Abstract
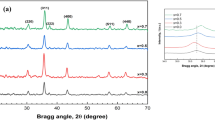
Inverse spinel Zn2SnO4 (ZTO) films have been grown on MgO(001) and MgAl2O4(001) substrates by pulsed laser deposition. Detailed structural investigation by high-resolution X-ray diffraction, including conventional θ–2θ linear scans, φ scans and reciprocal space mappings, revealed the epitaxial characteristics of the ZTO films. Meanwhile, the in-plane and out-of-plane lattice parameters were extracted to be about a = b=8.615 Å and c = 8.629 Å from the symmetry and asymmetry reflections. The surface morphologies of ZTO films were examined by atomic force microscopy, and all the films exhibit very smooth surfaces. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy measurement was taken to disclose the oxidation states of elements. The optical properties of ZTO films were probed by measuring the optical transmittances. The band gaps of ZTO films grown on MgO(001) and MgAl2O4(001) were extracted to be 4.26 eV and 4.30 eV by extrapolating the absorption edge, respectively. Theoretically, the band structure was also calculated using density functional theory. The results show that ZTO film is a direct band gap semiconductor with the band gap value of 2.64 eV. Such a wide band gap semiconductor with an inverse spinel structure should be of high interest for epitaxial heterojunction and optical device application.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Minami, H. Sonohara, S. Takata, H. Sato, Highly transparent and conductive zinc-stannate thin films prepared by RF magnetron sputtering. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 33, L1693 (1994)
J. Dou, X.Y. Li, Y.F. Li, Y.M. Chen, M.D. Wei, Fabrication of Zn2SnO4 microspheres with controllable shell numbers for highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. Sol. Energy 181, 424–429 (2019)
Y.C. Chen, Y.R. Shen, Growth and dielectric characterizations of zinc stannate thin films deposited by RF magnetron sputtering. Integr. Ferroelectr. 192, 80–87 (2018)
T. Minami, S. Takata, H. Sato, H. Sonohara, Properties of transparent zinc-stannate conducting films prepared by radio frequency magnetron sputtering. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 13, 1095 (1995)
M. Zhang, X. Cui, Y.F. Wang, B. Wang, M.D. Ye, W.L. Wang, C.Y. Ma, Z.Q. Lin, Simple route to interconnected hierarchically structured, porous Zn2SnO4 nanospheres as electron transport layers for efficient perovskite solar cells. Nano Energy 71, 104620 (2020)
M.A. Alpuche-Aviles, Y. Wu, Photoelectrochemical study of the band structure of Zn2SnO4 prepared by the hydrothermal method. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 3216–3224 (2009)
L.S. Oh, D.H. Kim, J.A. Lee, S.S. Seong, J.W. Lee, I.J. Park, M.J. Ko, N.G. Park, S.G. Pyo, K. Hong, J.Y. Kim, Zn2SnO4-based photoelectrodes for organolead halide perovskite solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 118, 22991–22994 (2014)
D.W. Kim, S.S. Shin, I.S. Cho, S. Lee, D.H. Kim, C.W. Lee, H.S. Jung, K.S. Hong, Synthesis and photovoltaic property of fine and uniform Zn2SnO4 nanoparticles. Nanoscale 4, 557–562 (2012)
M.Q. Tai, X.Y. Zhao, H.P. Shen, Y. Guo, M.H. Zhang, Y. Zhou, X. Li, Z.B. Yao, X.W. Yin, J.H. Han, H. Lin, Ultrathin Zn2SnO4 (ZTO) passivated ZnO nanocone arrays for efficient and stable perovskite solar cells. Chem. Eng. J. 361, 60–66 (2019)
S.S. Shin, W.S. Yang, J.H. Noh, J.H. Suk, N.J. Jeon, J.H. Park, J.S. Kim, W.M. Seong, S.I. Seok, High-performance flexible perovskite solar cells exploiting Zn2SnO4 prepared in solution below 100 °C. Nat. Commun. 6, 7410 (2015)
D. Segev, S.H. Wei, Structure-derived electronic and optical properties of transparent conducting oxides. Phys. Rev. B 71, 125129 (2005)
