Abstract
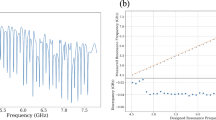
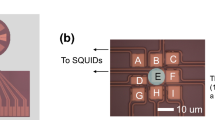
Photon imaging technology is applied in various research fields such as quantum information communication and biological imaging. We have been developing photon-counting devices using optical transition edge sensors (TES). We demonstrated a single-photon spectroscopic imaging system comprising an optical TES and a scanning microscope. However, a great number of TES pixels are required to increase the field of view in the imaging system. To read out the TES array, output signals need to be multiplexed. Microwave SQUID multiplexer (MW-Mux) is a kind of frequency multiplexing method with a carrier wave having a frequency of several GHz, and it can be used to widen the frequency band. In this paper, we report the first demonstration on readout of an optical TES with MW-Mux.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Niwa et al., Sci. Rep. 6, 45660 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep45660
D. Fukuda et al., J. Low Temp. Phys. 193, 1228–1235 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-018-1938-8
J.N. Ullom, D.A. Bennett, Supercond. Sci. Technol. 28, 084003 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-2048/28/8/084003
W.B. Doriese et al., J. Low Temp. Phys. 184, 389–395 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-015-1373-z
K.M. Morgan et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 109, 112604 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4962636
L. Gottardi et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 105, 162605 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4899065
H. Akamatsu et al., J. Low Temp. Phys. 184, 436–442 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-016-1525-9
J.A.B. Mates et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 023514 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2803852
D.A. Bennett et al., J. Astron. Telesc. Instrum. Syst. 5, 021007 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JATIS.5.2.021007
Y. Nakashima et al., IEICE Electron. Express 14, 20170271 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1587/elex.14.20170271
J.A.B. Mates et al., J. Low Temp. Phys. 167, 707–712 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-012-0518-6
A.J. Miller et al., Opt. Express 19, 9102–9110 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.19.009102
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by JST-CREST Grant Number JPMJCR17N4, Japan. MW-Mux chips were fabricated in CRAVITY (Cleanroom for analogue digital superconductivity) in AIST.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakada, N., Hattori, K., Nakashima, Y. et al. Microwave SQUID Multiplexer for Readout of Optical Transition Edge Sensor Array. J Low Temp Phys 199, 206–211 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-019-02298-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-019-02298-0