Abstract
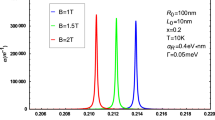
The ground state energy (GSE), ground state binding energy (GSBE), vibrational frequency (VF) and the mean number of LO phonons (MNLOP) of the strong-coupling magnetopolaron in an asymmetrical semi-exponential quantum well are studied theoretically under uniform magnetic field along the \(z\) direction. The anisotropic parabolic potential and asymmetrical semi-exponential confinement potential effects on the GSE, the GSBE, the VF and the MNLOP are acquired with the Lee-Low-Pines unitary transformation and linear combination operation method. The temperature properties of the GSE, the GSBE, the VF and the MLOPN of the strongly coupled polaron in asymmetrical semi-exponential quantum well is studied by using the quantum statistical theory. The changes of the GSE, the GSBE, the VF and MLOPN versus temperature and cyclotron frequency in a magnetic field were discussed. It is observed from the figures that the GSE, the GSBE, the VF and the MNLOP of the strong-coupling magnetopolaron in an asymmetrical semi-exponential quantum wells are an enlarging function of the parameter \(U_{0}\), whereas it elevates with decaying the other parameter \(\sigma\). The GSE, the GSBE, the VF and the MNLOP of strong-coupling magnetopolaron rapidly increase with the increase of the confinement strengths of an anisotropic parabolic potential in the x and y directions. The GSE, the GSBE, the VF and the MNLOP of the strong-coupling magnetopolaron rapidly increase with the decrease of the effective confinement lengths of an anisotropic parabolic potential in the x and y directions. The GSE, the GSBE, the VF and the MNLOP of the strong-coupling magnetopolaron rapidly increase with increasing the cyclotron frequency of magnetic field. The GSE and the GSBE of the strong-coupling magnetopolaron increase by decreasing the temperature, whereas the VF and the MNLOP increase by increasing the temperature.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Hindouri, S. Nasr, F Saidi. 173, 109182 (2020)
F. Ungan, M.K. Bahar, M.E. Mora-Ramos, Phys. Scr. 95(5), 055808 (2020)
X. Li, H. Wang, Z. Oiao et al., Appl Phys Lett 114(22), 221104 (2020)
K.D. Zhu, S.W. Gu, Phys. Rev. B 47, 12941 (1993)
K.D. Zhu, S.W. Gu, Commun. Theor. Phys. 19, 27 (1992)
H.V. Phuc, L.V. Tung, P.T. Vinh, L. Dinh, Superlattices Microstruct. 77, 267–275 (2015)
A.X. Gou, J.F. Du, Superlattices Microstruct. 64, 158–166 (2013)
J.L. Xiao, Superlattices Microstruct. 135, 106279 (2019)
B. Donfack, F. Fotio, A.J. Fotue, L.C. Fai, Chinese. J. Phys. 66, 573–579 (2020)
B. Donfack, F. Fotio, A.J. Fotue, Eur. Phys. J. Plus. 136(2), 1–15 (2021)
B. Donfack, G.T. Tedondje, T.M. Cedric, C.D.G. Ngoufack, A.J. Fotue, Am. J. Mod. Phys. 10(5), 101–110 (2021)
S. Mou, K.X. Guo, B. Xiao, Superlattices Microstruct. 72, 72–82 (2014)
K.X. Guo, B. Xiao, Y.C. Zhou, Z.M. Zhang, J. Opt. 17, 035505 (2015)
W. Xiao, Y.J. Chen, J.L. Xiao, Chinese. J. Phys. 61, 190–193 (2019)
S. Mou, K.X. Guo, G.H. Liu, B. Xiao, Phys. B 434, 84–88 (2014)
B. Xiao, K.X. Guo, S. Mou, Z.M. Zhang, Superlattices Microstruct. 69, 122–128 (2014)
Y. Sun, J.L. Xiao, Superlattices Microstruct. 145, 106617 (2020)
X.Q. Wang, Y.J. Chen, J.L. Xiao, Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 33(21), 1950239 (2019)
Y.L. Li, J.L. Xiao, Iran J. Sci. Technol. Trans. A: Sci. 43(4), 2013–2016 (2019)
W.J. Huybrechts, J. Phys. C: Solid State Phys. 10, 3761–3768 (1977)
J.L. Xiao, Superlattices Microstruct. 120, 459–462 (2018)
S. Mou, K.X. Guo, B. Xiao, Superlattices Microstruct. 65, 309–318 (2014)
J.L. Xiao, J Low Temp. Phys. 202, 196–204 (2021)
X.Q. Wang, J.L. Xiao, Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57, 3436–3442 (2018)
J T Devreese., (North-Holland Publishing Company, Amsterdam,1972)
S.H. Chen, J.L. Xiao, Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 21, 5331 (2007)
J.K. Sun, H.J. Li, J.L. Xiao, Superlattices Microstruct. 46, 476 (2009)
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by the National Science Foundation of China under Grant No.12164032.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, W., Miao, XJ., Sun, Y. et al. Parabolic Potential and Temperature Effects on the Magnetopolaron in a RbCl Asymmetrical Semi-exponential Quantum Well. J Low Temp Phys 210, 209–231 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-022-02840-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-022-02840-7