V. Stevanovic, M. d’Avezac, A. Zunger, Universal electrostatic origin of cation ordering in A(2)BO(4) spinel oxides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 11649–11654 (2011)
Y. Zhao, L.F. Hu, H. Liu, M.F. Liao, X.S. Fang, L.M. Wu, Band gap tunable Zn2SnO4 nanocubes through thermal effect and their outstanding ultraviolet light photoresponse. Sci. Rep. 4, 6847 (2014)
S. Kozhukharov, S. Tchaoushev, Spray pyrolysis equipment for various applications. J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 48, 111–118 (2013)
Y.C. Chen, H.M. You, Microstructures and dielectric properties of inverse-spinel structure Zn2SnO4 thin films by RF magnetron sputtering. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 2031–2035 (2016)
G. Fu, H. Chen, Z.X. Chen, J.X. Zhang, H. Kohler, Humidity sensitive characteristics of Zn2SnO4–LiZnVO4 thick films prepared by the sol–gel method. Sens. Actuators B 81, 308–312 (2002)
J.X. Wang, S.S. Xie, Y. Gao et al., Growth and characterization of axially periodic Zn2SnO4 (ZTO) nanostructures. J. Cryst. Growth 267, 177–183 (2004)
S.H. Wei, S.B. Zhang, First-principles study of cation distribution in eighteen closed-shell AIIBIII2 O4 and AIVBII2 O4 spinel oxides. Phys. Rev. B 63, 045112 (2001)
X.Y. Li, Y.L. Wang, W.F. Liu, G.S. Jiang, C.F. Zhu, Study of oxygen vacancies influence on the lattice parameter in ZnO thin film. Mater. Lett. 85, 25–28 (2012)
Y.T. Zhang, G.T. Du, X.Q. Wang, W.C. Li, X.T. Yang, Y. Ma, B.J. Zhao, H.J. Yang, D.L. Liu, S.R. Yang, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study of ZnO films grown bymetal-organic chemical vapor deposition. J. Cryst. Growth 252, 180–183 (2003)
T. Baidya, A. Gupta, P.A. Deshpandey, G. Madras, M.S. Hegde, High oxygen storage capacity and high rates of CO oxidation and NO reduction catalytic properties of Ce1−xSnxO2 and Ce0.78Sn0.2Pd0.02O2−δ. J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 4059–4068 (2009)
M. Kwoka, L. Ottaviano, M. Passacantando, S. Santucci, G. Czempik, J. Szuber, XPS study of the surface chemistry of L-CVD SnO2 thin films after oxidation. Thin Solid Films 490, 36–42 (2005)
F. Demichelis, G. Kanidakis, A. Tagliaferro, E. Tresso, New approach to optical analysis of absorbing thin solid films. Appl. Opt. 26, 1737 (1987)
D.L. Young, H. Moutinho, Y.F. Yan, T.J. Coutts, Growth and characterization of radio frequency magnetron sputter-deposited zincstannate thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 92, 310 (2002)
I. Saafi, R. Dridi, A. Mhamdi, M. Haj Lakhdar, K. Boubaker, A. Amlouk, M. Amlouk, Study of thickness effects on structural and optical properties of sprayed Zn2SnO4thin films. Optik 126, 4382–4386 (2015)
A.O. Salohub, A.A. Voznyi, O.V. Klymov, N.V. Safryuk, D.I. Kurbatov, A.S. Opanasyuk, Determination of fundamental optical constants of Zn2SnO4 films. Semicond. Phys. Quantum Electron. Optoelectron. 20, 79–84 (2017)
K. Satoh, Y. Kakehi, A. Okamoto, S. Murakami, F. Uratani, T. Yotsuya, Influence of oxygen flow ratio on properties of Zn2SnO4 thin films deposited by RF magnetron sputtering. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 44, 34–37 (2005)
L. Gracia, A. Beltran, J. Andres, A theoretical study on the pressure-induced phase transitions in the inverse spinel structure Zn2SnO4. J. Phys. Chem. C 115, 7740–7746 (2011)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11974127) and Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Higher Education Institutions of China (No. KJ2019ZD40).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, F., Liu, Q. Structure and Optical Band Gap of Inverse Spinel Zn2SnO4 Epitaxial Films. J Low Temp Phys 200, 142–151 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-020-02479-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-020-02479-2