rev. B 64, 121201 (2001)
L.B. Chandrasekar, K. Gnanasekar, M. Karunakaran, Superlattices Microstruct. 136, 106322 (2019)
E.A. Andrada, G.C. LaRocca, F. Bassani, Phys. Rev. B 50, 8523 (1994)
E.A. Andrada, G.C. LaRocca, F. Bassani, Phys. Rev. N 55, 16293 (1997)
J. Gang, X.X. Liang, S.L. Ban, J. Appl. Phys. 102, 073718 (2007)
K. Gnanasekar, K. Navaneethakrishnan, Physica E 28, 328 (2005)
J.D.S. Teixeira, H.O. Frota, A.C.R. Bittencourt, Phys. Scr. 89, 085804 (2014)
K. Gnanasekar, K. Navaneethakrishnan, Phys. Lett. A 341, 495 (2005)
L.B. Chandrasekar, K. Gnanasekar, M. Karunakaran, R. Chandramohan, Curr. Appl. Phys. 15, 1421 (2015)
L.B. Chandrasekar, M. Karunakaran, K. Gnanasekar, J. Semicond. 39, 112001 (2018)
M. Eric, J. Radovanovic, V. Milanovic, Z. Ikonic, D. Indjin, J. Appl. Phys. 103, 083701 (2008)
A. Voskoboynikov, S.S. Liu, C.P. Lee, Phys. Rev. B 59, 12514 (1999)
Y. Guo, H. Wang, B.L. Gu, Y. Kawazoe, J. Appl. Phys. 88, 6614 (2000)
J. Radovanovic, V. Milanovic, Z. Ikonic, D. Indjin, J. Appl. Phys. 99, 073905 (2006)
S.L. Chuang, Physics of Optoelectronic Devices (Wiley, New York, 1995)
S.G. Shen, X.Q. Fan, J. Phys. Condens. Matter 9, 3151 (1997)
V.I. Perel, S.A. Tarasenko, I.N. Yassievich, S.D. Ganichev, V.V. Bel’kov, W. Prettl, Phys. Rev. B 67, 201304(R) (2003)
X.F. Wang, P. Vasilopoulos, F.M. Peeters, Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 1400 (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chandrasekar, L.B., Karunakaran, M. & Gnanasekar, K. Spin-Polarized Transport in InAs/GaAs Double-Barrier Heterostructure with Electric and Magnetic Fields. J Low Temp Phys 210, 241–250 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-022-02872-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-022-02872-z