Abstract
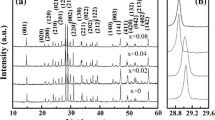
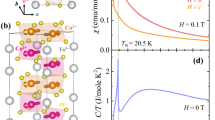
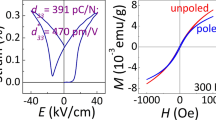
Negative magnetization effect in the quasi-two-dimensional distorted honeycomb-layered Ni4Nb2O9 ceramics is revealed through rigorous magnetic measurements. Owing to the different degrees of distortion, the Ni–Ni honeycomb layers with antiferromagnetic interlayered coupling demonstrate two types of temperature dependences, resulting in a negative magnetization effect. Here we report the structure, magnetism, magnetic switching effect and magnetocaloric effect in Ni4Nb2O9 compound, synthesized by the solid-state reaction method. The magnetization curves display a ferrimagnetic behavior with a critical temperature of 76 K. The negative magnetization state occurs at 32 K which can be ascribed to the different temperature dependence of two distorted honeycomb layers. Besides, the tunable magnetic switching effect can be obtained by changing the temperature or magnitude of the external field that shows the potential application prospects. These results provide a new platform and understanding of the negative magnetization effect in these series of materials which consist of antiferromagnetic coupling sublattices.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
L. Néel, Ann. Phys. Paris 3, 137–198 (1948)
A. Kumar, S.M. Yusuf, Phys. Rep. 556, 1–34 (2015)
S. Biswas, S. Pal, Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 53, 206–217 (2018)
M. Ghanathe, A. Kumar, S.M. Yusuf, J. Appl. Phys. 125, 093903 (2019)
Y. Ren, T.T.M. Palstra, D.I. Khomskii, E. Pellegrin, A.A. Nugroho, A.A. Menovsky, G.A. Sawatzky, Nature 396, 441 (1998)
Y. Ren, T.T.M. Palstra, D.I. Khomskii, A.A. Nugroho, A.A. Menovsky, G.A. Sawatzky, Phys. Rev. B 62, 6577 (2000)
N. Menyuk, K. Dwight, D. Wickham, Phys. Rev. Lett. 4, 119 (1960)
Y. Fang, Y.Q. Song, W.P. Zhou, R. Zhao, R.J. Tang, H. Yang, L.Y. Lv, S.G. Yang, D.H. Wang, Y.W. Du, Sci. Rep. 4, 3860 (2015)
N. Narayanan, A. Senyshyn, D. Mikhailova, T. Faske, T. Lu, Z. Liu, B. Weise, H. Ehrenberg, R.A. Mole, W.D. Hutchison, H. Fuess, G.J. McIntyre, Y. Liu, D. Yu, Phys. Rev. B 98, 134438 (2018)
S.N. Panja, L. Harnagea, J. Kumar, I.P.K. Mukharjee, R. Nath, A.K. Nigam, S. Nair, Phys. Rev. B 98, 024410 (2018)
A. Maignan, C. Martin, Phys. Rev. B 97, 161106 (2018)
N.D. Khanh, N. Abe, H. Sagayama, A. Nakao, T. Hanashima, R. Kiyanagi, Y. Tokunaga, T. Arima, Phys. Rev. B 93, 075117 (2016)
G. Deng, Y. Yu, Y. Cao, Z. Feng, W. Ren, S. Cao, A.J. Studer, J.R. Hester, Y. Kareri, C. Ulrich, G.J. McIntyre, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 31, 235801 (2019)
G.C. Deng, Y.M. Cao, W. Ren, S.X. Cao, A.J. Studer, N. Gauthier, M. Kenzelmann, G. Davidson, K.C. Rule, J.S. Gardner, P. Imperia, C. Ulrich, G.J. McIntyre, Phys. Rev. B 97, 085154 (2018)
E. Tailleur, C. Martin, F. Damay, F. Fauth, A. Maignan, J. Appl. Phys. 127, 063902 (2020)
M. Hase, V.Y. Pomjakushin, V. Sikolenko, L. Keller, H. Luetkens, A. Donni, H. Kitazawa, Phys. Rev. B 84, 104402 (2011)
Q.S. Fu, X.H. Chen, C. Chakrabarti, C.L. Li, J. Zheng, P.J. Wang, H.X. Yin, Y. Qiu, B. Meng, S.L. Yuan, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys 22, 7058 (2020)
Z.D. Fu, H.S. Nair, Y. Xiao, A. Senyshyn, V.Y. Pomjakushin, E. Feng, Y. Su, W.T. Jin, T. Bruckel, Phys. Rev. B 94, 125150 (2016)
L. Xie, H.G. Zhang, H.L. Huang, Y.L. Lu, J.Q. Yu, M.H. Li, X.Q. Tang, C. Wang, J. Alloys Compd. 772, 703–709 (2019)
S. Thota, M.S. Seehra, J. Appl. Phys. 113, 203905 (2013)
C.L. Li, C.L. Wang, Q.K. Lei, G.O. Barasa, Q.S. Fu, Y. Qiu, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 22, 28222 (2020)
R. Padam, S. Pandya, S. Ravi, S. Ramakrishnan, A.K. Nigam, A.K. Grover, D. Pal, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 29, 055803 (2017)
C.L. Li, T.Y. Yan, G.O. Barasa, Y.H. Li, R. Zhang, Q.S. Fu, X.H. Chen, S.L. Yuan, Ceram. Int. 44, 15446–15452 (2018)
L.G. Wang, C.M. Zhu, Z.M. Tian, H. Luo, D.L.G.C. Bao, S.L. Yuan, Appl. Phys. Lett. 107, 152406 (2015)
H. Yamamoto, S. Sekikawa, H. Taniguchi, M. Matsukawa, K. Shigematsu, T. Honda, K. Yamauchi, K. Ikeda, T. Otomo, T. Sakakura, M. Azuma, S. Nimori, Y. Noda, H. Kimura, Appl. Phys. Lett. 117, 112404 (2020)
S.M. Yusuf, A. Kumar, J.V. Yakhmi, Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 182506 (2009)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.11474111), Key Research Projects of Henan Provincial Department of Education (21A140024), and Nanhu Scholars Program for Young Scholars of XYNU. We would like to thank the staff of the Analysis Center of Huazhong University of Science and Technology for their help in various measurements.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11474111), Key Research Projects of Henan Provincial Department of Education (21A140024), and Nanhu Scholars Program for Young Scholars of XYNU.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Consent to Participate
We confirm that the manuscript has been read and approved by all named authors, and the order of authors listed in the manuscript has been approved by all of us.
Consent for Publication
We are approving to publish in journal of low-temperature physics if the manuscript can be accepted.
Ethical Approval
This manuscript, or any part of it, is original and has not been submitted previously to any other journal for reviews. The results are presented clearly, honestly, and without fabrication, falsification or inappropriate data manipulation.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, B., Ji, X.T., Chen, X.H. et al. Negative Magnetization Effect in Distorted Honeycomb Ni4Nb2O9 Ceramics. J Low Temp Phys 207, 115–126 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-022-02682-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-022-02682-3